CGS 21680 HClA2 adenosine receptor agonist CAS# 124431-80-7 |
- LY2835219
Catalog No.:BCC1113
CAS No.:1231930-82-7
- Roscovitine (Seliciclib,CYC202)
Catalog No.:BCC1105
CAS No.:186692-46-6
- Nu 6027
Catalog No.:BCC1154
CAS No.:220036-08-8
- SNS-032 (BMS-387032)
Catalog No.:BCC1152
CAS No.:345627-80-7
- AT7519 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1376
CAS No.:902135-91-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 124431-80-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10256643 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H30ClN7O6 | M.Wt | 535.98 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 20 mg/mL (37.31 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
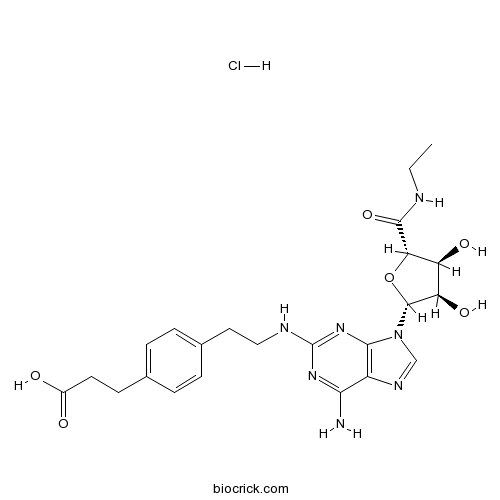
| Chemical Name | 3-[4-[2-[[6-amino-9-[(2R,3R,4S,5S)-5-(ethylcarbamoyl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]purin-2-yl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]propanoic acid;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CCNC(=O)C1C(C(C(O1)N2C=NC3=C2N=C(N=C3N)NCCC4=CC=C(C=C4)CCC(=O)O)O)O.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QPHVMNOEKKJYJO-MJWSIIAUSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H29N7O6.ClH/c1-2-25-21(35)18-16(33)17(34)22(36-18)30-11-27-15-19(24)28-23(29-20(15)30)26-10-9-13-5-3-12(4-6-13)7-8-14(31)32;/h3-6,11,16-18,22,33-34H,2,7-10H2,1H3,(H,25,35)(H,31,32)(H3,24,26,28,29);1H/t16-,17+,18-,22+;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | A2A adenosine receptor agonist (Ki = 27 nM). Has affinity for A1 and A3 adenosine receptors but can be used to distinguish A2A- and A2B-mediated effects. |

CGS 21680 HCl Dilution Calculator

CGS 21680 HCl Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8657 mL | 9.3287 mL | 18.6574 mL | 37.3148 mL | 46.6435 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3731 mL | 1.8657 mL | 3.7315 mL | 7.463 mL | 9.3287 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1866 mL | 0.9329 mL | 1.8657 mL | 3.7315 mL | 4.6644 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0373 mL | 0.1866 mL | 0.3731 mL | 0.7463 mL | 0.9329 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0187 mL | 0.0933 mL | 0.1866 mL | 0.3731 mL | 0.4664 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
CGS 21680 HCl is a selective agonist of A2 adenosine receptor with IC50 value of 22nM [1].
In rat striatal membranes, CGS 21680 potently prevents ligands from binding to A2 adenosine receptors with IC50 value of 22nM. In the binding assay, CGS 21680 shows no effect to other putative neurotransmitter/neuromodulator sites in brain membranes such as adrenergic, dopamine and serotonin. In the rat heart model, CGS 21680 is effective in increasing coronary flow with EC25 value of 2nM [1].
In vivo, the hydrochloride salt of CGS 21680 has potent efficacy to decrease blood pressure in the anesthetized normotensive rat with ED50 value of 9μg/kg. It also causes heart rate increasing up to 15%. Besides that, CGS 21680 HCl significantly lower the blood pressure at dose of 10mg/kg in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. A transient elecation of heart rate is also observed at 30 min in the model [1].
References:
[1] Hutchison A J, Webb R L, Oei H H, et al. CGS 21680C, an A2 selective adenosine receptor agonist with preferential hypotensive activity. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 1989, 251(1): 47-55.
- Cannabidiolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6127
CAS No.:1244-58-2
- MG 149
Catalog No.:BCC5149
CAS No.:1243583-85-8
- 9-(1H-Benzotriazol-1-ylmethyl)-9H-carbazole
Catalog No.:BCC8792
CAS No.:124337-34-4
- Lenalidomide hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1697
CAS No.:1243329-97-6
- Paucinervin A
Catalog No.:BCN7308
CAS No.:1243249-16-2
- LGK-974
Catalog No.:BCC5103
CAS No.:1243244-14-5
- Wnt-C59
Catalog No.:BCC3965
CAS No.:1243243-89-1
- RN486
Catalog No.:BCC3921
CAS No.:1242156-23-5
- 12-Ursene-3,16,22-triol
Catalog No.:BCN6126
CAS No.:1242085-06-8
- Laxiracemosin H
Catalog No.:BCN6910
CAS No.:1241871-28-2
- 6-O-Vanilloylajugol
Catalog No.:BCN6125
CAS No.:124168-04-3
- (R)-DRF053 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7726
CAS No.:1241675-76-2
- VU 0364739 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7875
CAS No.:1244640-48-9
- 16R-sitsirikine
Catalog No.:BCN3492
CAS No.:1245-00-7
- 2,2'-Bicinchoninic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8487
CAS No.:1245-13-2
- Retusin
Catalog No.:BCN7794
CAS No.:1245-15-4
- 16-Oxoalisol A
Catalog No.:BCN3460
CAS No.:124515-98-6
- PI4KIII beta inhibitor 3
Catalog No.:BCC1310
CAS No.:1245319-54-3
- Glucocorticoid receptor agonist
Catalog No.:BCC1596
CAS No.:1245526-82-2
- NVP-BGT226
Catalog No.:BCC3827
CAS No.:1245537-68-1
- GR 79236
Catalog No.:BCC7215
CAS No.:124555-18-6
- ent-Labda-8(17),13Z-diene-15,16,19-triol 19-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1598
CAS No.:1245636-01-4
- Brain natriuretic peptide (1-32) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC6034
CAS No.:124584-08-3
- Daidzin 6'-O-malonate
Catalog No.:BCN8245
CAS No.:124590-31-4
Adenosine receptors and their ligands.[Pubmed:11111832]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000 Nov;362(4-5):382-91.
The regulatory actions of adenosine are mediated via four subtypes of G protein-coupled receptors distinguished as A1, A2A, A2B and A3 receptors. Their presence on basically every cell makes them an interesting target for the pharmacological intervention in many pathophysiological situations. A large number of ligands have been synthesized over the last two decades and provide agonists and antagonists that are more or less selective for the known receptor subtypes. In addition, many radioligands are available in tritiated or radioiodinated form. The comparative pharmacological characterization of all four human adenosine receptor subtypes revealed that some of the compounds thought to be selective from data in other species have unexpected potencies at human receptors. As a result, compounds that exhibit high affinity to only one subtype are an exception. Although the selection of ligands is immense, it is less than satisfying for most subtypes of adenosine receptors.
Effects of CGS 21680, a selective A2A adenosine receptor agonist, on cardiac output and vascular resistance in acute heart failure in the anaesthetized rat.[Pubmed:9605574]
Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Apr;123(8):1666-72.
1. The effects of CGS 21680, a selective A2A adenosine receptor agonist, on cardiac output, blood pressure, mean circulatory filling pressure (Pmcf), arterial and venous resistances, heart rate and left ventricular end-diastolic pressure were assessed in rats with acute heart failure by means of coronary artery occlusion. 2. Animals (n=6 in each group) were divided into five groups: group I, sham-operated vehicle-treated (0.9% saline; 0.018 mL min(-1)); groups II-V, subject to coronary artery occlusion and treated with vehicle (0.9% saline; 0.018 ml min(-1)) and CGS 21680 (0.1, 0.3 and 1.0 microg kg(-1) min(-1)), respectively. Haemodynamic measurements were taken one hour after completion of surgery, ninety minutes after coronary artery occlusion (except in group I), and fifteen minutes after infusion of saline or CGS 21680. 3. Baseline haemodynamic measurements before occlusion were found not to differ significantly between the different groups of animals. However, after occlusion, cardiac output, rate of rise in left ventricular pressure (+ dP/dt) and blood pressure were significantly reduced when compared to corresponding values in sham-operated animals. In addition, occlusion of the coronary artery resulted in a significant elevation in venous resistance, Pmcf and left ventricular end-diastolic pressure as compared to corresponding values in sham-operated animals. 4. Infusion with CGS 21680 at the highest dose significantly reduced blood pressure, arterial resistance and left ventricular end-diastolic pressure when compared to occluded vehicle-treated animals (group II). Administration of CGS 21680 at the highest dose also significantly increased cardiac output (28%) and heart rate (10%) in comparison to occluded vehicle-treated animals. In addition, the highest dose of CGS 21680 significantly reduced Pmcf (9%) and venous resistance (62%) in comparison to occluded vehicle-treated animals. Administration of CGS 21680 did not significantly affect +dP/dt when compared to occluded vehicle-treated animals. 5. The results from the present investigation indicate that occlusion of the coronary artery in rats results in a state of heart failure characterized by reduced arterial pressure and cardiac output, and increased venous resistance, Pmcf and left ventricular end-diastolic pressure. Administration of CGS 21680 to animals with acute heart failure resulted in increased cardiac output which was due to reduced venous resistance, as well as increased heart rate.
The selective adenosine A2 receptor agonist, CGS 21680, is a potent depressant of cerebral cortical neuronal activity.[Pubmed:2322828]
Brain Res. 1990 Feb 19;509(2):328-30.
The A2 selective adenosine receptor agonist 2-p-(2-carboxyethyl)phenethylamino-5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (CGS 21680) depressed the spontaneous, acetylcholine- and glutamate-evoked firing of rat cerebral sensorimotor cortical neurons. Iontophoretically applied CGS 21680 was equipotent with adenosine as a depressant and its actions were antagonized by 8-p-sulphophenyltheophylline applied from another barrel of the multibarrelled micropipette. The observation of a potent depressant action of a selective A2 receptor agonist suggests that A2 receptors are involved in the modulation of cerebral cortical neuronal firing by adenosine.


