4-HydroxybenzaldehydeCAS# 123-08-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 123-08-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 126 | Appearance | Powder |
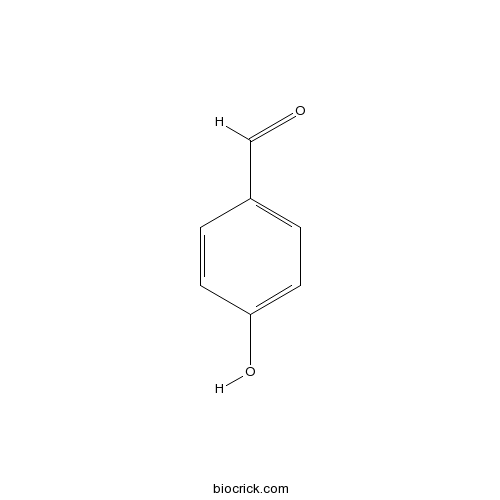
| Formula | C7H6O2 | M.Wt | 122.1 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RGHHSNMVTDWUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde shows an inhibitory effect on the GABA transaminase to contribute to an antiepileptic and anticonvulsive activity, and its inhibitory activity was higher than that of valproic acid, a known anticonvulsant. |
| Targets | GABA Receptor |
| Kinase Assay | Inhibition of GABA shunt enzymes' activity by 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde derivatives.[Pubmed: 16290145]Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Feb;16(3):592-5. Epub 2005 Nov 14.4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (HBA) derivatives were examined as inhibitors for GABA transaminase (GABA-T) and succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH). Investigation of structure-activity relation revealed that a carbonyl group or an amino group as well as a hydroxy group at the para position of the benzene ring are important for both enzymes' inhibition. HBA was shown to give competitive inhibition of GABA-T with respect to alpha-ketoglutarate and competitive inhibition of SSADH. 4-Hydroxybenzylamine (HBM) also showed the competitive inhibition on GABA-T with respect to GABA. |
| Structure Identification | Biochemistry. 2015 Feb 10;54(5):1219-32.Functional and structural characterization of an unusual cofactor-independent oxygenase.[Pubmed: 25565350]The vast majority of characterized oxygenases use bound cofactors to activate molecular oxygen to carry out oxidation chemistry. Here, we show that an enzyme of unknown activity, RhCC from Rhodococcus jostii RHA1, functions as an oxygenase, using 4-hydroxyphenylenolpyruvate as a substrate. This unique and complex reaction yields 3-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-pyruvate, 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde, and oxalic acid as major products. Incubations with H2(18)O, (18)O2, and a substrate analogue suggest that this enzymatic oxygenation reaction likely involves a peroxide anion intermediate. Analysis of sequence similarity and the crystal structure of RhCC (solved at 1.78 Å resolution) reveal that this enzyme belongs to the tautomerase superfamily. Members of this superfamily typically catalyze tautomerization, dehalogenation, or decarboxylation reactions rather than oxygenation reactions. The structure shows the absence of cofactors, establishing RhCC as a rare example of a redox-metal- and coenzyme-free oxygenase. This sets the stage to study the mechanistic details of cofactor-independent oxygen activation in the unusual context of the tautomerase superfamily. |

4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde Dilution Calculator

4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 8.19 mL | 40.95 mL | 81.9001 mL | 163.8002 mL | 204.7502 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.638 mL | 8.19 mL | 16.38 mL | 32.76 mL | 40.95 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.819 mL | 4.095 mL | 8.19 mL | 16.38 mL | 20.475 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1638 mL | 0.819 mL | 1.638 mL | 3.276 mL | 4.095 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0819 mL | 0.4095 mL | 0.819 mL | 1.638 mL | 2.0475 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Fmoc-Hyp(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3256
CAS No.:122996-47-8
- RG7388
Catalog No.:BCC1895
CAS No.:1229705-06-9
- HA 130
Catalog No.:BCC7884
CAS No.:1229652-21-4
- 6'-O-Galloyl paeoniflorin
Catalog No.:BCN2941
CAS No.:122965-41-7
- URMC-099
Catalog No.:BCC5563
CAS No.:1229582-33-5
- XE 991 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7232
CAS No.:122955-13-9
- N-(3-Methoxybenzyl)palmitamide
Catalog No.:BCN8086
CAS No.:847361-96-0
- Fmoc-L-Beta-Homoproline
Catalog No.:BCN8087
CAS No.:193693-60-6
- LY2784544
Catalog No.:BCC2200
CAS No.:1229236-86-5
- C 21
Catalog No.:BCC8013
CAS No.:1229236-78-5
- GS-9973
Catalog No.:BCC5278
CAS No.:1229208-44-9
- Edoxaban tosylate monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1545
CAS No.:1229194-11-9
- Anisic aldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN2618
CAS No.:123-11-5
- D-erythro-Sphingosine (synthetic)
Catalog No.:BCC6729
CAS No.:123-78-4
- Azelaic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC8300
CAS No.:123-99-9
- Azasetron HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5035
CAS No.:123040-16-4
- Bulleyanin
Catalog No.:BCN6120
CAS No.:123043-54-9
- Phyltetralin
Catalog No.:BCN3051
CAS No.:123048-17-9
- BAF312 (Siponimod)
Catalog No.:BCC5114
CAS No.:1230487-00-9
- 4,8-Dihydroxyeudesm-7(11)-en-12,8-olide
Catalog No.:BCN1600
CAS No.:1231208-53-9
- Uncaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN6121
CAS No.:123135-05-7
- Cefepime Dihydrochloride Monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5261
CAS No.:123171-59-5
- LY2835219 free base
Catalog No.:BCC1722
CAS No.:1231929-97-7
- LY2835219
Catalog No.:BCC1113
CAS No.:1231930-82-7
Functional and structural characterization of an unusual cofactor-independent oxygenase.[Pubmed:25565350]
Biochemistry. 2015 Feb 10;54(5):1219-32.
The vast majority of characterized oxygenases use bound cofactors to activate molecular oxygen to carry out oxidation chemistry. Here, we show that an enzyme of unknown activity, RhCC from Rhodococcus jostii RHA1, functions as an oxygenase, using 4-hydroxyphenylenolpyruvate as a substrate. This unique and complex reaction yields 3-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-pyruvate, 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde, and oxalic acid as major products. Incubations with H2(18)O, (18)O2, and a substrate analogue suggest that this enzymatic oxygenation reaction likely involves a peroxide anion intermediate. Analysis of sequence similarity and the crystal structure of RhCC (solved at 1.78 A resolution) reveal that this enzyme belongs to the tautomerase superfamily. Members of this superfamily typically catalyze tautomerization, dehalogenation, or decarboxylation reactions rather than oxygenation reactions. The structure shows the absence of cofactors, establishing RhCC as a rare example of a redox-metal- and coenzyme-free oxygenase. This sets the stage to study the mechanistic details of cofactor-independent oxygen activation in the unusual context of the tautomerase superfamily.
[Chemical constituents from safflower injection and their bioactivity].[Pubmed:25509295]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;39(16):3102-6.
The chemical constituents of Safflower injection were isolated and purified by polyamide, silica gel, Sephadex LH-20, ODS column chromatographies and preparative HPLC. As a result, sixteen compounds have been isolated. Based on the spectral data analysis, their structures were elucidated as scutellarin (1), kaempferol-3-O-beta-rutinoside(2), hydroxysafflor yellow A(3), rutin (4), coumalic acid(5), adenosine(6), syringoside(7), (3E)-4-(4'-hydroxyphenyl)-3-buten-2-one(8), (8Z)-decaene-4, 6-diyne-1-Obeta-D-glucopyranoside(9), 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (10), (2E, 8E) -tetradecadiene-4, 6-diyne-1, 12, 14-triol-1-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (11), kaem-pferol-3-O-beta-sophorose (12), uridine (13), roseoside (14), cinnamic acid (15), and kaempferol (16). Compounds 1,2,7,9,11 and 12 were isolated from the Safflower injection for the first time. The anti-platelet aggregation activities of the isolated compounds were assayed. The results indicated all tested compounds exhibited potent activity except for 5, while 2, 3, 9 and 12 showed strong activity against platelet aggregation.
Inhibition of GABA shunt enzymes' activity by 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde derivatives.[Pubmed:16290145]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Feb;16(3):592-5.
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (HBA) derivatives were examined as inhibitors for GABA transaminase (GABA-T) and succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH). Investigation of structure-activity relation revealed that a carbonyl group or an amino group as well as a hydroxy group at the para position of the benzene ring are important for both enzymes' inhibition. HBA was shown to give competitive inhibition of GABA-T with respect to alpha-ketoglutarate and competitive inhibition of SSADH. 4-Hydroxybenzylamine (HBM) also showed the competitive inhibition on GABA-T with respect to GABA. In conclusion, the inhibitory effects of HBA and HBM on both enzymes could result from the similarity between both molecules and the two enzymes' substrates in structure, as well as the conjugative effect of the benzene ring. This suggested that the presence of the benzene ring may be accepted by the active site of both enzymes, HBA and HBM may be considered as lead compounds to design novel GABA-T inhibitors.


