NSC 632839 hydrochlorideIsopeptidases inhibitor CAS# 157654-67-6 |
- P 22077
Catalog No.:BCC3616
CAS No.:1247819-59-5
- SJB2-043
Catalog No.:BCC1952
CAS No.:63388-44-3
- Vialinin A
Catalog No.:BCC2367
CAS No.:858134-23-3
- P005091
Catalog No.:BCC1287
CAS No.:882257-11-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 157654-67-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5351362 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H22ClNO | M.Wt | 339.86 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | F6 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 6.2 mg/mL (18.24 mM; Need warming) | ||
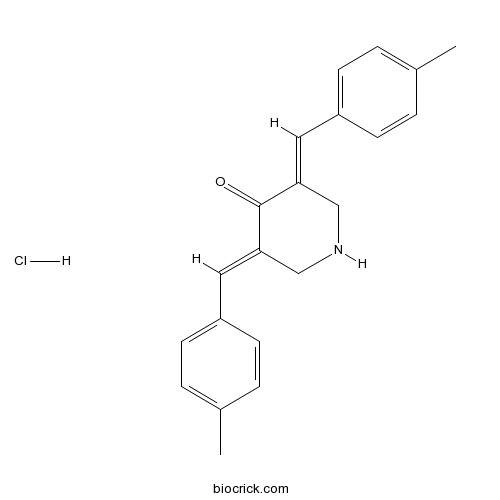
| Chemical Name | (3E,5E)-3,5-bis[(4-methylphenyl)methylidene]piperidin-4-one;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C=C2CNCC(=CC3=CC=C(C=C3)C)C2=O.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZOKZLTXPTLIWOJ-BYCVLTJGSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H21NO.ClH/c1-15-3-7-17(8-4-15)11-19-13-22-14-20(21(19)23)12-18-9-5-16(2)6-10-18;/h3-12,22H,13-14H2,1-2H3;1H/b19-11+,20-12+; | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of ubiquitin isopeptidase activity that displays no effect on the proteolytic activity of the proteasome. Induces apoptosis via a Bcl-2-dependent and apoptosome-independent pathway of caspase activation (IC50 values are 15.65 and 16.23 μM in E1A and E1A/C9CN cells respectively). |

NSC 632839 hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

NSC 632839 hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9424 mL | 14.7119 mL | 29.4239 mL | 58.8478 mL | 73.5597 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5885 mL | 2.9424 mL | 5.8848 mL | 11.7696 mL | 14.7119 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2942 mL | 1.4712 mL | 2.9424 mL | 5.8848 mL | 7.356 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0588 mL | 0.2942 mL | 0.5885 mL | 1.177 mL | 1.4712 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0294 mL | 0.1471 mL | 0.2942 mL | 0.5885 mL | 0.7356 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
NSC 632839 is a nonselective inhibitor of isopeptidases with IC50 values of 45 μM, 37μM, and 9.8μM, respectively for USP2, USP7, and SENP2 [1].
NSC 632839 is reported to have activity against the purified isopeptidases. It inhibits not only DUB (USP2, USP7) but also deSUMOylase (SENP2). It is also shown to inhibit cleavage of an Ub mimetic (z-LRGG-AMC) by transformed fibroblast lysates. However, NSC 632839 has no inhibition to the reporter enzyme PLA2, suggesting the inhibition is selective for isopeptidases [1].
NSC 632839 prevents removal of ubiquitin chains from polyubiquitinated proteins, inhibiting ubiquitin-dependent, proteasome-mediated degradation. It activates apoptosis in an apoptosome-independent manner [2, 3].
References:
[1] Nicholson B, Leach CA, Goldenberg SJ, Francis DM, Kodrasov MP, Tian X, Shanks J, Sterner DE, Bernal A, Mattern MR, Wilkinson KD, Butt TR. Characterization of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like-protein isopeptidase activities. Protein Sci. 2008 Jun;17(6):1035-43.
[2] Gupta-Saraf P, Miller CL. HIF-1α downregulation and apoptosis in hypoxic prostate tumor cells infected with oncolytic mammalian orthoreovirus. Oncotarget. 2014 Jan 30;5(2):561-74.
[3] Eldridge AG, O'Brien T. Therapeutic strategies within the ubiquitin proteasome system. Cell Death Differ. 2010 Jan;17(1):4-13.
- Boc-Pro-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3435
CAS No.:15761-39-4
- Boc-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3047
CAS No.:15761-38-3
- (S)-SNAP 5114
Catalog No.:BCC7117
CAS No.:157604-55-2
- BTS
Catalog No.:BCC5425
CAS No.:1576-37-0
- Coronarin D methyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN1705
CAS No.:157528-81-9
- Taxuspine B
Catalog No.:BCN6938
CAS No.:157414-05-6
- Bacoside A3
Catalog No.:BCC8128
CAS No.:157408-08-7
- MAP4
Catalog No.:BCC6758
CAS No.:157381-42-5
- DMP 777
Catalog No.:BCC1534
CAS No.:157341-41-8
- Travoprost
Catalog No.:BCC5189
CAS No.:157283-68-6
- ML-323
Catalog No.:BCC4313
CAS No.:1572414-83-5
- Bosentan Hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4494
CAS No.:157212-55-0
- Prenylpiperitol
Catalog No.:BCN1706
CAS No.:157659-20-6
- 7-Xylosyl-10-deacetylbaccatin III
Catalog No.:BCN7668
CAS No.:157664-03-4
- Perifosine
Catalog No.:BCC3673
CAS No.:157716-52-4
- Gentiournoside D
Catalog No.:BCN7855
CAS No.:157722-21-9
- Gypenoside A
Catalog No.:BCN8459
CAS No.:157752-01-7
- 5-Nonyloxytryptamine oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC6839
CAS No.:157798-13-5
- 5-Benzimidazolecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8739
CAS No.:15788-16-6
- (Z)-2-decenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC1295
CAS No.:15790-91-7
- Chitinase-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5533
CAS No.:1579991-61-9
- Chitinase-IN-2
Catalog No.:BCC5534
CAS No.:1579991-63-1
- ortho-iodoHoechst 33258
Catalog No.:BCC1824
CAS No.:158013-41-3
- meta-iodoHoechst 33258
Catalog No.:BCC1739
CAS No.:158013-42-4
Mitoxantrone hydrochloride (NSC-310739) in lymphoma. A Southwest Oncology Group study.[Pubmed:6678857]
Invest New Drugs. 1983;1(1):65-70.
The members of the Southwest Oncology Group have treated thirteen patients with Hodgkin's disease and thirty-seven with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma with mitoxantrone on the every three week schedule. While the result (3/13 responses in Hodgkin's; 9/37 responses in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma) is not striking, there is a definite antitumor activity in a very heavily pretreated group of patients. Toxicity was acceptable. Additional trials in lymphoma are planned using mitoxantrone in combination with BCNU.
Phase I-II study of pibenzimol hydrochloride (NSC 322921) in advanced pancreatic carcinoma.[Pubmed:1709152]
Invest New Drugs. 1991 Feb;9(1):53-7.
Pibenzimol is a fluorescent molecule known to bind to double stranded DNA. It also induces prolongation of the G2 phase of the cell cycle, inhibition of DNA replication and cessation of the growth of some cells in late S phase after DNA content has been doubled. It has been shown to increase the life span of mice bearing intraperitoneally implanted L1210 and P388 leukemia. These factors coupled with the affinity of pibenzimol for pancreatic tissue led us to conduct a phase I-II trial of pibenzimol hydrochloride in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Twenty-six patients were treated with a five day continuous infusion of pibenzimol at a dose ranging from 6-28 mg/m2/d. There were no treatment related deaths. Major toxicity was hyperglycemia which was self-limited. No objective responses were noted.
Investigational new drug-directed, 5-day repeat dose toxicity study of 4-[3-(2-nitro-1-imidazolyl)-propylamino]-7-chloroquinoline hydrochloride (NLCQ-1, NSC 709257) administered with or without Taxol in Sprague-Dawley rats.[Pubmed:20074267]
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010 Jun;106(6):497-504.
In pre-clinical studies, 4-[3-(2-nitro-1-imidazolyl)-propylamino]-7-chloroquinoline hydrochloride (NLCQ-1, NSC 709257) is a weak DNA-intercalating, hypoxia-selective cytotoxin with a promising profile as an adjuvant to radio/chemotherapy and it is about to enter phase I clinical trials. The present investigation was undertaken to further evaluate potential systemic toxicity induced by i.v. doses of NLCQ-1 alone or in combination with Taxol in Sprague-Dawley rats, in support of an investigational new drug application. Doses of NLCQ-1 were based on previous range-finding studies. In the present study, NLCQ-1 was administered either alone, at 0, 6, 9 or 12 mg/kg/dose to male rats and 8, 12 or 16 mg/kg/dose to female rats or, at 9 (male rats) and 12 (female rats) mg/kg/dose, in combination with Taxol, on a qd x 5 schedule. Taxol was administered i.v. at 3.5 mg/kg/dose 1 hr before NLCQ-1. Observations were recorded for mortality/moribundity, clinical signs of toxicity, body weights, food consumption, haematology, clinical chemistry, gross lesions at necropsy and histopathology. Blood samples were taken from 10 animals from each dose group on each of 2 days (days 8 and prior to scheduled necropsy on day 33). Administration of i.v. doses of NLCQ-1 alone, on a qdx5 schedule, resulted in no signs of toxicity over the 33-day study. Taxol-induced toxicity included minimal decreases in the group mean RBC, haemoglobin and haematocrit values, minimal increases in group mean reticulocyte counts (females), marked decreases in group mean neutrophil counts and minimal decreases in group mean monocyte and eosinophil counts. Lymphoid atrophy of thymus, atrophy of bone marrow and atrophy of the germinal epithelium of the testis were also associated with the administration of Taxol. There was no additional toxicity associated with the co-administration of NLCQ-1 and Taxol. In the present study, the 'no observable adverse effect level' for NLCQ-1, when administered on a qdx5 schedule, was >12 and >16 mg/kg/dose in male and female rats respectively. Daily administration of 9 (male rats) or 12 (female rats) mg/kg of NLCQ-1 1 hr after i.v. administration of Taxol (3.5 mg/kg) had no effect on Taxol-induced toxicity.
Investigational new drug-directed toxicology and pharmacokinetic study of 4-[3-(2-nitro-1-imidazolyl)-propylamino]-7-chloroquinoline hydrochloride (NLCQ-1, NSC 709257) in Beagle dogs.[Pubmed:20074266]
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010 Jun;106(6):511-22.
4-[3-(2-Nitro-1-imidazolyl)-propylamino]-7-chloroquinoline hydrochloride (NLCQ-1), a 2-nitroimidazole-based hypoxia-selective cytotoxin has been shown to target hypoxic regions of solid tumours. The present study is one of several pre-clinical toxicology studies conducted in support of an 'investigational new drug' (IND) application to test this agent as an adjuvant to radio/chemotherapy for the treatment of cancer in humans. Twenty-four dogs were each assigned to one vehicle control group or to one of three test article-treated groups (three dogs/sex/treatment group). Intravenous (i.v.) doses of 0, 2.74, 5.48 and 10.95 mg/kg/day (54.8, 109.6 or 219 mg/m(2)/day) were administered on a per day x 5 days (qd x 5) schedule. NLCQ-1 was formulated as a solution in sterile saline at 1.5 mg/ml. None of the dogs died during this 33-day study. With few exceptions, most of the clinical signs of toxicity were noted within 2 hr following dosing in the 10.95 mg/kg/day dose group. These observations included aggressive behaviour, ataxia, tachypnea, emesis, hypoactivity, excessive salivation, tremors, and involuntary urination and defecation. Aggressive behaviour was judged to be dose-limiting. No clinical signs of toxicity were noted during the 28-day observation period that followed the 5-day dose period. Findings in a functional observation battery examination were consistent with the clinical observations. No drug-related effects were noted on the body weight or food consumption values, and no drug-related changes were noted during ocular examinations made on these animals prior to scheduled necropsy or during examination of electrocardiogram recordings made at 15 min. and 2 hr after dosing on days 1 and 5. No definitive changes in haematology, clinical chemistry or coagulation values were noted in dogs treated with NLCQ-1. NLCQ-1 was detected in the plasma of treated dogs on days 1 and 5, up to 60 min. after dosing (2.74 and 5.48 mg/kg/day) and up to 8 hr after dosing (10.95 mg/kg/day). There was a dose-related increase in maximum plasma concentration of NLCQ-1 at 5 min. after dosing; comparable concentrations were noted on days 1 and 5. No definitive test article-related lesions were noted during microscopic evaluation of tissues from dogs in this study, although lesions noted at the injection site and in the vascular tissue, lungs, thymus, prostate gland, muscle, adrenal cortex and tongue may have resulted from treatment with this drug. Any drug-related toxicity noted was readily reversible and not cumulative. No sex difference was detected in the susceptibility to NLCQ-1-induced toxicity.
Identification of new compounds that trigger apoptosome-independent caspase activation and apoptosis.[Pubmed:16982768]
Cancer Res. 2006 Sep 15;66(18):9235-44.
Identification of alternative pathways of caspase activation is an important step to develop new antitumor treatments. We report here the result of a screening with a small chemical library, the Developmental Therapeutics Program-National Cancer Institute "challenge set," on cells expressing mutated caspase-9. We have identified two molecules capable of activating an apoptosome-independent apoptotic pathway. These compounds, named F6 and G5, target the ubiquitin-proteasome system by inhibiting the ubiquitin isopeptidases. We have shown that F6 and G5 induce a rather unique apoptotic pathway, which includes a Bcl-2-dependent but apoptosome-independent mitochondrial pathway with up-regulation of the BH3-only protein Noxa, stabilization of the inhibitor of apoptosis antagonist Smac, but also the involvement of the death receptor pathway. Noxa plays an important role in the induction of mitochondrial fragmentation and caspase activation, whereas the death receptor pathway becomes critical in the absence of a functional apoptosome. This study suggests that screening of chemical libraries on cancer cells with defined mutations in apoptotic key elements can lead to the identification of compounds that are useful to characterize alternative pathways of caspase activation.


