Flemingia prostrata
Flemingia prostrata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Flemingia prostrata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5567
Chrysophanol481-74-3
Instructions

-
BCN2396
Genistin529-59-9
Instructions

-
BCC4109
Salicylic acid69-72-7
Instructions

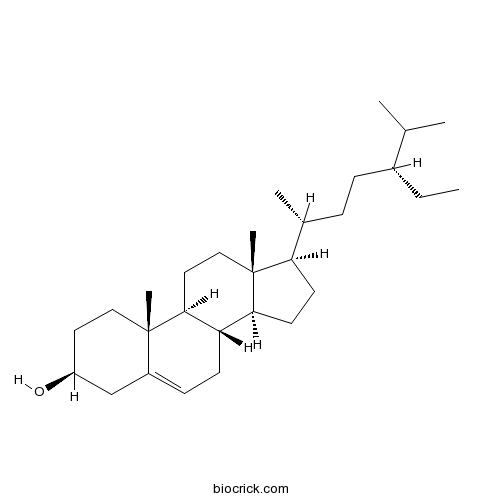
-
BCN1015
Beta-Sitosterol83-46-5
Instructions
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of the aqueous extracts from three Flemingia species.[Pubmed: 20503477]
I-Tiao-Gung has long been used in the Kinmen area of Taiwan as an anti-inflammatory agent for the treatment of rheumatic illness. The roots of Flemingia lineata (FL), Flemingia macrophylla (FM) and Flemingia prostrata (FP) are also used as I-Tiao-Gung in the Taiwan markets. In the present study, we investigated the analgesic effect of aqueous extracts of Flemingia lineata (FL), Flemingia macrophylla (FM), and Flemingia prostrata (FP) by acetic acid-induced writhing response, formalin test, and the anti-inflammatory effect of FM, FL and FP by lambda-carrageenan-induced paw edema in mice. We also detected the changes in the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione reductase (GRx) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) of liver in the lambda-carrageenan-induced paw edema in mice to investigate the anti-inflammatory mechanism of FL and FM. The results showed that FL and FM significantly inhibited the acetic acid-induced writhing response and formalin-induced licking time during the late phase (p < 0.001). FL and FM also significantly decreased the lambda-carrageenan-induced paw edema (p < 0.001). FL and FM significantly increased the GRx and GPx activities in the liver and decreased the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and nitric oxide (NO) in the edema paw (p < 0.001). These results indicated that FL and FM possessed analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of FL and FM might be related to the decrease in the level of MDA in the edema paw via increasing the activities of GPx and GRx in the liver and decreasing the NO level in the edema paw.


