Euphorbia helioscopia
Euphorbia helioscopia
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Euphorbia helioscopia
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
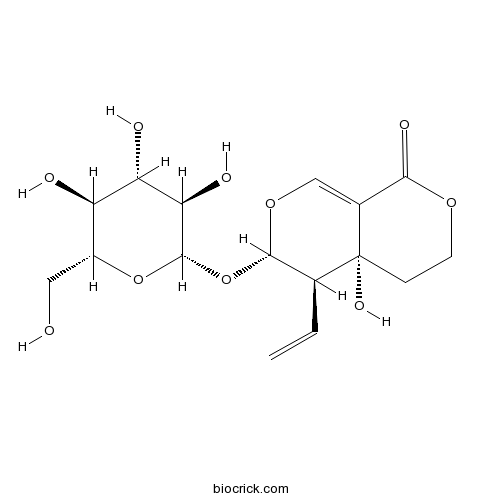
BCN1116
Swertiamarin17388-39-5
Instructions
-
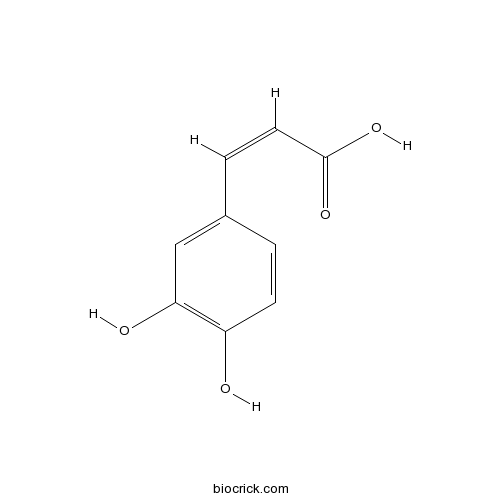
BCN5979
Caffeic acid331-39-5
Instructions
-
BCN4963
Lathyrol34420-19-4
Instructions

-
BCN5570
Hyperoside482-36-0
Instructions

-
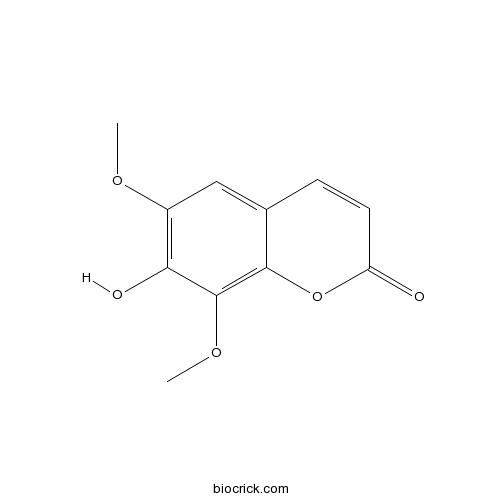
BCN2327
Isofraxidin486-21-5
Instructions
-
BCN5388
Luteolin-7-O-glucoside5373-11-5
Instructions

-
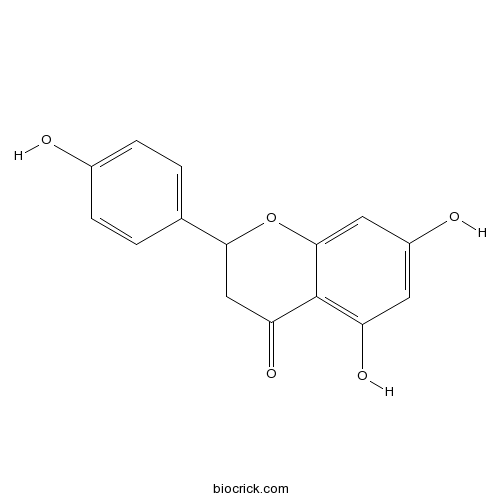
BCN9061
(±)-Naringenin67604-48-2
Instructions
-
BCN4373
Ethyl gallate831-61-8
Instructions

-
BCN4424
Pyrogallol87-66-1
Instructions

Jatrophane diterpenoids from Euphorbia helioscopia and their lipid-lowering activities.[Pubmed: 29772305]
The phytochemical study of Euphorbia helioscopia led to the isolation of 33 jatrophane diterpenoids (1-33), of which six (1-6) were new. This small jatrophane library was established to screen for potential lipid modulators. LDL-Uptake screening assay demonstrated that most of them improved LDL-Uptake rate in HepG2 cells, with compounds 16, 21 and 26 exhibiting more outstanding effects. Further exploration found that these three compounds could increase LDLR protein level in HepG2 cells dose-dependently. SAR studies suggested that substituted patterns of C-9, steric hindrance between C-14 and C-15, and the long conjugated fragment from C-5 to the carbonyl (C-9) were essential for the activity. Moreover, compound 21, a relatively abundant chemical in E. helioscopia, showed remarkable lipid-lowering effect in vivo, which makes it a promising lead for development of new lipid-lowering agents.
Heliojatrones A and B, Two Jatrophane-Derived Diterpenoids with a 5/10 Fused-Ring Skeleton from Euphorbia helioscopia: Structural Elucidation and Biomimetic Conversion.[Pubmed: 29733612]
Heliojatrones A and B (1 and 2), two jatrophane-derived diterpenoids with an unprecedented trans-bicyclo[8.3.0]tridecane core, were isolated from the whole plants of Euphorbia helioscopia. Their structures and absolute configurations were unequivocally determined by a combination of spectroscopic data, electronic circular dichroism calculations, biomimetic conversion, and X-ray diffraction analyses. Their plausible biosynthetic pathways were also proposed. Compounds 1 and 2 were biomimetically synthesized from 3 and 4 through a photochemical rearrangement reaction of β,γ-unsaturated ketone, respectively. Compound 2 showed significant P-glycoprotein inhibitory activity compared with the positive control (cyclosporine A).
Jatrophanes as promising multidrug resistance modulators: Advances of structure-activity relationships.[Pubmed: 29447979]
The phytochemical study of Euphorbia helioscopia afforded euphornin (1) in a large amount. Alkaline hydrolysis of 1 using potassium carbonate yielded the main product monodeacetyleuphornin (2), whose structural modification at 14-OH gave rise to 21 acylated derivatives euphornoate A-U (3-23). Thus, a mini compound library of jatrophanes was established to screen for MDR modulators. Biological studies clearly demonstrated the effect of C-14 pattern modification in MDR reversal activity and several compounds with RF values over 300 fold at 20 μM (6, 16, 20, 22, 23) were thought to be promising MDR modulators. The SARs are discussed, which reveal that introduction of an alkyl acyl group bearing 4 carbons at C-14 or an aryl acyl group with electron donating groups is favorable for the activity.
(19αH)-lupane and (9βH)-lanostane triterpenes from Euphorbia helioscopia trigger apoptosis of tumor cell.[Pubmed: 29269231]
None
Identification and cytochemical immunolocalization of acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase involved in the terpenoid mevalonate pathway in Euphorbia helioscopia laticifers.[Pubmed: 29247328]
Terpenoids, the largest class of natural products in the plant kingdom, have been widely used in medicine. The precursors of terpenoids, isoprene phosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), were synthesized from a mevalonate (MVA) pathway and a 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) pathway respectively. The acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase (AACT) is the initial enzyme in MVA pathway and is considered presently to be essential for terpenoid backbone biosynthesis. The basic research on cytochemistry of terpenoid metabolic enzymes is important for understanding the mechanisms underlying major metabolic processes. However, compartmentalization of AACT in plants is in controversy. Euphorbia helioscopia L. containing laticifers in the whole plant is a famous ancient folk medicine for tumor treatment, and the terpenoid is an active ingredient. Furthermore, the laticifer cell is the main synthesizing and storing site for terpenoids.
Secoheliosphanes A and B and Secoheliospholane A, Three Diterpenoids with Unusual seco-Jatrophane and seco-Jatropholane Skeletons from Euphorbia helioscopia.[Pubmed: 29188714]
None
Highly oxygenated and structurally diverse diterpenoids from Euphorbia helioscopia.[Pubmed: 29107811]
A phytochemical investigation on the aerial part of Euphorbia helioscopia (Euphorbiaceae) led to the isolation of 22 highly oxygenated diterpenoids with structural types of ent-abietane, ent-kaurane, lathyrane, ent-atisane and ingenane. 17 of them, named euphelionolides A - N, 16-epi-18-hydroxy-abbeokutone, as well as eupheliotriols A and B, were identified to be previously undescribed compounds by extensive analysis of spectroscopic data. The stereostructures of euphelionolides A - K were determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction combined with analysis of substituent effects and comparison of optical characteristics. Eupheliotriol B is the first example of natural occurring lathyrol with 12Z-ene, while ent-atisanes are the first reported from the title plant. Furthermore, euphelionolides F and L exhibited significant cytotoxicity against MCF-7 and PANC-1 cell lines.


