p-ChlorophenylalanineTryptophan hydroxylase inhibitor CAS# 7424-00-2 |
- USP7-USP47 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4113
CAS No.:1247825-37-1
- NSC 632839 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2088
CAS No.:157654-67-6
- PR-619
Catalog No.:BCC3627
CAS No.:2645-32-1
- WP1130
Catalog No.:BCC3686
CAS No.:856243-80-6
- Vialinin A
Catalog No.:BCC2367
CAS No.:858134-23-3
- P005091
Catalog No.:BCC1287
CAS No.:882257-11-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 7424-00-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 4652 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H10ClNO2 | M.Wt | 199.64 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | PCPA; CP-10188 | ||
| Solubility | H2O : 2 mg/mL (10.02 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : 1 mg/mL (5.01 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
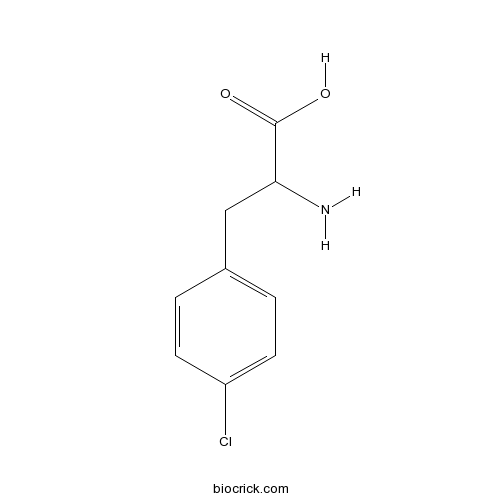
| Chemical Name | 2-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)propanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1CC(C(=O)O)N)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NIGWMJHCCYYCSF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H10ClNO2/c10-7-3-1-6(2-4-7)5-8(11)9(12)13/h1-4,8H,5,11H2,(H,12,13) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Binds irreversibly to tryptophan hydroxylase to cause depletion of serotonin in the brain. |

p-Chlorophenylalanine Dilution Calculator

p-Chlorophenylalanine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.009 mL | 25.0451 mL | 50.0902 mL | 100.1803 mL | 125.2254 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0018 mL | 5.009 mL | 10.018 mL | 20.0361 mL | 25.0451 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5009 mL | 2.5045 mL | 5.009 mL | 10.018 mL | 12.5225 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1002 mL | 0.5009 mL | 1.0018 mL | 2.0036 mL | 2.5045 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0501 mL | 0.2505 mL | 0.5009 mL | 1.0018 mL | 1.2523 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
4-Chloro-DL-phenylalanine is a pharmaceutical intermediate.
- Baogongteng A
Catalog No.:BCN1874
CAS No.:74239-84-2
- Doronenine
Catalog No.:BCN2066
CAS No.:74217-57-5
- OSU-03012 (AR-12)
Catalog No.:BCC1255
CAS No.:742112-33-0
- Carbenoxolone disodium
Catalog No.:BCC3745
CAS No.:7421-40-1
- Vintafolide
Catalog No.:BCC5265
CAS No.:742092-03-1
- 3-Bromo-7-nitroindazole
Catalog No.:BCC6770
CAS No.:74209-34-0
- Uplandicine
Catalog No.:BCN2055
CAS No.:74202-10-1
- Doxazosin
Catalog No.:BCC4218
CAS No.:74191-85-8
- Cyclokievitone
Catalog No.:BCC8159
CAS No.:74175-82-9
- Haginin A
Catalog No.:BCN6861
CAS No.:74174-29-1
- R547
Catalog No.:BCC3927
CAS No.:741713-40-6
- 2,3-Dehydrokievitone
Catalog No.:BCN4294
CAS No.:74161-25-4
- 7-Acetylintermedine
Catalog No.:BCN1998
CAS No.:74243-01-9
- 12-Oxograndiflorenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7624
CAS No.:74284-42-7
- Triptophenolide
Catalog No.:BCN2546
CAS No.:74285-86-2
- Sinapine thiocyanate
Catalog No.:BCN2765
CAS No.:7431-77-8
- Quercetin-3-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCN3878
CAS No.:7431-83-6
- Somatostatin 1-28
Catalog No.:BCC5715
CAS No.:74315-46-1
- Z-Trp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2750
CAS No.:7432-21-5
- Schisandrin A
Catalog No.:BCN5815
CAS No.:7432-28-2
- 4',4'''-Di-O-methylcupressuflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4295
CAS No.:74336-91-7
- (RS)-AMPA
Catalog No.:BCC6560
CAS No.:74341-63-2
- Chidamide
Catalog No.:BCC6445
CAS No.:743420-02-2
- Ent-16Α,17-Dihydroxy-19-Kauranoic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC9227
CAS No.:74365-74-5
P-chlorophenylalanine increases glutamate receptor 1 transcription in rat amygdala.[Pubmed:21876464]
Neuroreport. 2011 Oct 26;22(15):758-61.
The amygdala is a key limbic structure strongly implicated in both epilepsy and anxiety disorders. Epilepsy-like mechanisms involve an increased glutamatergic activity, whereas disturbances in serotonin [5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)] systems are associated with anxiety-like behavior. Previous studies suggest that low 5-HT increases amygdala excitability, but the molecular mechanisms are not well characterized. Herein we explore the ability of low serotonin to increase glutamate receptor transcription. Using quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, we found that rats treated with p-Chlorophenylalanine, an inhibitor of tyrosine-5-hydroxylase, resulted in a 21-fold increase in glutamate receptor 1 (GluR1) mRNA expression in the amygdala. These results suggest that low 5-HT induces hyperexcitability of amygdala neurons by increasing GluR1 transcription, and the upregulation of amygdala GluR1 may be important in the pathophysiology of anxiety disorders.
Lipidomic analysis of p-chlorophenylalanine-treated mice using continuous-flow two-dimensional liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:26212164]
Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2015 Aug 30;29(16):1491-500.
RATIONALE: Although serotonin deficiency is involved with various physiological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia and depression, the serotonin-dependent pathomechanisms remain poorly understood, particularly from a lipidomics perspective. METHODS: This study therefore aimed to identify novel lipid biomarkers associated with serotonin deficiency by lipid profiling of p-Chlorophenylalanine (pCPA)-treated, serotonin-deficient mice using continuous-flow normal-phase/reversed-phase two-dimensional liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (NP/RP 2D LC/QTOFMS). Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to distinguish significantly altered lipids between the pCPA-treated mice and control mice. RESULTS: Eighteen lipid biomarkers were associated with pCPA-induced serotonin deficiency. Specifically, lipid species of lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), sphingomyelin (SM), galactosylceramide (GalCer), glucotosylceramide (GluCer), lactosylceramide (LacCer) and triacylglycerol (TG) were down-regulated whereas glycerophosphocholine (PC) and phosphatidylinositol (PI) were up-regulated in the pCPA-treated mice compared with control mice. CONCLUSIONS: This work demonstrates the significant effects of serotonin deficiency on lipid metabolisms and will facilitate improved understanding of pathomechanisms in serotonin deficiency, particularly from a lipidomics perspective.
DNA damage induced by phenylalanine and its analogue p-chlorophenylalanine in blood and brain of rats subjected to a model of hyperphenylalaninemia.[Pubmed:24032682]
Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;91(5):319-24.
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a disease caused by a deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), resulting in an accumulation of phenylalanine (Phe) in the brain tissue, cerebrospinal fluid, and other tissues of PKU patients. Considering that high levels of Phe are associated with neurological dysfunction and that the mechanisms underlying the neurotoxicity in PKU remain poorly understood, the main objective of this study was to investigate the in vivo and in vitro effects of Phe on DNA damage, as determined by the alkaline comet assay. The results showed that, compared to control group, the levels of DNA migration were significantly greater after acute administration of Phe, p-Chlorophenylalanine (p-Cl-Phe, an inhibitor of PAH), or a combination thereof in cerebral cortex and blood, indicating DNA damage. These treatments also provoked increase of carbonyl content. Additionally, when Phe or p-Cl-Phe was present in the incubation medium, we observed an increase in the frequency and index of DNA damage in the cerebral cortex and blood, without affecting lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release. Our in vitro and in vivo findings indicate that DNA damage occurs in the cerebral cortex and blood of rats receiving Phe, suggesting that this mechanism could be, at least in part, responsible for the neurological dysfunction in PKU patients.
Gan-Dan-Liang-Yi-Tang alleviates p-chlorophenylalanine-induced insomnia through modification of the serotonergic and immune system.[Pubmed:27882122]
Exp Ther Med. 2016 Nov;12(5):3087-3092.
Gan-Dan-Liang-Yi-Tang (GDLYT) is a Traditional Chinese Medicine that has been historically used for the treatment of insomnia. However, investigations into its pharmacological ingredients and the mechanism underlying its sedative and hypnotic effects remain limited. The present study reported the detailed mechanisms underlying the sedative and hypnotic effects of GDLYT. Kunming mice were administered GDLYT at various sub-hypnotic doses, which underwent sodium pentobarbital treatment test, pentetrazole induced convulsant studies and p-Chlorophenylalanine (PCPA) induced insomnia model. Potentiated hypnotic and sedative effects in mice was studied, and also the changes in related neurotransmitter and immune factors were evaluated. The results suggested that GDLYT possessed weak sedative effects on pentetrazole-induced convulsive activity in normal mice at a dose of 1.3 mg/kg, with an increase in sleep onset in subhypnotic dose of sodium pentobarbital-treated mice. GDLYT was also able to alleviate insomnia induced by PCPA in the rodent models, and increased 5-hydroxytryptamine levels in the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus and corpus striatum of PCPA-treated rats. Furthermore, the hypnotic effects of GDLYT were modified, which allowed for PCPA-induced immune system changes, including increased interleukin (IL)-1beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-2 expression levels. The results of the present study indicated that GDLYT induced sedative and hypnotic bioactivity by regulating serotonergic activity in the central nervous system and immune system.
Effect of p-chlorophenylalanine at moderate dosage on 5-HT and 5-HIAA concentrations in brain regions of control and p-chloroamphetamine treated rats.[Pubmed:8783206]
Neuropharmacology. 1996 Mar;35(3):315-20.
The effects of p-Chlorophenylalanine (PCPA, 100-150 mg/kg x 1. i.p.), doses which decrease brain 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) by 30-50%, were investigated in both intact rats and 14 days after giving p-chloroamphetamine (PCA, 10 mg/kg/day x 2, i.p.). The PCPA dose-dependently decreased brain regional 5-HT and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) 24 hr later. As per cent decreases of 5-HIAA were greater than those of 5-HT in cortex, striatum and hippocampus 5-HIAA/5-HT ratios fell, suggesting that partial inhibition of 5-HT synthesis by PCPA increases 5-HT conservation in these terminal regions. In the hypothalamus and brain stem, decreases of the ratio were small or absent. The PCA given without subsequent PCPA treatment decreased 5-HT and 5-HIAA so that 5-HT fell by about 70% in the cortex, striatum and hippocampus, 55% in the brain stem but only by 27% in the hypothalamus. The PCPA given after PCA decreased 5-HT and 5-HIAA further but not the 5-HIAA/5-HT ratios and increased the ratio in the brain stem. The 5-HIAA/5-HT findings imply that the increase of 5-HT conservation after PCPA treatment does not occur after partial depletion of 5-HT by PCA. The increase of the 5-HIAA/5-HT ratio in the brain stem is explicable by the resistance to both PCA and PCPA of 5-HT in cell bodies where the ratio is high. Results are discussed in relation to the question of whether the PCA treatment used destroys axon terminals projecting from the dorsal but not from the median raphe.
The effects of DL-p-chlorophenylalanine and DL-alpha-methyl-p-tyrosine on the brain catecholamine, serotonin and free amino acid contents in rat.[Pubmed:129787]
Psychopharmacologia. 1975 Dec 31;45(2):163-6.
The changes in the brain levels of catecholamines, serotonin and free amino acids have been considered as a factor in the development of the physical dependence on and tolerance to some drugs. In order to show the relationships among the brain levels of these substances, three groups of rats were given i.p. DL-alphaMpT alone, DL-pCPA alone, or DL-alphaMpT and DL-pCPA together, twice a day for three days. Another group was kept as control. The brain levels of catecholamines, serotonin and free amino acids were determined. Although DL-alphaMpT and DL-pCPA alone caused a decrease in the levels of catecholamines and serotonin respectively, the administration of DL-alphaMpT and DL-pCPA together did not. The changes in the levels of free amino acids which were found were related to the metabolism of catecholamines and serotonin.


