AZD3514Androgen receptor downregulator CAS# 1240299-33-5 |
- 17 alpha-propionate
Catalog No.:BCC1296
CAS No.:19608-29-8
- Andarine
Catalog No.:BCC1168
CAS No.:401900-40-1
- MDV3100 (Enzalutamide)
Catalog No.:BCC1268
CAS No.:915087-33-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1240299-33-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 46893585 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H32F3N7O2 | M.Wt | 519.56 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | AZD-3514 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (192.47 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
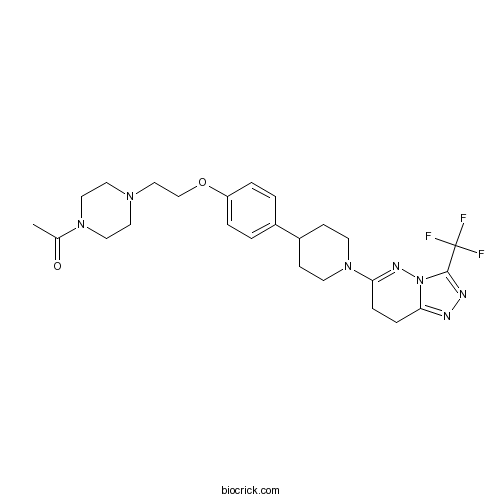
| Chemical Name | 1-[4-[2-[4-[1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl]piperidin-4-yl]phenoxy]ethyl]piperazin-1-yl]ethanone | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)N1CCN(CC1)CCOC2=CC=C(C=C2)C3CCN(CC3)C4=NN5C(=NN=C5C(F)(F)F)CC4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JMEYDSHPKCSIJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H32F3N7O2/c1-18(36)33-14-12-32(13-15-33)16-17-37-21-4-2-19(3-5-21)20-8-10-34(11-9-20)23-7-6-22-29-30-24(25(26,27)28)35(22)31-23/h2-5,20H,6-17H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AZD3514 is a small-molecule downregulator of androgen receptor with Ki value of 2.2 μM. | |||||
| Targets | androgen receptor | |||||
| IC50 | 2.2 μM (Ki) | |||||

AZD3514 Dilution Calculator

AZD3514 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9247 mL | 9.6235 mL | 19.2471 mL | 38.4941 mL | 48.1176 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3849 mL | 1.9247 mL | 3.8494 mL | 7.6988 mL | 9.6235 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1925 mL | 0.9624 mL | 1.9247 mL | 3.8494 mL | 4.8118 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0385 mL | 0.1925 mL | 0.3849 mL | 0.7699 mL | 0.9624 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0192 mL | 0.0962 mL | 0.1925 mL | 0.3849 mL | 0.4812 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AZD3514 is a potent and oral androgen receptor (AR) inhibitor with Ki value of 2.2 μM [1].
AR is a member of the steroid hormone receptor family and functions as a ligand-dependent transcription factor. AR signaling participates in the antiandrogen therapies [2].
In LNCaP and LAPC4 prostate cancer cells, AZD3514 inhibited DHT-driven proliferation of LNCaP cells in a dose-dependent way and inhibited the ligand-driven expression of AR-regulated genes PSA and TMPRSS2. Also, AZD3514 reduced AR protein expression in a dose-dependent way [2].
In male Copenhagen rats with prostate tumors, Oral treatment of AZD3514 (50 mg/kg) once daily inhibited tumor growth by 64%. Also, AZD3514 reduced nuclear AR protein expression. In the Dunning R3327H tumor model, treatment with AZD3514 significantly reduced AR staining in the nucleus of tumor cells, which were caused by reducing the rate of AR synthesis [2].
References:
[1]. Bradbury RH, Acton DG, Broadbent NL, et al. Discovery of AZD3514, a small-molecule androgen receptor downregulator for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2013, 23(7): 1945-1948.
[2]. Loddick SA, Ross SJ, Thomason AG, et al. AZD3514: a small molecule that modulates androgen receptor signaling and function in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther, 2013, 12(9): 1715-1727.
- Kobophenol A
Catalog No.:BCN3444
CAS No.:124027-58-3
- 1beta,10beta-Epoxydesacetoxymatricarin
Catalog No.:BCN7307
CAS No.:124020-39-9
- Triamcinolone
Catalog No.:BCC4741
CAS No.:124-94-7
- Oxycodone hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6090
CAS No.:124-90-3
- Picrotoxin
Catalog No.:BCC5705
CAS No.:124-87-8
- Isoborneol
Catalog No.:BCN7158
CAS No.:124-76-5
- Decane
Catalog No.:BCN8138
CAS No.:124-18-5
- Topotecan
Catalog No.:BCC5646
CAS No.:123948-87-8
- Hypocrellin B
Catalog No.:BCN3397
CAS No.:123940-54-5
- (R)-(+)-HA-966
Catalog No.:BCC6588
CAS No.:123931-04-4
- Cassiaside
Catalog No.:BCN2939
CAS No.:123914-49-8
- Gentiside J
Catalog No.:BCN7306
CAS No.:1238837-50-7
- 7',8'-Dihydroobolactone
Catalog No.:BCN7196
CAS No.:1240403-82-0
- Etomoxir
Catalog No.:BCC1564
CAS No.:124083-20-1
- 16-Epikoumidine
Catalog No.:BCN3915
CAS No.:124096-81-7
- (-)-Hydroxydihydrobovolide
Catalog No.:BCN7890
CAS No.:124097-54-7
- 1-Caffeoylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5911
CAS No.:1241-87-8
- 2-Hydroxytetracosanoic acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1599
CAS No.:124111-47-3
- Scutebarbatine O
Catalog No.:BCN8377
CAS No.:960302-88-9
- Alcesefoliside
Catalog No.:BCN2933
CAS No.:124151-38-8
- (R)-DRF053 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7726
CAS No.:1241675-76-2
- 6-O-Vanilloylajugol
Catalog No.:BCN6125
CAS No.:124168-04-3
- Laxiracemosin H
Catalog No.:BCN6910
CAS No.:1241871-28-2
- 12-Ursene-3,16,22-triol
Catalog No.:BCN6126
CAS No.:1242085-06-8
The value of integrating pre-clinical data to predict nausea and vomiting risk in humans as illustrated by AZD3514, a novel androgen receptor modulator.[Pubmed:26876616]
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 Apr 1;296:10-8.
Nausea and vomiting are components of a complex mechanism that signals food avoidance and protection of the body against the absorption of ingested toxins. This response can also be triggered by pharmaceuticals. Predicting clinical nausea and vomiting liability for pharmaceutical agents based on pre-clinical data can be problematic as no single animal model is a universal predictor. Moreover, efforts to improve models are hampered by the lack of translational animal and human data in the public domain. AZD3514 is a novel, orally-administered compound that inhibits androgen receptor signaling and down-regulates androgen receptor expression. Here we have explored the utility of integrating data from several pre-clinical models to predict nausea and vomiting in the clinic. Single and repeat doses of AZD3514 resulted in emesis, salivation and gastrointestinal disturbances in the dog, and inhibited gastric emptying in rats after a single dose. AZD3514, at clinically relevant exposures, induced dose-responsive "pica" behaviour in rats after single and multiple daily doses, and induced retching and vomiting behaviour in ferrets after a single dose. We compare these data with the clinical manifestation of nausea and vomiting encountered in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer receiving AZD3514. Our data reveal a striking relationship between the pre-clinical observations described and the experience of nausea and vomiting in the clinic. In conclusion, the emetic nature of AZD3514 was predicted across a range of pre-clinical models, and the approach presented provides a valuable framework for predicition of clinical nausea and vomiting.
AZD3514, an oral selective androgen receptor down-regulator in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer - results of two parallel first-in-human phase I studies.[Pubmed:25920479]
Invest New Drugs. 2015 Jun;33(3):679-90.
BACKGROUND: AZD3514 is a first-in-class, orally bio-available, androgen-dependent and -independent androgen receptor inhibitor and selective androgen-receptor down-regulator (SARD). METHODS: In study 1 and 2, castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) patients (pts) were initially recruited into a once daily (QD) oral schedule (A). In study 1, pharmacokinetic assessments led to twice daily (BID) dosing (schedule B) to increase exposure. Study 2 explored a once daily schedule. RESULTS: In study 1, 49 pts were treated with escalating doses of AZD3514 (A 35 pts, B 14 pts). Starting doses were 100 mg (A) and 1000 mg (B). The AZD3514 formulation was switched from capsules to tablets at 1000 mg QD. 2000 mg BID was considered non-tolerable due to grade (G) 2 toxicities (nausea [N], vomiting [V]). No adverse events (AEs) met the dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) definition. Thirteen pts received AZD3514 in study 2, with starting doses of 250 mg QD. The most frequent drug-related AEs were N: G1/2 in 55/70 pts (79 %); G3 in 1 pt (1.4 %); & V: G1/2 in 34/70 pts (49 %) & G3 in 1 pt (1.4 %). PSA declines (>/=50 %) were documented in 9/70 patients (13 %). Objective soft tissue responses per RECIST1.1 were observed in 4/24 (17 %) pts in study 1. CONCLUSION: AZD3514 has moderate anti-tumour activity in pts with advanced CRPC but with significant levels of nausea and vomiting. However, anti-tumour activity as judged by significant PSA declines, objective responses and durable disease stabilisations, provides the rationale for future development of SARD compounds.
Continual reassessment method for dose escalation clinical trials in oncology: a comparison of prior skeleton approaches using AZD3514 data.[Pubmed:27581751]
BMC Cancer. 2016 Aug 31;16:703.
BACKGROUND: The continual reassessment method (CRM) requires an underlying model of the dose-toxicity relationship ("prior skeleton") and there is limited guidance of what this should be when little is known about this association. In this manuscript the impact of applying the CRM with different prior skeleton approaches and the 3 + 3 method are compared in terms of ability to determine the true maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and number of patients allocated to sub-optimal and toxic doses. METHODS: Post-hoc dose-escalation analyses on real-life clinical trial data on an early oncology compound (AZD3514), using the 3 + 3 method and CRM using six different prior skeleton approaches. RESULTS: All methods correctly identified the true MTD. The 3 + 3 method allocated six patients to both sub-optimal and toxic doses. All CRM approaches allocated four patients to sub-optimal doses. No patients were allocated to toxic doses from sigmoidal, two from conservative and five from other approaches. CONCLUSIONS: Prior skeletons for the CRM for phase 1 clinical trials are proposed in this manuscript and applied to a real clinical trial dataset. Highly accurate initial skeleton estimates may not be essential to determine the true MTD, and, as expected, all CRM methods out-performed the 3 + 3 method. There were differences in performance between skeletons. The choice of skeleton should depend on whether minimizing the number of patients allocated to suboptimal or toxic doses is more important. TRIAL REGISTRATION: NCT01162395 , Trial date of first registration: July 13, 2010.
AZD3514: a small molecule that modulates androgen receptor signaling and function in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:23861347]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Sep;12(9):1715-27.
Continued androgen receptor (AR) expression and signaling is a key driver in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) after classical androgen ablation therapies have failed, and therefore remains a target for the treatment of progressive disease. Here, we describe the biological characterization of AZD3514, an orally bioavailable drug that inhibits androgen-dependent and -independent AR signaling. AZD3514 modulates AR signaling through two distinct mechanisms, an inhibition of ligand-driven nuclear translocation of AR and a downregulation of receptor levels, both of which were observed in vitro and in vivo. AZD3514 inhibited testosterone-driven seminal vesicle development in juvenile male rats and the growth of androgen-dependent Dunning R3327H prostate tumors in adult rats. Furthermore, this class of compound showed antitumor activity in the HID28 mouse model of CRPC in vivo. AZD3514 is currently in phase I clinical evaluation.


