Euphorbia pekinensis
Euphorbia pekinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Euphorbia pekinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN1668
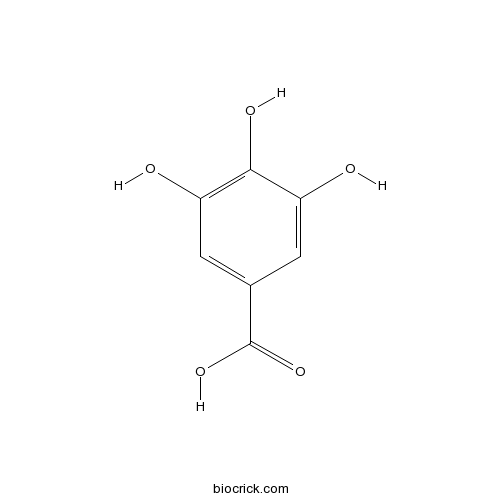
Gallic acid149-91-7
Instructions
-
BCN5290
Ziyuglycoside I35286-58-9
Instructions

-
BCN7790
Euphol514-47-6
Instructions

[Investigation of Variations of Components in Euphorbia pekinensis Root and Its Processed Products Based on Plant Metabolomics].[Pubmed: 30088875]
An ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry( UPLC-MS) based on plant metabonomics method was proposed and developed for the investigation of variations of components in Euphorbia pekinensis root after herb-processing procedure.
Metabolomic evaluation of Euphorbia pekinensis induced nephrotoxicity in rats.[Pubmed: 29421944]
Euphorbia pekinensis Rupr. (Euphorbiaceae) has long been used in the Orient, while its clinical use was limited due to its nephrotoxic effect.
Polyphenols from Euphorbia pekinensis Inhibit AGEs Formation In Vitro and Vessel Dilation in Larval Zebrafish In Vivo.[Pubmed: 29165729]
None
Upregulation of aquaporin 3 expression by diterpenoids in Euphorbia pekinensis is associated with activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in the co-culture system of HT-29 and RAW 264.7 cells.[Pubmed: 29129744]
This study was designed to evaluate the toxic effects of diterpenoids separated from the roots of Euphorbia pekinensis, a type of widely used traditional Chinese medicine. This herb has intestinal toxicity associated with its complex diterpenoids. In this study, the diterpenoids (pekinenin A, pekinenin C, pekinenin F, pekinenin G, yuexiandajisu A, (-)-(1S)-15-hydroxy-18-carboxycembrene) elevated the expression of interleukin 1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha in a dose-dependent manner at doses of 6.25, 12.5, and 25 μM in RAW264.7 monocultures. Pekinenin C increased the expression of phosphorylated IκB and phosphorylated p65 in RAW264.7 monocultures, indicating that it stimulated a substantial inflammatory response and activated the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling pathway. A co-culture model of RAW 264.7 mouse macrophage cells and HT-29 human intestinal epithelial cells was established to study the correlation between inflammation and aquaporin (AQP) expression and to evaluate the toxicity of different diterpenoids from E. pekinensis. Pekinenin C (6.25, 12.5, and 25 μM) increased AQP3 mRNA and protein expression of HT-29 cells in the co-culture system in a dose-dependent manner but not in HT-29 monocultures. AQP3 mRNA and protein expression peaked at 2 and 3 h of HT-29 cells in the co-culture system, respectively. In contrast, their expression peaked more slowly in the monoculture system. After the specific NF-κB inhibitor BAY11-7082 (5, 10, and 20 μM) was added to the co-culture system, the release of cytokines and increased AQP3 expression caused by pekinenin C were inhibited. Comparisons of the representative monomeric compound pekinenin C, diterpenoid monomer mixtures, and total diterpenoids from E. pekinensis showed that the monomer mixtures had the most toxicity. In conclusion, this study demonstrated that E. pekinensis induces inflammation and increases the expression of AQP3, causing disorders of water metabolism, which may lead to gastrointestinal side effects such as diarrhea.
Anti-angiogenic activity of water extract from Euphorbia pekinensis Rupr.[Pubmed: 28602865]
Euphorbia pekinensis Rupr. (EP) is a Euphorbia species of Euphorbiaceae, which is widely used in traditional Chinese medicine. It has been reported to exhibit therapeutic effects on solid tumors, leukemias, and malignant ascites although underlying molecular mechanisms are poorly delineated. Anti-angiogenic therapy is a recognized strategy for treating cancer-based solid tumors, and is also associated with malignant ascites treatment.
Laxative Effects of Total Diterpenoids Extracted from the Roots of Euphorbia pekinensis Are Attributable to Alterations of Aquaporins in the Colon.[Pubmed: 28335427]
This study was designed to evaluate the toxic effects of total diterpenoids extracted from the roots of Euphorbia pekinensis (TDEP) on the mouse colon and to clarify the mechanism. Dried powdered roots of E. pekinensis were extracted with chloroform, and then the extract (6.7 g) was subjected to column chromatography and preparative TLC, giving TDEP. Using the HPLC-DAD method, the purity of TDEP was determined as 85.26%. Mice were orally administered with TDEP (3.942, 19.71 and 39.42 mg/kg), after which fecal water content and colon water content were examined. Both of them increased over time after TDEP administration, accompanied by severe diarrhea. Three hours after TDEP administration, the animals were sacrificed to obtain their colons. The mRNA and protein expression levels of aquaporin 1 (AQP1), AQP3 and AQP4 in the colon were measured using real-time RT-PCR and Western blotting, respectively. TDEP significantly increased the levels of AQP3 and AQP4, but decreased that of AQP1 in dose-dependent manners. Similarly, Pekinenin C, a casbane diterpenoid, significantly increased AQP3 protein and mRNA expressions in human intestinal epithelial cells (HT-29). Histopathological examination revealed that the colon was not significantly damaged. The laxative effects of E. pekinensis were associated with the alterations of AQPs in the colon by TDEP.
Four New Diterpenoids from the Roots of Euphorbia pekinensis.[Pubmed: 27447875]
Three new isopimarane diterpenoids (1 - 3) and one new abietane diterpenoid (4) were isolated and identified from the roots of Euphorbia pekinensis, together with four known diterpenoids. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of extensive spectroscopic methods (IR, MS, NMR, and CD), and their cytotoxicities and anticomplement activities were evaluated.


