Ellagic acidCasein kinase 2 (CK2) inhibitor CAS# 476-66-4 |
- Gatifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC1064
CAS No.:112811-59-3
- Dexrazoxane HCl (ICRF-187, ADR-529)
Catalog No.:BCC1087
CAS No.:149003-01-0
- Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1117
CAS No.:25316-40-9
- Etoposide
Catalog No.:BCC1151
CAS No.:33419-42-0
- Genistein
Catalog No.:BCN5499
CAS No.:446-72-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 476-66-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281855 | Appearance | Beige-grey powder |
| Formula | C14H6O8 | M.Wt | 302.2 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Alizarin Yellow; Benzoaric acid; Elagostasine; Eleagic acid; Gallogen; Lagistase | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 3.33 mg/mL (11.02 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
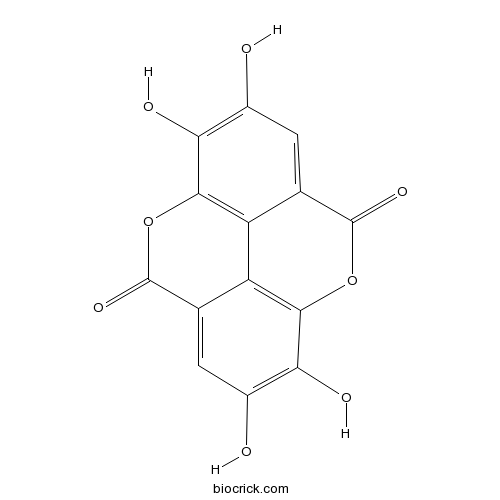
| SMILES | C1=C2C3=C(C(=C1O)O)OC(=O)C4=CC(=C(C(=C43)OC2=O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AFSDNFLWKVMVRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H6O8/c15-5-1-3-7-8-4(14(20)22-11(7)9(5)17)2-6(16)10(18)12(8)21-13(3)19/h1-2,15-18H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ellagic acid is a potent and ATP-competitive CK2 inhibitor, with an IC50 of 40 nM and a Ki of 20 nM. Ellagic acid has anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative and antioxidant properties, it can prevent cognitive and LTP deficits and also prevent brain inflammation following TBI. Ellagic acid reduced the expression of NO, MDA, IL-1β, TNF-α, COX-2 and NF-κB, and induced the production of GSH and IL-10. |
| Targets | ROS | Calcium Channel | Caspase | p21 | p53 | IL Receptor | NO | TNF-α | NF-kB | COX | CK2 | MDA | GSH |
| In vitro | Ellagic acid induces apoptosis in TSGH8301 human bladder cancer cells through the endoplasmic reticulum stress- and mitochondria-dependent signaling pathways.[Pubmed: 23554011]Environ Toxicol. 2014 Nov;29(11):1262-74.
|
| In vivo | Effect of ellagic acid on some haematological, immunological and antioxidant parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).[Pubmed: 24401136]J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2014 Oct;98(5):936-41.In this study, effect of Ellagic acid on some haematological, immunological and antioxidant parameters in the blood and various tissues of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) were examined.
Ellagic acid protects against carrageenan-induced acute inflammation through inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B, inducible cyclooxygenase and proinflammatory cytokines and enhancement of interleukin-10 via an antioxidant mechanism.[Pubmed: 24534771]Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Apr;19(2):290-9.There are several hypotheses that explain the process of acute inflammation, including free radical overproduction, pro-inflammatory enzyme activation, and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. In this study, the protective role of Ellagic acid against carrageenan-induced acute inflammation was assessed. In addition, the immunomodulatory action, the antioxidant effects, and the role of COX-2 and NF-κB were also investigated.
|
| Animal Research | Ellagic acid prevents cognitive and hippocampal long-term potentiation deficits and brain inflammation in rat with traumatic brain injury.[Pubmed: 25637685]Life Sci. 2015 Mar 1;124:120-7.Traumatic brain injury (TBI) remains one of the main clinical problems globally and is a common cause of death among youth. Cognitive defects such as thinking, memory and behavior or mental health disorders are considered as the most frequent effects of severe and moderate TBI. It has been reported that Ellagic acid (EA), a natural polyphenol, exhibits protective effects against oxidative damage. This study was performed to examine the EA preventive effects on cognitive impairments, long-term potentiation (LTP) deficits in hippocampus and brain inflammation induced by diffuse TBI in rat.
|

Ellagic acid Dilution Calculator

Ellagic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3091 mL | 16.5453 mL | 33.0907 mL | 66.1813 mL | 82.7267 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6618 mL | 3.3091 mL | 6.6181 mL | 13.2363 mL | 16.5453 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3309 mL | 1.6545 mL | 3.3091 mL | 6.6181 mL | 8.2727 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0662 mL | 0.3309 mL | 0.6618 mL | 1.3236 mL | 1.6545 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0331 mL | 0.1655 mL | 0.3309 mL | 0.6618 mL | 0.8273 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Selective, ATP-competitive inhibitor of casein kinase 2 (CK2) (IC50 values are 40, 2900, 3500, 4300 and 9400 nM for CK2, Lyn, PKA, Syk?and FGR respectively). Exhibits antioxidant, antitumor and anticarcinogenic activity and also inhibits glutat
- Chelidonine
Catalog No.:BCN2463
CAS No.:476-32-4
- Lycorine
Catalog No.:BCN2409
CAS No.:476-28-8
- Xylotriose
Catalog No.:BCN8428
CAS No.:47592-59-6
- Isotretinoin
Catalog No.:BCC2284
CAS No.:4759-48-2
- MCL 0020
Catalog No.:BCC6025
CAS No.:475498-26-1
- NVP-AEW541
Catalog No.:BCC1180
CAS No.:475489-16-8
- NVP-ADW742
Catalog No.:BCC4553
CAS No.:475488-23-4
- Aleglitazar
Catalog No.:BCC1337
CAS No.:475479-34-6
- CORM-3
Catalog No.:BCC5108
CAS No.:475473-26-8
- Nogo-66 (1-40)
Catalog No.:BCC5862
CAS No.:475221-20-6
- Sorafenib Tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC3654
CAS No.:475207-59-1
- A-317491
Catalog No.:BCC1320
CAS No.:475205-49-3
- Corydine
Catalog No.:BCN2669
CAS No.:476-69-7
- Boldine
Catalog No.:BCN5534
CAS No.:476-70-0
- VO-Ohpic trihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC2043
CAS No.:476310-60-8
- Eupaglehnin C
Catalog No.:BCN7118
CAS No.:476630-49-6
- Lushanrubescensin H
Catalog No.:BCN3235
CAS No.:476640-22-9
- 6,9,10-Trihydroxy-7-megastigmen-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN1435
CAS No.:476682-97-0
- 3-(2-Benzothiazolylthio)propionic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8586
CAS No.:4767-00-4
- Boc-Tyr(2-Br-Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3460
CAS No.:47689-67-8
- Lycorenine
Catalog No.:BCN2507
CAS No.:477-19-0
- Demecolcine
Catalog No.:BCC9223
CAS No.:477-30-5
- Samidin
Catalog No.:BCN6665
CAS No.:477-33-8
- Dehydrocostus lactone
Catalog No.:BCN5536
CAS No.:477-43-0
Effect of ellagic acid on some haematological, immunological and antioxidant parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).[Pubmed:24401136]
J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2014 Oct;98(5):936-41.
In this study, effect of Ellagic acid on some haematological, immunological and antioxidant parameters in the blood and various tissues of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) were examined. Four groups of rainbow trout were fed experimental diets containing either no Ellagic acid (control) or supplemented with Ellagic acid at 50 mg/kg diet (EA-50), 100 mg/kg diet (EA-100) or 150 mg/kg diet (EA-150) for 21 days. Samples of the blood and tissue (liver, kidney and spleen) were collected at the end of the experiment and analysed for their haematological profile (the red blood cell count, the haemoglobin concentration and the haematocrit level), immune response (the white blood cell count, the oxidative radical production (NBT activity), the total plasma protein and total immunoglobulin level) and oxidant/antioxidant status (the malondialdehyde level, the superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase activity as well as the reduced glutathione concentration). The findings of this study demonstrated that Ellagic acid had a positive effect on the haematological parameters, the immune response and the antioxidant enzyme activities of the fish.
Ellagic acid prevents cognitive and hippocampal long-term potentiation deficits and brain inflammation in rat with traumatic brain injury.[Pubmed:25637685]
Life Sci. 2015 Mar 1;124:120-7.
AIMS: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) remains one of the main clinical problems globally and is a common cause of death among youth. Cognitive defects such as thinking, memory and behavior or mental health disorders are considered as the most frequent effects of severe and moderate TBI. It has been reported that Ellagic acid (EA), a natural polyphenol, exhibits protective effects against oxidative damage. This study was performed to examine the EA preventive effects on cognitive impairments, long-term potentiation (LTP) deficits in hippocampus and brain inflammation induced by diffuse TBI in rat. MAIN METHODS: Subchronic oral administration of 100 mg/kg EA, 7 consecutive days before induction of trauma (once daily) was used to elucidate the EA effects on passive avoidance memory and hippocampal LTP following TBI. To illustrate the possible mechanisms related to the preventive effects of EA on brain function following TBI, brain content of IL-1beta, IL-6 and blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability were determined. KEY FINDINGS: EA pretreatment significantly (P<0.001) prevented TBI-induced memory and hippocampal LTP impairments in rat. Furthermore TBI induced elevation in brain content of IL-1beta, IL-6 and BBB permeability were decreased significantly (P<0.001) due to EA pre-treatment. SIGNIFICANCE: Our findings suggest that EA can prevent cognitive and LTP deficits and also prevent brain inflammation following TBI.
Ellagic acid protects against carrageenan-induced acute inflammation through inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B, inducible cyclooxygenase and proinflammatory cytokines and enhancement of interleukin-10 via an antioxidant mechanism.[Pubmed:24534771]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Apr;19(2):290-9.
There are several hypotheses that explain the process of acute inflammation, including free radical overproduction, pro-inflammatory enzyme activation, and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. In this study, the protective role of Ellagic acid against carrageenan-induced acute inflammation was assessed. In addition, the immunomodulatory action, the antioxidant effects, and the role of COX-2 and NF-kappaB were also investigated. Inflammation was induced by the injection of 100 mul of 1.5% carrageenan solution. Ellagic acid (10, 25, 50, 100 and 200mg/kg), indomethacin (10 mg/kg), meloxicam (4 mg/kg), and saline, were injected 2h before carrageenan injection. The percentage inhibition in the paw weight was calculated. Paws, MDA, NO, GSH, IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, IL-10 and NF-kappaB mRNA expression were estimated. Formalin fixed hind paws were used for histopathological examination and immunohistochemical staining for COX-2 expression. Ellagic acid, meloxicam and indomethacin reduced paws, edema, MDA and NO formation. In addition, all of them restored the depleted GSH contents in the paws. Ellagic acid, meloxicam and indomethacin reduced NF-kappaB mRNA expression. Ellagic acid ameliorated COX-2 expression; meloxicam inhibited while indomethacin failed. Both Ellagic acid and meloxicam increased IL-10 while indomethacin did not. The docking study revealed a high affinity of Ellagic acid towards COX-2. Ellagic acid exhibited a potent anti-inflammatory effect against carrageenan-induced inflammation. The mechanisms of Ellagic acid induced protection were proved to be due to reduction of NO, MDA, IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, COX-2 and NF-kappaB expression and induction of GSH and IL-10 production.
Ellagic acid induces apoptosis in TSGH8301 human bladder cancer cells through the endoplasmic reticulum stress- and mitochondria-dependent signaling pathways.[Pubmed:23554011]
Environ Toxicol. 2014 Nov;29(11):1262-74.
To investigate the effects of Ellagic acid on the growth inhibition of TSGH8301 human bladder cancer cells in vitro, cells were incubated with various doses of Ellagic acid for different time periods. The phase-contrast microscope was used for examining and photographing the morphological changes in TSGH8301 cells. Flow cytometric assay was used to measure the percentage of viable cells, cell cycle distribution, apoptotic cells, ROS, mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsim), Ca(2+) , caspase-9 and -3 activities in TSGH8301 cells after exposure to Ellagic acid. Western blotting was used to examine the changes of cell cycle and apoptosis associated proteins levels. Results indicated that Ellagic acid induced morphological changes, decreased the percentage of viable cells through the induction of G0/G1 phase arrest and apoptosis, and also showed that Ellagic acid promoted ROS and Ca(2+) productions and decreased the level of DeltaPsim and promoted activities of caspase-9 and -3. The induction of apoptosis also confirmed by annexin V staining, comet assay, DAPI staining and DNA gel electrophoresis showed that Ellagic acid induced apoptosis and DNA damage in TSGH8301 cells. Western blotting assay showed that Ellagic acid promoted p21, p53 and decreased CDC2 and WEE1 for leading to G0/G1 phase arrest and promoting BAD expression, AIF and Endo G, cytochrome c, caspase-9 and -3 for leading to apoptosis in TSGH8301 cells. On the basis of these observations, we suggest that Ellagic acid induced cytotoxic effects for causing a decrease in the percentage of viable cells via G0/G1 phase arrest and induction of apoptosis in TSGH8301 cells.


