6'-O-beta-D-GlucosylgentiopicrosideCAS# 115713-06-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
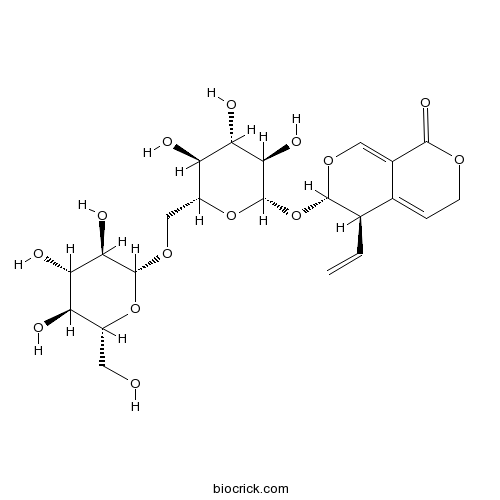
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 115713-06-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10864232 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H30O14 | M.Wt | 518.47 |
| Type of Compound | Iridoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (3S,4R)-4-ethenyl-3-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxy-4,6-dihydro-3H-pyrano[3,4-c]pyran-8-one | ||
| SMILES | C=CC1C(OC=C2C1=CCOC2=O)OC3C(C(C(C(O3)COC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BERNCPGDRADLCG-KEXDUYRESA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. 6'-O-beta-D-Glucosylgentiopicroside may have antifungal activity. |
| Targets | Antifection |

6'-O-beta-D-Glucosylgentiopicroside Dilution Calculator

6'-O-beta-D-Glucosylgentiopicroside Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9288 mL | 9.6438 mL | 19.2875 mL | 38.575 mL | 48.2188 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3858 mL | 1.9288 mL | 3.8575 mL | 7.715 mL | 9.6438 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1929 mL | 0.9644 mL | 1.9288 mL | 3.8575 mL | 4.8219 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0386 mL | 0.1929 mL | 0.3858 mL | 0.7715 mL | 0.9644 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0193 mL | 0.0964 mL | 0.1929 mL | 0.3858 mL | 0.4822 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Adonifoline
Catalog No.:BCN2056
CAS No.:115712-88-4
- Daidzein dimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN6761
CAS No.:1157-39-7
- B2
Catalog No.:BCC7505
CAS No.:115687-05-3
- H-DL-Pro-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC3027
CAS No.:115630-49-4
- Cinnamyl caffeate
Catalog No.:BCN7721
CAS No.:115610-32-7
- Cinnamyl isoferulate
Catalog No.:BCN7718
CAS No.:115610-31-6
- Cinnamyl coumarate
Catalog No.:BCN7739
CAS No.:115610-30-5
- 4-Androstenediol
Catalog No.:BCC8692
CAS No.:1156-92-9
- 2'-Hydroxygenistein
Catalog No.:BCN6036
CAS No.:1156-78-1
- Marbofloxacin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4250
CAS No.:115551-26-3
- Marbofloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC2510
CAS No.:115550-35-1
- BI 224436
Catalog No.:BCC5531
CAS No.:1155419-89-8
- 1-O-galloyl-6-O-cinnamoylglucose
Catalog No.:BCN8264
CAS No.:115746-69-5
- Galanolactone
Catalog No.:BCN6037
CAS No.:115753-79-2
- 15,16-Dihydro-15-methoxy-16-oxohardwickiic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1612
CAS No.:115783-35-2
- ent-Atisane-3beta,16alpha,17-triol
Catalog No.:BCN6626
CAS No.:115783-44-3
- Tubeimoside II
Catalog No.:BCN2955
CAS No.:115810-12-3
- Tubeimoside III
Catalog No.:BCN2956
CAS No.:115810-13-4
- 2,7-Dideacetoxytaxinine J
Catalog No.:BCN7281
CAS No.:115810-14-5
- Salvianolic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN5376
CAS No.:115841-09-3
- Aurora A Inhibitor I
Catalog No.:BCC2182
CAS No.:1158838-45-9
- N1-Methoxymethyl picrinine
Catalog No.:BCN6038
CAS No.:1158845-78-3
- Tos-Arg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2873
CAS No.:1159-15-5
- Angoroside C
Catalog No.:BCN4997
CAS No.:115909-22-3
Acyl secoiridoids and antifungal constituents from Gentiana macrophylla.[Pubmed:9397205]
Phytochemistry. 1996 Jul;42(5):1305-13.
LC-UV-mass spectrometry and bioassay co-directed fractionation of an aqueous acetone extract of the roots of Gentiana macrophylla gave three new chromene derivatives and two novel and six known secoiridoids, along with kurarinone, kushenol I, beta-sitosterol, stigmasterol, daucosterol, beta-sitosterol-3-O-gentiobioside, alpha-amyrin, oleanolic acid, isovitexin, gentiobiose and methyl 2-hydroxy-3-(1-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxybenzoate. The structures of the new products were established from spectral and chemical evidence as 2-methoxyanofinic acid and macrophyllosides A-D. The six known secoiridoids were gentiopicroside, sweroside, 6'-O-beta-D-glucosylgentiopicroside, 6'-O-beta-D-glucosylsweroside, trifloroside and rindoside. The new acid (2-methoxyanofinic acid), its methyl ester, kurarinone and kushenol I were shown to be active against the plant pathogenic fungus Cladosporium cucumerinum. The methyl ester and kurarinone inhibited also the growth of the human pathogenic yeast Candida albicans. Structure-activity relationships were studied. Thus, addition of a methoxyl group to the benzene nucleus of anofinic acid (2,2-dimethyl-2H-1-benzopyran-6-carboxylic acid) increased the antifungal activity remarkably whereas glycosylation at the carboxylic moiety was found to remove the activity. Esterification of the new acid induced its activity against C. albicans, but decreased its growth inhibition properties against C. cucumerinum. Hydroxylation of kurarinone at the 3 beta-position removed its activity against C. albicans and decreased the inhibition of C. cucumerinum. In addition, the chemotaxonomic significance of the identified constituents is discussed.
Inhibitory effects of secoiridoids from the roots of Gentiana straminea on stimulus-induced superoxide generation, phosphorylation and translocation of cytosolic compounds to plasma membrane in human neutrophils.[Pubmed:21584870]
Phytother Res. 2012 Feb;26(2):168-73.
Gentiana straminea Maxim. has been used widely as a traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of rheumarthritis, icterepatitis, constipation, pain and hypertension. Five secoiridoids, gentiopicroside (GTP), 6'-O-(2-hydroxy-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-benzoyl)-sweroside (HGBS), 6'-O-beta-D-glucosylgentiopicroside (GGTP), sweroside (SW) and swertiamarin (STM) were isolated from the roots of G. straminea. The effect of these secoiridoids on stimulus-induced superoxide generation in human neutrophils was assayed by measuring the reduction of ferricytochrome c. Tyrosyl or serine/threonine phosphorylation of neutrophil proteins, and translocation of the cytosolic compounds to the cell membrane were also investigated using specific monoclonal antibodies. The five secoiridoids used in the present experiment suppressed N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP)-induced superoxide generation in a concentration dependent manner. GTP and HGBS also suppressed phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and arachidonic acid (AA)-induced superoxide generation. However, the other three secoiridoids showed no effect on PMA- and AA-induced superoxide generation. fMLP-, PMA- and AA-induced tyrosyl or serine/threonine phosphorylation and translocation of the cytosolic proteins to the cell membrane were suppressed in parallel with the suppression of the stimulus-induced superoxide generation.


