DeoxypodophyllotoxinCAS# 19186-35-7 |
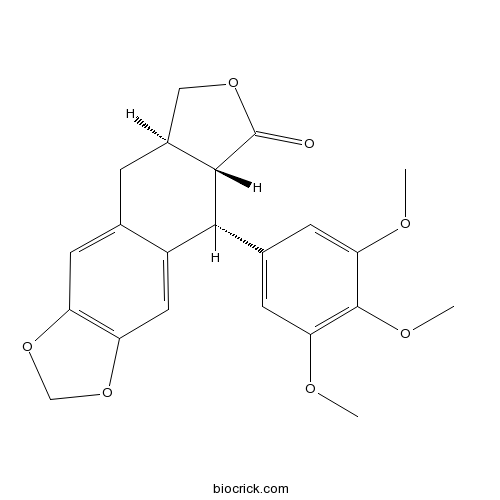
- Isoanthricin
Catalog No.:BCN3531
CAS No.:17301-70-5
- Furo[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d]-1,3-dioxol-6(5aH)-one,5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)- (9CI)
Catalog No.:BCX0958
CAS No.:69222-20-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 19186-35-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 345501 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H22O7 | M.Wt | 398.4 |
| Type of Compound | Lignans | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (5R,5aR,8aR)-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-5a,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5H-[2]benzofuro[5,6-f][1,3]benzodioxol-6-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1OC)OC)C2C3C(CC4=CC5=C(C=C24)OCO5)COC3=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZGLXUQQMLLIKAN-SVIJTADQSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H22O7/c1-24-17-6-12(7-18(25-2)21(17)26-3)19-14-8-16-15(28-10-29-16)5-11(14)4-13-9-27-22(23)20(13)19/h5-8,13,19-20H,4,9-10H2,1-3H3/t13-,19+,20-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Deoxypodophyllotoxin shows cytotoxic , antineoplastic, antitumor, insecticidal, anti-angiogenic, vascular disrupting, insecticidal, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory activities. Deoxypodophyllotoxin induces G2 /M cell-cycle arrest followed by apoptosis through multiple cellular processes, involving the activation of ATM, upregulation of p53 and Bax, activation of caspase-3 and -7, and accumulation of PTEN resulting in the inhibition of the Akt pathway. Deoxypodophyllotoxin maybe applicable to treat hyperpigmentation, it decreases UV-induced skin pigmentation of brown guinea pigs. |
| Targets | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | PARP | NF-kB | IkB | TNF-α | Calcium Channel | p53 | Akt | Antifection | p21 | IKK | PTEN |
| In vitro | Deoxypodophyllotoxin exerts both anti-angiogenic and vascular disrupting effects.[Pubmed: 23702033]Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;45(8):1710-9.The anti-angiogenic and vascular disrupting activities of Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPT), a natural microtubule destabilizer, were examined with several in vitro, ex vivo and/or in vivo models. Deoxypodophyllotoxin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells and inhibits tumor growth in vivo.[Pubmed: 25608854]Molecules. 2015 Jan 20;20(1):1661-75.Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPT), a natural microtubule destabilizer, was isolated from Anthriscus sylvestris, and a few studies have reported its anti-cancer effect. However, the in vivo antitumor efficacy of DPT is currently indeterminate. Pharmacological effect of deoxypodophyllotoxin: a medicinal agent of plant origin, on mammalian neurons.[Pubmed: 20705089 ]Neurotoxicology. 2010 Dec;31(6):680-6.Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DOP) is a natural product that can be isolated from a variety of medicinal herb plants. It is well known for its antitumor, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory activities. However, there are few investigations that address neurotoxic effect of DOP in animal nervous system. Insecticidal activity of deoxypodophyllotoxin, isolated from Juniperus sabina L, and related lignans against larvae of Pieris rapae L.[Pubmed: 15532689 ]Pest Manag Sci. 2004 Nov;60(11):1131-6.In the course of screening for naturally occurring insecticides from plants from the northwestern part of China, a petroleum ether extract of Juniperus sabina L was found to show insecticidal activity against fifth-instar larvae of Pieris rapae L. |
| In vivo | Deoxypodophyllotoxin, a naturally occurring lignan, inhibits the passive cutaneous anaphylaxis reaction.[Pubmed: 15124098]Planta Med. 2004 May;70(5):474-6.This study examined the effect of a podophyllotoxin derivative, Deoxypodophyllotoxin (anthricin), which is a medicinal herb product isolated from Anthriscus sylvestris Hoffm. |
| Kinase Assay | Deoxypodophyllotoxin inhibits the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in murine lung epithelial cells.[Pubmed: 20045926]Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(1):1-5.Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is associated with processes of inflammation. |
| Cell Research | Antineoplastic effects of deoxypodophyllotoxin, a potent cytotoxic agent of plant origin, on glioblastoma U-87 MG and SF126 cells.[Pubmed: 25712646]Pharmacol Rep. 2015 Apr;67(2):245-52.Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPT) is a semi-synthetic compound derived from the extract of Dysosma versipellis (Hance) M. Cheng, one of the most popular Chinese herbal medicines. The present study evaluates the in vitro cytotoxicity of Deoxypodophyllotoxin on a wide panel of human cancer cell lines and investigates its molecular mechanism of action on high grade glioma U-87 MG and SF126 cells. |
| Animal Research | Deoxypodophyllotoxin reduces skin pigmentation of brown Guinea pigs.[Pubmed: 15095159 ]Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPT) inhibits eosinophil recruitment into the airway and Th2 cytokine expression in an OVA-induced lung inflammation.[Pubmed: 16732515 ]Planta Med. 2006 Jul;72(9):786-91.The effect of Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPT) isolated from Anthriscus sylvestris Hoffm. was evaluated in an IN VIVO animal model for antiasthmatic activity. Planta Med. 2004 Apr;70(4):378-80.In this report, we have demonstrated that Deoxypodophyllotoxin from Anthriscus sylvestris (L.) Hoffm decreases UV-induced skin pigmentation of brown guinea pigs. |

Deoxypodophyllotoxin Dilution Calculator

Deoxypodophyllotoxin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.51 mL | 12.5502 mL | 25.1004 mL | 50.2008 mL | 62.751 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.502 mL | 2.51 mL | 5.0201 mL | 10.0402 mL | 12.5502 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.251 mL | 1.255 mL | 2.51 mL | 5.0201 mL | 6.2751 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0502 mL | 0.251 mL | 0.502 mL | 1.004 mL | 1.255 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0251 mL | 0.1255 mL | 0.251 mL | 0.502 mL | 0.6275 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Cyclo(Pro-Gly)
Catalog No.:BCN2417
CAS No.:19179-12-5
- Lenalidomide (CC-5013)
Catalog No.:BCC2245
CAS No.:191732-72-6
- Tenacissoside H
Catalog No.:BCN2570
CAS No.:191729-45-0
- Tenacissoside I
Catalog No.:BCN4681
CAS No.:191729-44-9
- Tenacissoside G
Catalog No.:BCN4682
CAS No.:191729-43-8
- Pomalidomide (CC-4047)
Catalog No.:BCC2246
CAS No.:19171-19-8
- SIB 1553A hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6284
CAS No.:191611-89-9
- Trimethylgallic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN3369
CAS No.:1916-07-0
- 2-Deacetoxytaxinine B
Catalog No.:BCN1181
CAS No.:191547-12-3
- Epieriocalyxin A
Catalog No.:BCN1180
CAS No.:191545-24-1
- 2-Hydroxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7545
CAS No.:1915-98-6
- Isoficusin A
Catalog No.:BCN6865
CAS No.:1914963-20-4
- BIBO 3304 trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC7355
CAS No.:191868-14-1
- Flutax 1
Catalog No.:BCC7298
CAS No.:191930-58-2
- NTNCB hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7270
CAS No.:191931-56-3
- HIV-1 Tat Protein Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC4417
CAS No.:191936-91-1
- 12-Hydroxymyricanone
Catalog No.:BCN8046
CAS No.:191999-68-5
- Hinokiflavone
Catalog No.:BCN2989
CAS No.:19202-36-9
- Tenulin
Catalog No.:BCN7961
CAS No.:19202-92-7
- MRS 1334
Catalog No.:BCC5753
CAS No.:192053-05-7
- Harpagoside
Catalog No.:BCN4995
CAS No.:19210-12-9
- Prazosin
Catalog No.:BCC4081
CAS No.:19216-56-9
- Tipifarnib (Zarnestra)
Catalog No.:BCC2253
CAS No.:192185-72-1
- Carboxypeptidase G2 (CPG2) Inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1452
CAS No.:192203-60-4
Insecticidal activity of deoxypodophyllotoxin, isolated from Juniperus sabina L, and related lignans against larvae of Pieris rapae L.[Pubmed:15532689]
Pest Manag Sci. 2004 Nov;60(11):1131-6.
In the course of screening for naturally occurring insecticides from plants from the northwestern part of China, a petroleum ether extract of Juniperus sabina L was found to show insecticidal activity against fifth-instar larvae of Pieris rapae L. From the extract, an insecticidal compound was isolated by bioassay-guided fractionation. The compound was identified as Deoxypodophyllotoxin (1) by comparison of its spectroscopic characteristics with literature data. In bioassays, 1 showed antifeedant activity against fifth-instar larvae of P rapae at 0.05-1.00 g litre(-1) and its AFC50 (concentration for 50% antifeedant activity) values at 12 and 48h were 0.170 and 0.060 g litre(-1), respectively. In that concentration range, all treated insects died within 48 h after treatment and compound 1 showed delayed insecticidal activity. At 0.015-0.100 g litre(-1), 1 showed insecticidal activity, with an LC50 of 0.020 g litre(-1). The related compound deoxypicropodophyllotoxin (2), however, showed lower antifeedant and insecticidal activities than 1 in bioassay. This indicated that the trans-lactone ring is an important moiety for enhancing activity in these compounds. Comparison of the insecticidal activities of 1 and another related compound, podophyllotoxin (3), suggested that varying the substituent at C-4 is an exciting possibility for synthesizing more potent analogues.
Deoxypodophyllotoxin inhibits the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in murine lung epithelial cells.[Pubmed:20045926]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(1):1-5.
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is associated with processes of inflammation. We investigated the effects of Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPT) on tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) induced ICAM-1 expression in the mouse lung epithelial cell line, LA4. DPT (5 to 20 nM) inhibited TNF-alpha-induced ICAM-1 expression through nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) in a dose-dependent manner and repressed ICAM-1 promoter activity. NF-kappaB reporter gene activity and DNA binding activity were also strongly inhibited. In addition, DPT inhibited degradation by the TNF-alpha induced inhibitory kappaB-alpha (IkappaB-alpha) in a concentration-dependent manner. Taken together with our previous results suggest DPT might provide a basis for novel anti-inflammatory drug development.
Deoxypodophyllotoxin reduces skin pigmentation of brown Guinea pigs.[Pubmed:15095159]
Planta Med. 2004 Apr;70(4):378-80.
In this report, we have demonstrated that Deoxypodophyllotoxin from Anthriscus sylvestris (L.) Hoffm decreases UV-induced skin pigmentation of brown guinea pigs. Deoxypodophyllotoxin (0.05 % in propylene glycol: ethanol: water = 5 : 3:2) was topically applied twice daily for two weeks to dorsal skin of brown guinea pigs that were exposed to UV irradiation using a solar simulator. Visual inspection and Fontana-Masson staining both demonstrated that Deoxypodophyllotoxin reduced skin pigmentation and total epidermal melanin when compared to that of vehicle-treated areas, suggesting that Deoxypodophyllotoxin maybe applicable to treat hyperpigmentation.
Deoxypodophyllotoxin, a naturally occurring lignan, inhibits the passive cutaneous anaphylaxis reaction.[Pubmed:15124098]
Planta Med. 2004 May;70(5):474-6.
This study examined the effect of a podophyllotoxin derivative, Deoxypodophyllotoxin (anthricin), which is a medicinal herb product isolated from Anthriscus sylvestris Hoffm. Deoxypodophyllotoxin was tested in a rat PCA (passive cutaneous anaphylaxis) assay by administering Deoxypodophyllotoxin intraperitoneally (1.0 to 10 mg/kg, i.p.) and intravenously (0.25 to 1.0 mg/kg, i.v.). Deoxypodophyllotoxin dose-dependently inhibited the PCA reaction activated by anti-dinitrophenyl (DNP) IgE. The PCA inhibitory activity of Deoxypodophyllotoxin was stronger than those of prednisolone and indomethacin, which were used as positive controls. These results suggest that Deoxypodophyllotoxin may be beneficial in regulating the immediate-type allergic reaction.
Antineoplastic effects of deoxypodophyllotoxin, a potent cytotoxic agent of plant origin, on glioblastoma U-87 MG and SF126 cells.[Pubmed:25712646]
Pharmacol Rep. 2015 Apr;67(2):245-52.
BACKGROUND: Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPT) is a semi-synthetic compound derived from the extract of Dysosma versipellis (Hance) M. Cheng, one of the most popular Chinese herbal medicines. The present study evaluates the in vitro cytotoxicity of DPT on a wide panel of human cancer cell lines and investigates its molecular mechanism of action on high grade glioma U-87 MG and SF126 cells. METHODS: The growth inhibitory effect of DPT on different types of human cancer cells was measured by the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. For the elucidation of the nature of the cellular response to DPT-treatment; flow cytometry-based assays, light and fluorescent microscopy, caspase colorimetric and inhibition assays, and Western blot analysis were performed. RESULTS: Our data show that DPT possesses a potent growth-inhibitory action, with IC50 values in nanomolar ranges. Cell cycle analysis revealed G2/M phase arrest in a dose- and time-dependent manner before cell death occurred. Additional studies indicated that DPT induced G2 arrest in U-87 MG cells by decreasing the expression of Cdc2, cyclin B1, and Cdc25C proteins. In contrast, DPT failed to down-regulate these cell cycle regulatory molecules in SF126 glioblastoma cells and stopped the cell cycle at M phase. Interestingly, morphological changes and biochemical markers such as phosphatydylserine externalization, DNA fragmentation, and caspase activation, confirmed that DPT-treatment resulted in an induction of apoptosis in both examined cell lines via caspase-dependent pathways. CONCLUSIONS: Taken together, our data demonstrated that DPT possesses a potent in vitro cytotoxic activity and exerts its effect via G2/M arrest and apoptosis.
Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPT) inhibits eosinophil recruitment into the airway and Th2 cytokine expression in an OVA-induced lung inflammation.[Pubmed:16732515]
Planta Med. 2006 Jul;72(9):786-91.
The effect of Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPT) isolated from Anthriscus sylvestris Hoffm. was evaluated in an IN VIVO animal model for antiasthmatic activity. DPT (1.0 to 5 mg/kg) was given orally to ovalbumin (OVA)/alum-induced asthmatic mice. DPT reduced the number of infiltrated eosinophils in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid in a dose-dependent manner. Dexamethasone (5 mg/kg), which was used as a positive control, also strongly inhibited the number of infiltrated eosinophils. The effect of DPT on a transcript profile in a murine asthma model was determined by RT-PCR, which showed that DPT decreased the mRNA levels of the Th2 cytokines. Northern blot analysis showed that DPT also reduced both the eotaxin and arginase I mRNA levels in a dose-dependent manner.
Deoxypodophyllotoxin exerts both anti-angiogenic and vascular disrupting effects.[Pubmed:23702033]
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;45(8):1710-9.
A functioning vascular supply is essential for solid tumor growth and metastases, which means that blood vessels are an ideal target for antitumor drug discovery. Targeting tumor vasculature involves two main approaches, anti-angiogenesis and vascular disruption. The anti-angiogenic and vascular disrupting activities of Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPT), a natural microtubule destabilizer, were examined with several in vitro, ex vivo and/or in vivo models. First, we demonstrated that DPT significantly inhibits the proliferation, migration and tube formation of endothelial cells and inhibits angiogenesis in rat aortic ring and chick chorioallantoic membrane assays. In further studies, DPT induced cytoskeleton reorganization in endothelial cells, which likely contributed to the anti-angiogenic effect at non-cytotoxic concentrations. DPT treatment at higher concentrations for longer time induced the cell cycle arrest, which may contributes to its anti-proliferation effect and anti-angiogenic activity. And DPT dramatically inducted the expression of cyclin B1 and p21 (WAF1/CIP1). Meanwhile, DPT disrupted capillary-like networks in vitro and newly formed vessels from rat aortic rings. Endothelial cell contraction associated with an increase in F-actin via the Rho/Rho kinase pathway likely contributed to the vascular disrupting activity. Taken together, our results provided the initial evidence that DPT exerts potent anti-angiogenic and vascular disrupting effects. This study also provides important insight into the mechanism of action of promising new anticancer drugs with both anti-angiogenic and vascular disrupting activities.
Pharmacological effect of deoxypodophyllotoxin: a medicinal agent of plant origin, on mammalian neurons.[Pubmed:20705089]
Neurotoxicology. 2010 Dec;31(6):680-6.
Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DOP) is a natural product that can be isolated from a variety of medicinal herb plants. It is well known for its antitumor, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory activities. However, there are few investigations that address neurotoxic effect of DOP in animal nervous system. In this study, whole-cell patch clamp and calcium imaging techniques were employed to investigate effects of DOP on electrophysiological properties and calcium regulation of rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. DOP inhibited both TTX-S (tetrodotoxin-sensitive) and TTX-R (tetrodotoxin-resistant) sodium currents in voltage clamp recording and caused a decrease in the number of action potentials (APs) in current clamp experiment. Suppressive and unfavorable effects of DOP on the kinetics of sodium currents in terms of excitability of DRG neurons may greatly contribute to its antitumor and anti-inflammatory activities. Moreover, DOP evoked increase of intracellular Ca(2+) concentrations ([Ca(2+)](i)) in DRG neurons, and this effect may lead to neuronal cytotoxicity.
Deoxypodophyllotoxin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells and inhibits tumor growth in vivo.[Pubmed:25608854]
Molecules. 2015 Jan 20;20(1):1661-75.
Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPT), a natural microtubule destabilizer, was isolated from Anthriscus sylvestris, and a few studies have reported its anti-cancer effect. However, the in vivo antitumor efficacy of DPT is currently indeterminate. In this study, we investigated the anti-gastric cancer effects of DPT both in vitro and in vivo. Our data showed that DPT inhibited cancer cell proliferation and induced G2/M cell cycle arrest accompanied by an increase in apoptotic cell death in SGC-7901 cancer cells. In addition, DPT caused cyclin B1, Cdc2 and Cdc25C to accumulate, decreased the expression of Bcl-2 and activated caspase-3 and PARP, suggesting that caspase-mediated pathways were involved in DPT-induced apoptosis. Animal studies revealed that DPT significantly inhibited tumor growth and decreased microvessel density (MVD) in a xenograft model of gastric cancer. Taken together, our findings provide a framework for further exploration of DPT as a novel chemotherapeutic for human gastric cancer.


