Fritillaria unibracteata
Fritillaria unibracteata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Fritillaria unibracteata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5816
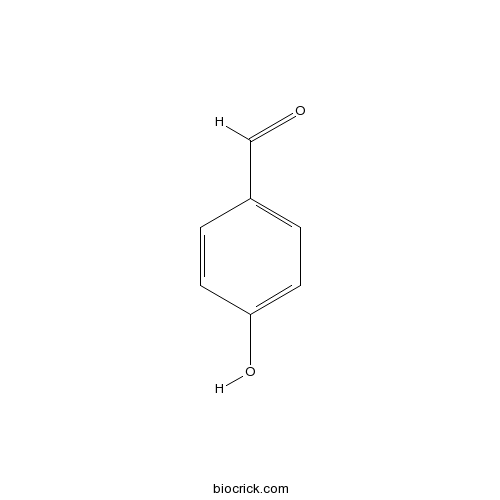
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde123-08-0
Instructions
-
BCN6771
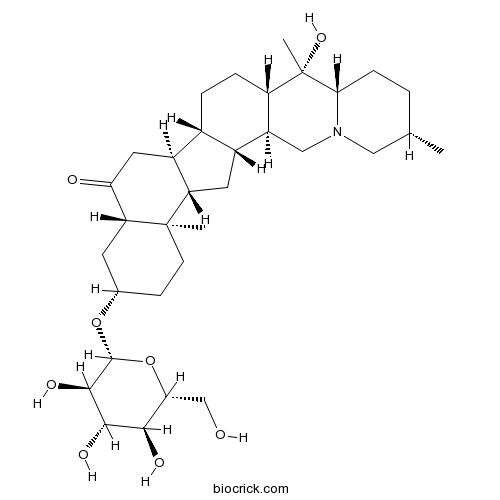
Edpetiline32685-93-1
Instructions
-
BCN5807
Caffeine58-08-2
Instructions

-
BCN9041
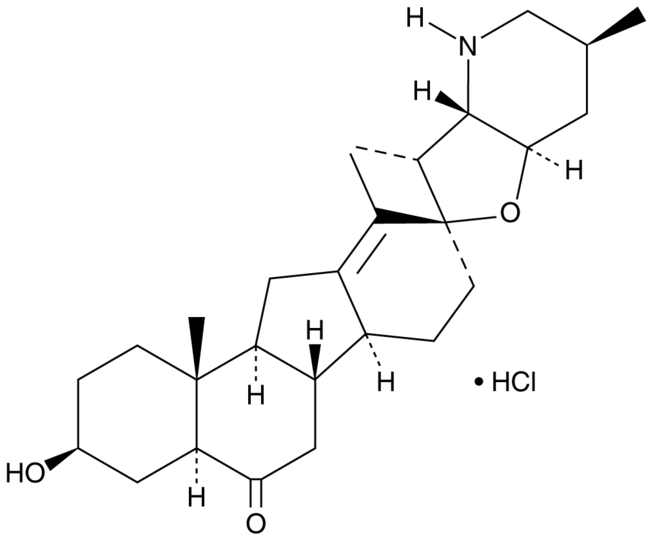
Peimisine hydrochloride900498-44-4
Instructions
Extraction, purification and antioxidation of a polysaccharide from Fritillaria unibracteata var. wabuensis.[Pubmed: 29447973]
Rich polysaccharides were directly observed in the bulbs of Fritillaria unibracteata var. wabuensis (FUW) using the periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) method and microexamination. An acidic water-soluble heteropolysaccharide (FWPS1-1) was isolated from FUW through ethanol precipitation, decoloration, deproteinization, dialysis and separation using a DE-52 anion-exchange column and a Sepharose G-150 gel filtration column. FWPS1-1 (average molecular weight: ~7.44 kDa) has many branches and long side chains; holds the triple-helix conformation; was composed of mannose (Man), galacturonic acid (GalA), galactose (Gal), xylose (Xyl) and arabinose (Ara) with a molar ratio of 2.62:5.59:10.00:0.76:9.38; and features side chains that may be composed of Ara, Man, Gal and GalA, while the backbone may be composed of Xyl, Ara and Gal. In addition, the backbone of FWPS1-1 mainly consists of α-type glycosidic bonds. Bioactivity tests in vitro showed that the polysaccharide exhibited weak 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity and low ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) but high 2,2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)l (ABTS) radical scavenging activity, good Fe(II)-chelating ability and remarkable DNA damage protective activity. FWPS1-1 was the first heteropolysaccharide purified from FUW and showed good antioxidant activity and DNA protective effect. The results confirmed that macromolecule is also bioactive ingredient that requires attention like the small-molecule active compounds in FUW.
[Screening, identification and antimicrobial activity of alkaloid produced by endophytic actinomycetes from Fritillaria unibracteata in western Sichuan plateau].[Pubmed: 29376255]
To explore the resource of endophytic actinomycete in Fritillaria unibracteata, and alleviate the shortage of F. unibracteata resource, using F. unibracteata as experimental materials which growth in the western Sichuan plateau and cut its healthy bulb. Pure culture, insert, TLC and Oxford cup were applied to observe the mycelial morphology, research the ability of producing alkaloid and its antibacterial activity. Totally, 14 endophytic actinomycete strains were isolated by using Gao culture media. Based on the color reaction, 5 typical strains were selected for producing alkaloid. Through the TLC technique, all strains produced 2 obvious alkaloids spots. Antibacterial activity determination showed that the antimicrobial effects of 2 strains is prominent, the diameter up to 11 mm.16S rRNA gene sequence comparison analysis showed that 5 strains belonging to the Streptomyces. The alkaloids produced by endophytic actinomycetes are not related to F. unibracteata, but its fermentation liquid has antibacterial effect, it is worthy of further study.
Fungal endophyte-derived Fritillaria unibracteata var. wabuensis: diversity, antioxidant capacities in vitro and relations to phenolic, flavonoid or saponin compounds.[Pubmed: 28165019]
Diverse fungal endophytes are rich fungal resources for the production of an enormous quantity of natural products. In the present study, 53 fungal endophytes were isolated from the bulbs of Fritillaria unibracteata var. wabuensis (FUW). Of these, 49 strains were identified and grouped into 17 different taxa, and priority was conferred to the Fusarium genus. All fungal fermented filtrates displayed antioxidant activities. The DPPH activity, total antioxidant capacities (ABTS), reduction power (FRAP), total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC) and total saponin content (TSC) were evaluated using petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, n-butyl alcohol and ethanol fractions extracted from five representative fungal cultures. The last three fractions showed more potent antioxidant activity than the first fraction. Significant positive correlations were found between the compositions (TPC, TFC and TSC) and antioxidant capacities (DPPH, ABTS and FRAP). In addition, multifarious natural antioxidant components were identified from the fungal extracts, including gallic acid, rutin, phlorizin, 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol and 2,6-di-tert-butyl hydroquinone; these were determined preliminarily by TLC-bioautography, HPLC and GC-MS analysis. This study showed abundant fungal resources in FUW. Phenolics, flavonoids and saponins are crucial bioactive constituents in these abundant fungal endophytes and can be viewed as new potential antioxidant resources.
[Physicochemical property and antioxidant activity of exopolysaccharide produced by endophytic fungal Fusarium redolens 6WBY3 isolated from Fritillaria unibracteata var. wabuensis].[Pubmed: 29750487]
To study the exopolysaccharide (EPS) of endophytic fungal Fusarium redolens 6WBY3 isolated from Fritillaria unibracteata var. wabuensis (FUW) including its antioxidant activities.
Global detection and semi-quantification of Fritillaria alkaloids in Fritillariae Ussuriensis Bulbus by a non-targeted multiple reaction monitoring approach.[Pubmed: 26530331]
Methods based on triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry have been widely used and reported as highly selective and sensitive methods for quantifying substances of herbal medicines. However, most of them were limited to targeted components, due to the difficulties to optimize the multiple reaction monitoring transitions without authentic standards. This study proposed a novel strategy for non-targeted optimization of multiple reaction monitoring method based on the diagnostic ion guided family classifications, tandem mass spectrometry database establishment, and transitions and collision energy screening. Applying this strategy, 59 Fritillaria alkaloids in Fritillariae Ussuriensis Bulbus have been classified, and 51 of these Fritillaria alkaloids were successfully detected by the optimal multiple reaction monitoring method. For semi-quantification, the easy-to-obtain Fritillaria alkaloids of each type, such as verticinone for cevanine type and peimisine for jervine type, were used as the reference standards to calibrate the other Fritillaria alkaloids in the same type. The method was demonstrated a good linearity (R(2) > 0.998) with satisfactory accuracy and precision, and the lower limits of quantification of verticinone and peimisine were estimated to be 0.076 and 0.216 pg, respectively. In addition, the results suggested that the proposed strategy might obtained high quality metabolomics data in discrimination of Fritillaria unibracteata and Fritillaria ussuriensis.
Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Fritillaria unibracteata var. wabuensis based on SMRT Sequencing Technology.[Pubmed: 26370383]
Fritillaria unibracteata var. wabuensis is an important medicinal plant used for the treatment of cough symptoms related to the respiratory system. The chloroplast genome of F. unibracteata var. wabuensis (GenBank accession no. KF769142) was assembled using the PacBio RS platform (Pacific Biosciences, Beverly, MA) as a circle sequence with 151 009 bp. The assembled genome contains 133 genes, including 88 protein-coding, 37 tRNA, and eight rRNA genes. This genome sequence will provide important resource for further studies on the evolution of Fritillaria genus and molecular identification of Fritillaria herbs and their adulterants. This work suggests that PacBio RS is a powerful tool to sequence and assemble chloroplast genomes.
Fusarium redolens 6WBY3, an endophytic fungus isolated from Fritillaria unibracteata var. wabuensis, produces peimisine and imperialine-3β-D-glucoside.[Pubmed: 25869849]
The major biological active ingredients of Bulbus Fritillariae cirrhosae (BFC) are steroidal alkaloids, such as peimisine, imperialine-3β-D-glucoside, and peimine. The bulbus of Fritillaria unibracteata var. wabuensis (FUW) was officially recorded in the National Pharmacopoeia of China (2010 edition) as one of the sources of BFC because of its positive therapeutic effects and few side effects. The endophytic fungus strain 6WBY3 was isolated from the fresh bulbus of FUW that had been cultivated for six years. Based on morphological methods and the phylogenetic analysis of internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequences, this strain was identified as Fusarium redolens. Using color reaction analysis, high performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection (HPLC-ELSD), and mass spectrometry (MS), it was demonstrated that F. redolens 6WBY3 could produce peimisine and imperialine-3β-D-glucoside, similar to its host plant. The yields of peimisine and imperialine-3β-D-glucoside were 16.0 μg·l(-1) and 18.8 μg·l(-1), respectively, in one week of culture. These results indicate that F. redolens 6WBY3 is a promising candidate for the large scale production of peimisine and imperialine-3β-D-glucoside. In addition, the results from the strain 6WBY3 lay the foundation for further study into the mechanism of Fritillaria alkaloids biosynthesis in fungi.
New amino butenolides from the bulbs of Fritillaria unibracteata.[Pubmed: 25064215]
Five new amino γ-butenolides, fritenolide A (1), B (2), C (3), D (4), and E (5), along with four known compounds, were isolated from the bulbs of Fritillaria unibracteata. Their structures were determined by spectroscopic analysis, including 1D NMR, 2D NMR, HRESIMS, HRESIMS/MS, IR, and CD techniques. All isolates were evaluated for the protective activity on injured hepatocytes and cytotoxic activity on human cancer cells in vitro. The unusual amino butenolides were isolated from the Liliaceae family for the first time.


