Dracocephalum moldavica
Dracocephalum moldavica
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Dracocephalum moldavica
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5948
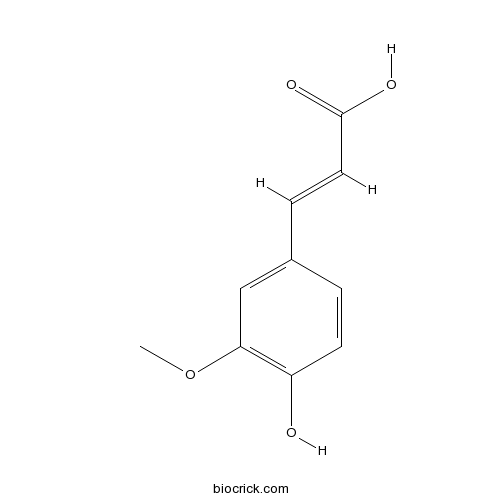
Ferulic acid1135-24-6
Instructions
-
BCN5549
Astragalin480-10-4
Instructions

-
BCN5560
Acacetin480-44-4
Instructions

-
BCN5600
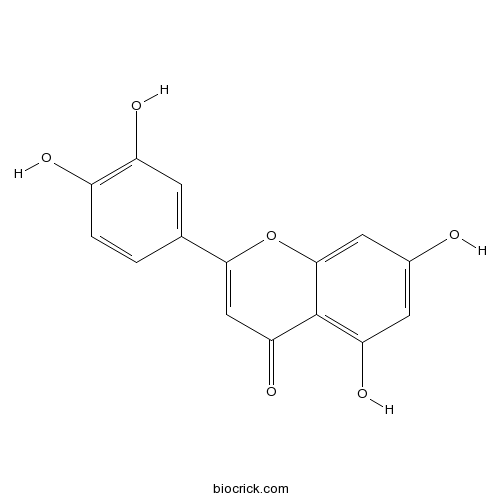
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
-
BCN5653
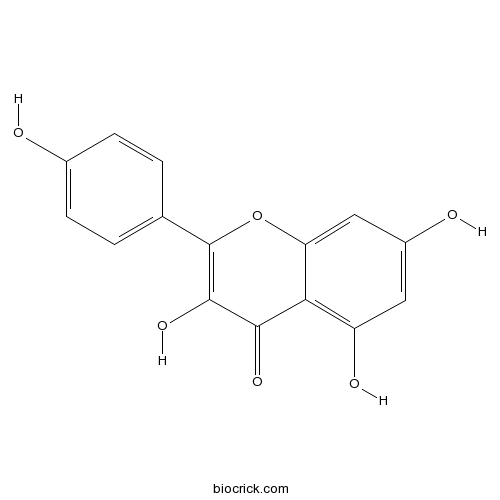
Kaempferol520-18-3
Instructions
-
BCN4327
Ursolic acid77-52-1
Instructions

-
BCN4376
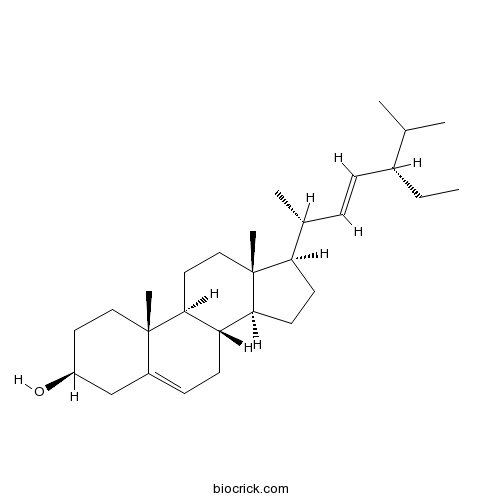
Stigmasterol83-48-7
Instructions
Effects of small-scale clustering of flowers on pollinator foraging behaviour and flower visitation rate.[Pubmed: 29136042]
Plants often grow in clusters of various sizes and have a variable number of flowers per inflorescence. This small-scale spatial clustering affects insect foraging strategies and plant reproductive success. In our study, we aimed to determine how visitation rate and foraging behaviour of pollinators depend on the number of flowers per plant and on the size of clusters of multiple plants using Dracocephalum moldavica (Lamiaceae) as a target species. We measured flower visitation rate by observations of insects visiting single plants and clusters of plants with different numbers of flowers. Detailed data on foraging behaviour within clusters of different sizes were gathered for honeybees, Apis mellifera, the most abundant visitor of Dracocephalum in the experiments. We found that the total number of flower visitors increased with the increasing number of flowers on individual plants and in larger clusters, but less then proportionally. Although individual honeybees visited more flowers in larger clusters, they visited a smaller proportion of flowers, as has been previously observed. Consequently, visitation rate per flower and unit time peaked in clusters with an intermediate number of flowers. These patterns do not conform to expectations based on optimal foraging theory and the ideal free distribution model. We attribute this discrepancy to incomplete information about the distribution of resources. Detailed observations and video recordings of individual honeybees also showed that the number of flowers had no effect on handling time of flowers by honeybees. We evaluated the implications of these patterns for insect foraging biology and plant reproduction.
Characterization of a novel biodegradable edible film obtained from Dracocephalum moldavica seed mucilage.[Pubmed: 29102793]
None
[Effect of Dracocephalum moldavica total flavones on expression of TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and matrix metalloproteinase of atherosclerosis ApoE-/- mice].[Pubmed: 29098831]
To investigate the effect and mechanism of Dracocephalum moldovica total flavones (TFDM) on the formation of atherosclerosis ApoE-/- mice induced by high fat diet. A total of 40 SPF 8-week-old male ApoE-/- mice were fed with high fat diet and randomly divided into 5 groups. TFDM high, medium, low-dose group were given 21, 42, 84 mg•kg⁻¹•d⁻¹ by gavage; Simvastatin group was fed with simvastatin 3.5 mg•kg⁻¹•d⁻¹; and model group was given the same dose of normal saline. The other eight male C57BL/6J mice of the same genetic background and age were set up as control group and fed with common diet. All of the groups were intragastrically intervened for 12 weeks. The aortic pathologic changes were observed with HE; qRT-PCR was adopted to detect TGF-β1, Smad2, Smad3, MMP-2 and MMP-9 gene levels in tissues. Compared with model group, HE staining in TFDM group showed obvious relief of aortic atherosclerotic tissue injury; each TFDM group showed inhibition in mRNA expressions of TGF-β1, Smad2, Smad3, MMP-2 and MMP-9. This suggests that TFDM can inhibit atherosclerosis formation, which may be related to the intervention of TGF-β1/Smads signal transduction.
The inhibitory effects of Dracocephalum moldavica L. (DML) on rat cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury.[Pubmed: 28876179]
Ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI) is closely associated with oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. Dracocephalum moldavica L. (DML), a Chinese herbal medicine is known to exert protective effects on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting oxidation damage and inflammatory reactions. However, the effectiveness of DML in cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury (CIRI) as a protective substance and the underlying mechanisms remain to be determined. The aim of this study was thus to examine the influence of DML on CIRI using a rat model induced by 2-h transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) produced by intraluminal suture blockade followed by 22 h reperfusion. The parameters determined include neurological behavior, histochemical assessment of cerebral infarct volume, and determination of various metabolic biomarkers. Data showed that DML markedly improved neurobehavioral scores and reduced cerebral edema and infarction. In addition, DML significantly reduced malondialdehyde (MDA) content and elevated activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), in addition, marked decrease in levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Data suggest that the protective effects of DML on CIRI may be related to processes involving antioxidation and anti-inflammation.
A new caffeic acid tetramer from the Dracocephalum moldavica L.[Pubmed: 28805461]
None
Effects of Tilianin on Proliferation, Migration and TGF-β/Smad Signaling in Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Induced with Angiotensin II.[Pubmed: 28620995]
Flavonoid Tilianin was isolated from Dracocephalum moldavica, and its pharmacological mechanism on proliferation, migration and the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in rat vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) induced with Angiotensin II (Ang II) was systematically evaluated. Primary rat VSMCs were stimulated with Ang II to induce proliferation. The cells were then treated with Tilianin for 24 or 48 h. MTT assay and Transwell assays were used to evaluate the effects of Tilianin on proliferation and migration. The expression of intracellular proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) were measured by immunohistochemistry as verification of effects on proliferation and migration. The expression of TGF-β1, Smad2 and Smad3 mRNA was measured by qRT-PCR, and the expression of TGF-β1 and P-Smad2/3 protein was measured by Western blotting. The results show that Tilianin can inhibit proliferation and expression of intracellular PCNA in VSMCs induced with Ang II, in a dose-dependent manner. Tilianin also mediates a dose-dependent inhibition of migration and the expression of intracellular ICAM-1, VCAM-1, MMP-2 and MMP-9. Furthermore, TGF-β1, Smad2, Smad3, Smad2/3 and P-Smad2/3 in Ang II-induced VSMCs are suppressed by Tilianin. The inhibitory effects of Tilianin support its use in the suppression and treatment of atherosclerosis.


