Galium spurium
Galium spurium
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Galium spurium
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
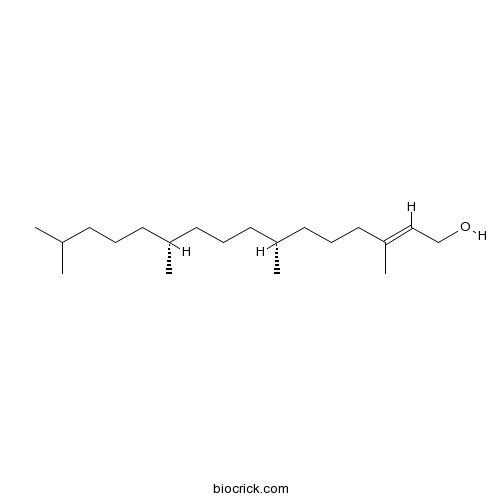
BCN1673
Phytol150-86-7
Instructions
-
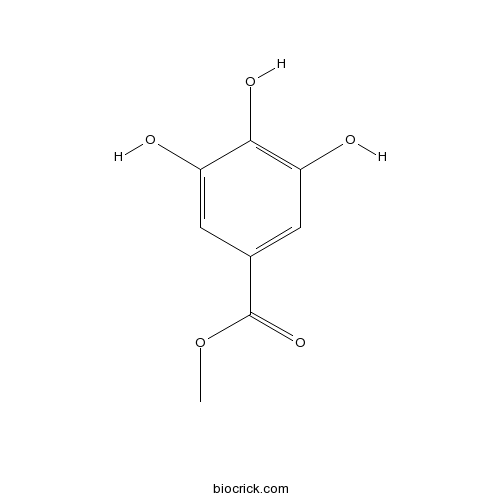
BCN3823
Methyl gallate99-24-1
Instructions
In vitro antibacterial and antitumor activities of some medicinal plant extracts, growing in Turkey.[Pubmed: 23790332]
To investigate antibacterial and antitumor activities of 51 different extracts prepared with 3 types of solvents (water, ethanol and methanol) of 16 different plant species (Ajuga reptans (A. reptans) L., Phlomis pungens (P. pungens) Willd., Marrubium astracanicum (M. astracanicum) Jacq., Nepeta nuda (N. nuda) L., Stachys annua (S. annua) L., Genista lydia (G. lydia) Boiss., Nuphar lutea (N. lutea) L., Nymphaea alba (N. alba) L., Vinca minor (V. minor) L., Stellaria media (S. media) L., Capsella bursa-pastoris (C. bursa-pastoris) L., Galium spurium (G. spurium) L., Onosma heterophyllum (O. heterophyllum) Griseb., Reseda luteola (R. luteola) L., Viburnum lantana (V. lantana) L. and Mercurialis annua (M. annua) L.) grown in Turkey was conducted.
UPLC-TOF-MS analysis of Galium spurium towards its neuroprotective and anticonvulsant activities.[Pubmed: 22348922]
Galium species have been reported to be used against epilepsy in traditional Turkish folk medicine.
Physiological and biochemical characterization of quinclorac resistance in a false cleavers (Galium spurium L.) biotype.[Pubmed: 15713032]
The physiological and biochemical basis for quinclorac resistance in a false cleavers (Galium spurium L.) biotype was investigated. There was no difference between herbicide resistant (R) and susceptible (S) false cleavers biotypes in response to 2,4-D, clopyralid, glyphosate, glufosinate-ammonium, or bentazon. On the basis of GR(50) (growth reduction of 50%) or LD(50) (lethal dose to 50% of tested plants) values, the R biotype was highly resistant to the acetolactate synthase (ALS) inhibitor, thifensulfuron-methyl (GR(50) resistance ratio R/S = 57), and quinolinecarboxylic acids (quinclorac R/S = 46), resistant to MCPA (R/S = 12), and moderately resistant to the auxinic herbicides picloram (R/S = 3), dicamba (R/S = 3), fluroxypyr (R/S = 3), and triclopyr (R/S = 2). The mechanism of quinclorac resistance was not due to differences in [(14)C]quinclorac absorption, translocation, root exudation, or metabolism. Seventy-two hours after root application of quinclorac, ethylene increased ca. 3-fold in S but not R plants when compared to controls, while ABA increased ca. 14-fold in S as opposed to ca. 3-fold in R plants suggesting an alteration in the auxin signal transduction pathway, or altered target site causes resistance in false cleavers. The R false cleavers biotype may be an excellent model system to further examine the auxin signal transduction pathway and the mechanism of quinclorac and auxinic herbicide action.
Biological control of weeds: research by the United States Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Research Service: selected case studies.[Pubmed: 12846317]
Research by the USDA-Agricultural Research Service (ARS) on biological control of weeds has been practiced for many years because of its inherent ecological and economic advantages. Today, it is further driven by ARS adherence to Presidential Executive Order 13112 (3 February 1999) on invasive species and to USDA-ARS policy toward developing technology in support of sustainable agriculture with reduced dependence on non-renewable petrochemical resources. This paper reports examples or case studies selected to demonstrate the traditional or classical approach for biological control programs using Old World arthropods against Tamarix spp, Melaleuca quinquenervia (Cav) ST Blake and Galium spurium L/G aparine L, and the augmentative approach with a native plant pathogen against Pueraria lobata Ohwi = P montana. The examples illustrated various conflicts of interest with endangered species and ecological complexities of arthropods with associated microbes such as nematodes.
Differentiation of spring emerging and autumn emerging ecotypes in Galium spurium L. var. echinospermon.[Pubmed: 28313393]
Ecotypes of Galium spurium L. var. echinospermon with distinct germination phenologies were found to occur in two adjacent plots of a grassland nature reserve with different management histories: a spring-germinating population is present in a winter-burnt plot, and an autumn-germinating type in an unburnt plot. These ecotypes share common flowering and fruiting phenologies, and disperse their seeds in early summer. Markedly contrasting thermal dormancy/germination characteristics were demonstrated for their seeds in systematic laboratory tests performed after several types of seed storage including storage in the field. The primary dormancy of seeds of the spring germinator was removed by moist-chilling or field winter-chilling, while that of the autumn germinator was removed by moist storage at 25°C or field summer temperatures. Biseasonal seedling emergence of the species appears to be due to a local differentiation of distinct ecotypes.


