Gentiana tibetica
Gentiana tibetica
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Gentiana tibetica
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
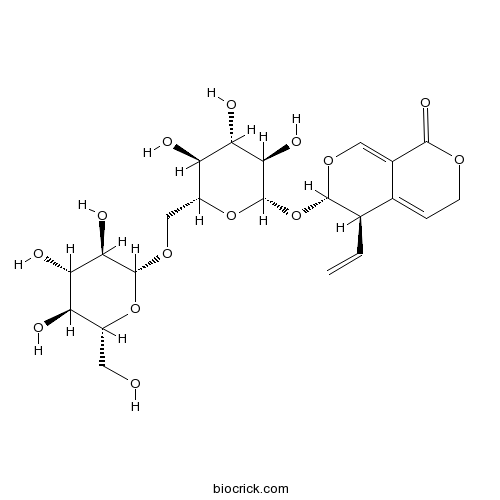
BCN2814
6'-O-beta-D-Glucosylgentiopicroside115713-06-9
Instructions
-
BCN5441
Isovitexin38953-85-4
Instructions
-
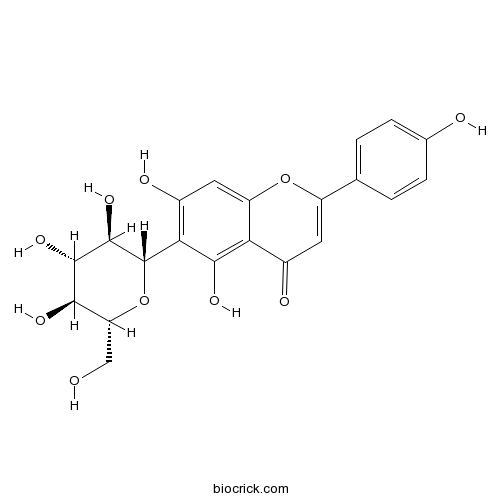
BCN4985
Luteolin-6-C-glucoside4261-42-1
Instructions

Cryopreservation by encapsulation of Gentiana spp cell suspensions maintains regrowth, embryogenic competence and DNA content.[Pubmed: 18946555]
A reliable technique for cryopreservation by encapsulation was developed for two suspension cultures of gentian species (Gentiana tibetica and G. cruciata) of different ages and embryogenic potential. The effect of water content, aggregate size and the subculture time on viability was determined by the 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) test. Regrowth of a proembryogenic mass (PEM) on agar, liquid or agar/liquid media was assayed by measuring the increase in biomass. A water content of 24-30% (fresh weight basis) after 5-6 h dehydration of encapsulated cells of gentians yielded the highest survival (68% for G. tibetica and 83% for G. cruciata) after cryopreservation. Regardless of species, aggregate size and subculture time, the lowest PEM survival was 44%. These parameters did not influence the survival of G. tibetica PEM, but the survival of G. cruciata was higher when the smaller aggregates were cryopreserved on the 5th day of culture. Agar/liquid culture caused the greatest biomass increase. Cryopreservation did not affect the characteristics of suspension cultures and their regrowth after thawing, nor the number and dynamics of somatic embryos formed. Flow cytometry showed that cryopreservation did not change the genome size of the PEMs or regenerants.
Comparison of three techniques for cryopreservation and reestablishment of long-term Gentiana tibetica suspension culture.[Pubmed: 17256062]
Cryogenic storage of cell suspensions allows long-term maintenance of cultures. The main purpose of the study was to develop a successful cryogenic protocol for 10-year-old embryogenic cell suspensions of G. tibetica. We examined three techniques of freezing: (I) controlled-rate cooling with various cryoprotectants (0.1-0.5 M DMSO, 0.5-1.0 M sucrose, 0.5-1.0 M glycerol, 0.25-1.0 M proline) or preculture with 0.4 M sorbitol and cryoprotectants (0.065-0.1 M DMSO, 0.2-0.8 M proline), (II) vitrification (PVS2) and (III) encapsulation. Cell viability was assessed by the TTC test and biomass increase. After controlled-rate cooling the majority of cells were lethally damaged, with only 3% viability observed. Vitrification and encapsulation approaches were more effective, assuring high levels of post-thaw viability ca. 85% and 7%, respectively. The encapsulation procedure gave faster recovery of the culture suspension than did vitrification, and ensured culture homogeneity and embryogenic competence.
Ultrastructure of Gentiana tibetica proembryogenic cells before and after cooling treatments.[Pubmed: 16547551]
The influence of increased concentrations of sucrose, 0.4 M sorbitol, DMSO and vitrification solution (PVS2) on the ultrastructure of non-frozen and frozen suspensions of Gentiana tibetica King ex Hook. F.tissue cells was investigated. Embryogenic aggregates were composed of three groups of cells of different size with various types of plastids. The ultrastructural changes resulting from increasing the sucrose concentration in the medium from 3 to 6 percent for 4 weeks and from treatment with 0.4 M sorbitol for 48 h were similar. Observations showed replacement of large vacuoles by numerous small ones, condensation of cytoplasm, accumulation of starch, and fragmentation of endoplasmic reticulum. Treatment with PVS2 led to degradation of starch, coalescence of amyloplasts and to shrinking of nucleoli from the third group of cells when originating from 6 percent sucrose medium. The mitochondria initially had various shapes, but after PVS2 treatment showed only spherical shapes with sparse cristae. After programmed freezing of tissue protected by sorbitol and DMSO, lethal damage was observed: membrane and nuclei degradation, and cell destruction. Reversible changes after freezing were observed in tissue pretreated with vitrification solution: dilation of cell membranes, mitochondria with electron-lucent vessels, aggregation of numerous vesicles, and degradation of starch in amyloplasts. In cells cooled by a vitrification method, cell organelles appeared normal as early as 5 h after thawing, and anomalies were not observed after 48 h of post-thawing culture.
Secoiridoid glycosides and an antifungal anthranilate derivative from Gentiana tibetica.[Pubmed: 9611826]
Repetitive chromatography of the methanol extract of the roots of Gentiana tibetica afforded two new secoiridoid glycosides and a novel antifungal anthranilic acid derivative, together with beta-sitosterol, daucosterol, oleanolic acid, loganic acid, gentiopicroside, sweroside, 2'-(2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)sweroside, trifloroside, rindoside and macrophylloside A. The structures of the new products were determined mainly by spectroscopic methods as 8-hydroxy-10-hydrosweroside, isomacrophylloside and ethyl N-docosanoylanthranilate. Ethyl N-docosanoylanthranilate inhibited the growth of the human pathogenic fungi Candida albicans and Aspergillus flavus. The taxonomic significance of the constituent is discussed briefly.


