Dryopteris crassirhizoma
Dryopteris crassirhizoma
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Dryopteris crassirhizoma
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN6276
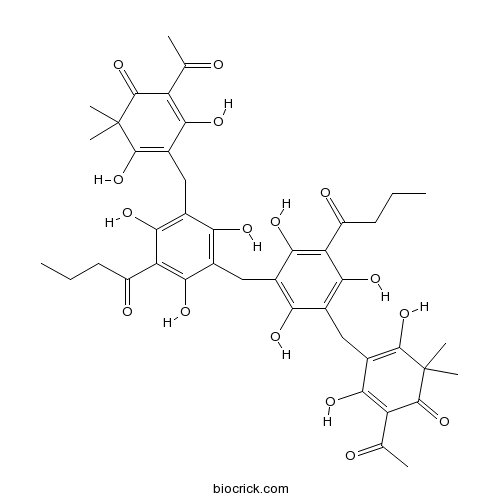
Dryocrassin ABBA12777-70-7
Instructions
-
BCN5300
Albaspidin AA3570-40-9
Instructions

Anti-Influenza Virus (H5N1) Activity Screening on the Phloroglucinols from Rhizomes of Dryopteris crassirhizoma.[Pubmed: 28282885]
None
Photobiologic-mediated fabrication of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity.[Pubmed: 27348063]
We present the simple, eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using sunlight or green, red, blue, or white LED light together with Dryopteris crassirhizoma rhizome extract (DCRE) as the reducing and capping agent. The preliminary indication of AgNP production was a color change from yellowish green to brown after light exposure in the presence of DCRE. Optimization of parameters such as pH, inoculum dose, and metal ion concentration played an important role in achieving nanoparticle production in 30min. The spectroscopic and morphological properties of AgNPs were characterized using UV-Vis spectroscopy through the presence of a characteristic surface plasmon resonance (SPR) band for AgNPs, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The FT-IR results indicated that the phytochemical present in DCRE was the probable reducing/capping agent involved in the synthesis of AgNPs, and light radiation enhanced nanoparticle production. HR-TEM revealed that the AgNPs were almost spherical with an average size of 5-60nm under all light sources. XRD studies confirmed the face cubic center (fcc) unit cell structure of AgNPs. The synthesized AgNPs showed good antimicrobial activity against Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This study will bring a new insight in ecofriendly production of metal nanoparticles.
Immunomodulatory Effects of a Bioactive Compound Isolated from Dryopteris crassirhizoma on the Grass Carp Ctenopharyngodon idella.[Pubmed: 27294155]
In the present study, we investigated effects of compound kaempferol 3-a-L-(4-O-acetyl)rhamnopyranoside-7-a-L-rhamnopyranoside (SA) isolated from Dryopteris crassirhizoma during immune-related gene expression in Ctenopharyngodon idella head kidney macrophages (CIHKM). The expression of immune-related genes (IL-1β, TNF-α, MyD88, and Mx1) were investigated using real-time PCR at 2 h, 8 h, 12 h, and 24 h after incubation with 1, 10, and 50 μg mL(-1) of SA. Furthermore, fish were injected intraperitoneally with 100 μL of SA, and immune parameters such as lysozyme activity, complement C3, SOD, phagocytic activity, and IgM level were examined at 1, 2, and 3 weeks after injection. The differential expression of cytokines was observed after exposure to SA. IL-1β genes displayed significant expression at 2 and 8 h after exposure to 1-10 μg mL(-1) of SA. SA also induced gene expression of cytokines such as MyD88, Mx1, and TNF-α. Furthermore, enhanced immune parameters in grass carp confirmed the immunomodulatory activity of SA. Interestingly, this compound has no toxic effect on CIHKM cells as tested by MTT assay. In addition, fish immunised with 10 μg mL(-1) of SA exhibited maximum resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. These results suggest that SA has the potential to stimulate immune responses in grass carp.
Dryocrassin ABBA Induces Apoptosis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells Through a Caspase-Dependent Mitochondrial Pathway.[Pubmed: 27221859]
Biological and pharmacological activities of dryocrassin ABBA, a phloroglucinol derivative extracted from Dryopteris crassirhizoma, have attracted attention. In this study, the apoptotic effect of dryocrassin ABBA on human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells was investigated.
Identification of linoleic acid, a main component of the n-hexane fraction from Dryopteris crassirhizoma, as an anti-Streptococcus mutans biofilm agent.[Pubmed: 25115514]
Dryopteris crassirhizoma is a semi-evergreen plant. Previous studies have shown the potential of this plant as an agent for the control of cariogenic biofilms. In this study, the main antibacterial components of the plant were identified by correlating gas chromatography-mass spectrometry data with the antibacterial activity of chloroform and n-hexane fractions and then evaluating the activity of the most potent antibacterial component against Streptococcus mutans UA159 biofilms. The most potent antibacterial component was linoleic acid, a main component of the n-hexane fraction. Linoleic acid reduced viability in a dose dependent manner and reduced biofilm accumulation during initial and mature biofilm formation. Furthermore, when the biofilms were briefly treated with linoleic acid (10 min/treatment, a total of six times), the dry weight of the biofilms was significantly diminished. In addition, the anti-biofilm activity of the n-hexane fraction was similar to that of linoleic acid. These results suggest that the n-hexane fraction of D. crassirhizoma and linoleic acid may be useful for controlling cariogenic biofilms.
Dryocrassin suppresses immunostimulatory function of dendritic cells and prolongs skin allograft survival.[Pubmed: 24816456]
Dendritic cells (DCs) are the major specialized antigen-presenting cells for the development of optimal T-cell immunity. DCs can be used as pharmacological targets to monitor novel biological modifiers for the cure of harmful immune responses, such as transplantation rejection. Dryopteris crassirhizoma Nakai (Aspiadaceae) is used for traditional herbal medicine in the region of East Asia. The root of this fern plant has been listed for treating inflammatory diseases. Dryocrassin is the tetrameric phlorophenone component derived from Dryopteris. Here we tested the immunomodulatory potential of dryocrassin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated activation of mouse bone marrow-derived DCs in vitro and in skin allograft transplantation in vivo. Results demonstrated that dryocrassin reduced the emission of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and interleukin-12p70 by LPS-stimulated DCs. The expression of LPS-induced major histocompatibility complex class II, CD40, and CD86 on DCs was also blocked by dryocrassin. Moreover, LPS-stimulated DC-elicited allogeneic T-cell proliferation was alleviated by dryocrassin. In addition, dryocrassin inhibited LPS-induced activation of IκB kinase, JNK/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, and the translocation of NF-κB. Treatment with dryocrassin noticeably diminished 2,4-dinitro-1-fluorobenzene-reduced delayed-type hypersensitivity and extended skin allograft survival. Dryocrassin may be one of the potent immunosuppressive agents for transplant rejection via the destruction of DC maturation and function.
The type 1 copper site of pseudoazurin: axial and rhombic.[Pubmed: 24813397]
We report on a high-frequency electron-paramagnetic-resonance study of the type 1 copper site of pseudoazurin. The spectra fully resolve the contribution of a nearly axial spectrum besides the rhombic spectrum, which unequivocally proves the existence of two conformations of the copper site. Pseudoazurins have been considered from Achromobacter cycloclastes including eight mutants and from Alcaligenes faecalis. The two conformations are virtually the same for all pseudoazurins, but the rhombic/axial population varies largely, between 91/9 and 33/67. These observations are discussed in relation to optical absorption spectra and X-ray diffraction structures. A similar observation for fern plastocyanin from Dryopteris crassirhizoma suggests that dual conformations of type 1 copper sites are more common.
Application of a sensitive and accurate LC-MS/MS method for determination of dryocrassin ABBA in rat plasma for a bioavailability study.[Pubmed: 24497015]
A sensitive and accurate liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method was developed and validated for the determination of dryocrassin ABBA, a potential active component isolated from Dryopteris crassirhizoma, in rat plasma. Chromatographic separation was achieved on a Zorbax SB-C18 column (50 × 2.1 mm, 1.8 µm), with elution consisting of eluent (A) 10 mm ammonium acetate in methanol containing 0.1% formic acid and (B) 10 mm ammonium acetate in water containing 0.1% formic acid (A:B = 99:1, v/v) at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. Multiple reaction monitoring mode was used to monitor the precursor-product ion transitions of m/z 819.3 → 403.4 for dryocrassin ABBA and m/z 426.2 → 409.2 for internal standard. This assay exhibited a good linearity with a correlation coefficient >0.99 and showed no endogenous interference with the analyte and internal standard. The lower limit of quantification of dryocrassin ABBA was 4 ng/mL in 50 μL of rat plasma. The method was successfully applied in the pharmacokinetic study of dryocrassin ABBA in rats after intravenous (2.35 mg/kg) and oral (23.5 mg/kg) doses of dryocrassin ABBA. The oral bioavailability (F) of dryocrassin ABBA was estimated to be 50.1%. Our study is the first to clarify the pharmacokinetic behaviors of dryocrassin ABBA in animals.
Effects of chloroform extract of Dryopteris crassirhizoma on the ultramicroscopic structures of Meloidogyne incognita.[Pubmed: 24282379]
In our early experiments, the chloroform extract of D. crassirhizoma was demonstrated to contain the highest concentrations of total phloroglucinols among several extract fractions and possessed the most effective nematicidal activity. This study aimed to ascertain the ultrastructural changes in M. incognita after treatment with a D. crassirhizoma chloroform extract at 1 mg·mL⁻¹ for 24 h. It was found that the extract exhibited significant destructive effects on the worm's ultrastructure and caused distinctive damage to body surfaces and internal structures. These results will contribute to a deeper understanding of the nematicidal mechanism of D. crassirhizoma, as well as in the design of efficient bionematicides.


