Drosera peltata
Drosera peltata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Drosera peltata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
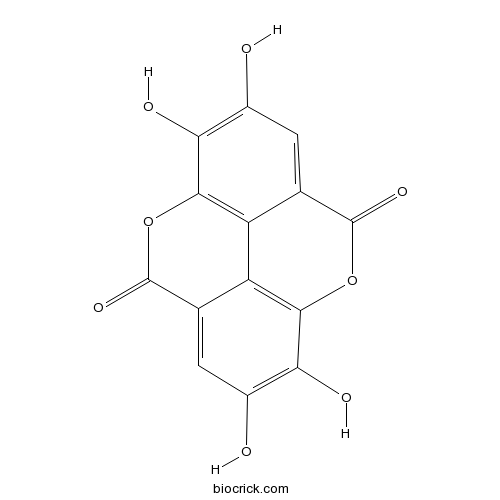
BCN5533
Ellagic acid476-66-4
Instructions
-
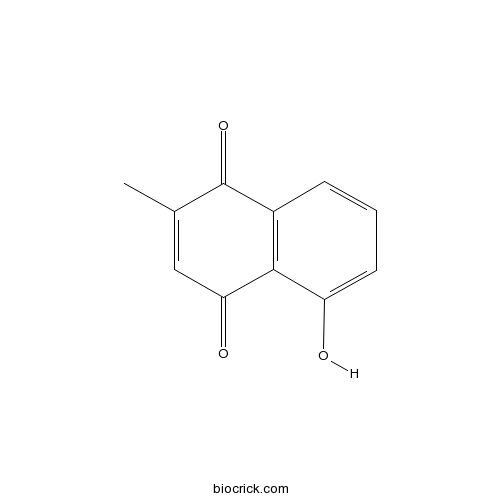
BCN2586
Plumbagin481-42-5
Instructions
Population history of the two carnivorous plants Drosera peltata var. nipponica and Drosera rotundifolia (Droseraceae) in Korea.[Pubmed: 24186960]
Drosera peltata var. nipponica, an element of the East Asia warm-temperate vegetation, and D. rotundifolia, a widely distributed boreal species, reach one of their northernmost and southernmost limits, respectively, on the Korean Peninsula. Because the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM)-Holocene dynamics of warm-temperate and boreal paleovegetation differed considerably on the Peninsula, the population history of these two sundews is expected to be different, leaving differential imprints in their genetic structure.
Determination of quercetin, plumbagin and total flavonoids in Drosera peltata Smith var. glabrata Y.Z.Ruan.[Pubmed: 24082628]
Drosera peltata Smith var. glabrata Y.Z.Ruan, a kind of wild carnivorous plants in the family Droseraceae, has been used for the treatment of rheumatism and bruises in Chinese folk. None of compounds in this herb has been quantified in the previous studies.
Drosera peltata Smith var. lunata (Buch.-Ham.) C. B. Clarke as a feasible source of plumbagin: phytochemical analysis and antifungal activity assay.[Pubmed: 24078108]
Drosera peltata Smith var. lunata (Buch.-Ham.) C. B. Clarke (DPVL) fractions and plumbagin were tested via broth microdilution techniques on Rhizopus oryzae, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus oryzae, Penicillium citrinum. All of the test substances [petroleum ether, chloroform, ethyl acetate, n-butanol fraction and aqueous residue (AR)] except for the AR were active against all the tested strains. The petroleum ether fraction (PEF) was the most active (MIC = 5.86-46.88 μg/ml, MFC = 23.44-93.75 μg/ml) of the five tested substances and therefore, was selected for further analysis. Based on antifungal activity, bioactivity-guided fractionation of the PEF led to the isolation of plumbagin. The structure of plumbagin was elucidated by ¹H and ¹³C NMR. Using HPLC, DPVL was found to be a new source of plumbagin. Reversed-phase HPLC was performed using a mobile phase of water and methanol, and peaks were detected at 254 nm. Plumbagin showed a good linear relationship at concentrations ranging from 0.625 to 10 μg/ml. Both the intraday and the interday precision showed that the method was precise, with RSDs of at least 3% at different concentrations. Recovery rates ranging from 97.86 to 99.94% were observed, which indicate that the method is accurate. The specificity of the method was established by checking the peak purity of plumbagin. For six independent measurements, the average plumbagin content in DPVL was 11.05 ± 0.31 mg/g of dried material. The validated HPLC method provides a new basis for assessing DPVL quality.
LC-NMR, NMR, and LC-MS identification and LC-DAD quantification of flavonoids and ellagic acid derivatives in Drosera peltata.[Pubmed: 23831703]
The herb of Drosera peltata, commonly named the shield sundew, is used as an antitussive in phytotherapy, although the plants' composition has not been determined in detail so far. Hence, in this study, we present a validated, sensitive, reliable, and cheap narrow-bore LC-DAD method for the simultaneous quantification of flavonoids and ellagic acid derivatives in this herbal drug. In addition, the structures of 13 compounds have been elucidated by LC-MS, LC-NMR, and offline NMR experiments after isolation: herbacetin-3-O-glucoside (1), gossypitrin (2), ellagic acid (3), quercetin-7-O-glucoside (4), isoquercitrin (5), kaempferol-3-O-(6″-O-galloyl)-glucoside (6), herbacetin-7-O-glucoside (7), astragalin (8), gossypetin (9), herbacetin (10), quercetin (11), 3,3'-di-O-methyl ellagic acid (12), and kaempferol (13). Compounds 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 10 have been identified in D. peltata for the first time, and compounds 1, 4, 6, 7, and 10 have not been detected in any Drosera species before.
[Study on chemical constituents of Drosera peltata var. multisepala].[Pubmed: 22737855]
Chemical investigatation of Drosera peltata var. multisepala led to the isolation of eleven compounds using various chromatographic techniques. The structures of these compounds were elucidated as isoshinanolone-4-O-beta-D-glucoside (1), isoshinanolone (2), epi-isoshinanolone (3), plumbagin (4), droserone (5), droserone-5-O-glucoside (6), quercetin (7), kaempferol (8) , gossypetin-8-O-glucoside (9), 3,3'-dimethoxy ellagic acid (10), and ellagic acid (11) by their physicochemical properties and spectral data analysis. Compound 1 was a new compound. Compounds 3, 8, 10, and 11 were isolated from this plant for the first time.
[Chemical constituents of Drosera peltata Smith var. lunata (Buch.-Ham.) C.B. clarke collected in Tibet].[Pubmed: 11599349]
To investigate the chemical constituents of the whole plant of Drosera peltata var. lunata collected in Tibet.
Fire Control - A Conservation Tool for certain Medical Plants in Grass Hills Ecosystem, The Western Ghats.[Pubmed: 22557019]
Grass Hills ecosystem lies in Anaimalais. The western ghats possesses rich biodiversity, The annual summer fire, an integral part of this ecosystem, promotes the ecological status of certain perennial grasses including the dominant grass. Chrysopogon zeylanicus Thw. On the other hand, some medicinal plants Viz., Impatiens tomentosa Heyne, Drosera peltata Sm Osbeckia parviflora Arn., Emilia sonchifolia Dc. Lecanthus penduncularis Wedd. And Lobelia nicotianifolia Heyne were identiflora Arn. Emilia sonchifolia Dc. Lecanthus penduncularis wedd and lobelia nicotianifolia Heyne were identified as fire threatened species and it has been observed that their sociological attributes were hampered severely by fire. Hence, the conservation of such species is needed through effective fire control measures.
Antimicrobial activity of aerial parts of Drosera peltata Smith on oral bacteria.[Pubmed: 9533437]
The antimicrobial activity of extracts of aerial parts of Drosera peltata Smith against oral bacteria was investigated using agar diffusion and dilution micromethods. The chloroformic extract, active against all the bacteria tested, showed the most significant antimicrobial properties. Plumbagin, isolated from the extract, is the active principle. Results obtained suggest that Drosera peltata extract could be used in the treatment of oral infectious diseases like dental caries and periodontitis.


