Euphorbia dracunculoides
Euphorbia dracunculoides
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Euphorbia dracunculoides
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
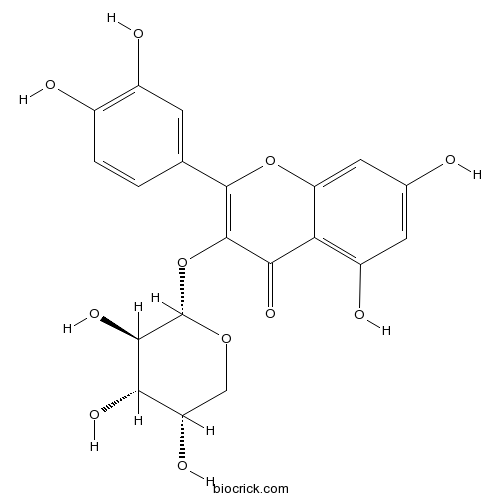
BCN5056
Guaijaverin22255-13-6
Instructions
-
BCN5549
Astragalin480-10-4
Instructions

-
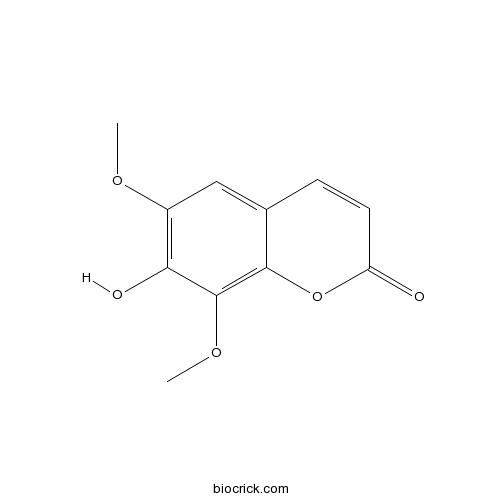
BCN2327
Isofraxidin486-21-5
Instructions
Natural and Semisynthetic Tigliane Diterpenoids with New Carbon Skeletons from Euphorbia dracunculoides as a Wnt Signaling Pathway Inhibitor.[Pubmed: 28703597]
None
Euphorbia dracunculoides L. abrogates carbon tetrachloride induced liver and DNA damage in rats.[Pubmed: 28427398]
None
A new tigliane-type diterpene from Euphorbia dracunculoides Lam.[Pubmed: 26729599]
One new tigliane-type diterpene, 4-deoxy-4(β)H-8-hydroperoxyphorbol-12-benzoate-13-isobutyrate (1), together with two known diterpenoids, 3-acetyl-5,8-dibenzoyl-14α-propanoyl-13,17-epoxy-7-myrsinaone diterpene with C9-C10 cyclised to form an additional lactone ring (2), Euphodendriane A (3) have been isolated from the whole plants of Euphorbia dracunculoides Lam. Their structures were elucidated by means of extensive spectroscopic analysis (NMR and HR-ESI-MS) and comparison with data reported in the literature. This is the first isolation of 8-hydroperoxy tigliane diterpene (1) from the genus of Euphorbia. All compounds were evaluated for their antifungal activities.
Studies on phytochemical, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of Euphorbia dracunculoides.[Pubmed: 26445953]
Plants provide an alternative source to manage various human disorders due to diverse metabolites. Euphorbia dracunculoides of family Euphorbiaceae is used by local practitioners in rheumatism, epilepsy, edema, snake bite, warts and also possesses diuretic and purgative effects. The present study evaluated the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of various extracts of E. dracunculoides. Further, phytochemical constituents of the leading extracts were also investigated.
Identity and pharmacognosy of Ruta graveolens Linn.[Pubmed: 23929988]
Ruta graveolens L., is a odoriferous herb belonging to the family Rutaceae. It is the source of Rue or Rue oil, called as Sadab or Satab in Hindi. It is distributed throughout the world and cultivated as a medicinal and ornamental herb. The ancient Greeks and Romans, held the plant in high esteem. It is used in Ayurveda, Homoeopathy and Unani. Phytochemical constituents and pharmacological properties were studied in depth. In 14 species of genus Ruta, R. graveolens and R. chalepensis are available in India and also cultivated in gardens. Taxonomical characters to identify the Indian plants are very clear with fringed and or non-fringed petals. However, references to it are confused in the traditional literature. Due to sharing of regional language name, its identity is confused with Euphorbia dracunculoides. Morphological and anatomical characters were described. Pharmacognostic studies with microscopic characters were also published. Upon reviewing the anatomical characters and pharmacognostic characters one finds that it is highly confused and conflicting. The characters described are opposite of each other and authenticity of the market sample of R. graveolens cannot be guaranteed and able to be differentiated from R. chalepensis. Present work is to describe the pharmacognostic characters of R. graveolens to differentiate it from R. chalepensis. It is concluded that morphologically, R. graveolens can be identified with its non-fringed petals and blunted apices of fruit lobes. Whereas, in R. chalepensis petals are fringed or ciliated and apices of the fruit lobes are sharp and projected. Microscopically, in stem of R. graveolens pericyclic fibers have wide lumen. Whereas, in R. chalepensis, it is narrow. The published pharmacognosy reports do not pertain to authentic plant or some of the characteristic features like glandular trichomes are not observed in our samples.
Molecular authentication of the medicinal herb Ruta graveolens (Rutaceae) and an adulterant using nuclear and chloroplast DNA markers.[Pubmed: 22095605]
Dried parts of different plant species often look alike, especially in powdered form, making them very difficult to identify. Ruta graveolens, sold as a dried medicinal herb, can be adulterated with Euphorbia dracunculoides. The genomic DNA was isolated from the leaf powder (100 mg each) using the modified CTAB method. Internal transcribed spacer sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA (nrDNA-ITS), and chloroplast spacer sequences (rpoB and rpoC1) are regarded as potential genes for plant DNA barcoding. We amplified and sequenced these spacer sequences and confirmed the sequences with a BLAST search. Sequence alignment was performed using ClustalX to look for differences in the sequences. A DNA marker was developed based on rpoB and rpoC1 of the nrDNA-ITS for the identification of the adulterant E. dracunculoides in samples of R. graveolens that are sold in local herbal markets. Sequence-characterized amplified region markers of 289 and 264 bp for R. graveolens and 424 bp for E. dracunculoides were developed from dissimilar sequences of this nrDNA-ITS to speed up the authentication process. This marker successfully distinguished these species in extracted samples with as little as 5 ng DNA/μL extract.


