Aurora A Inhibitor IAurora A inhibitor CAS# 1158838-45-9 |
- MLN8237 (Alisertib)
Catalog No.:BCC2166
CAS No.:1028486-01-2
- SCH-1473759
Catalog No.:BCC1934
CAS No.:1094069-99-4
- Reversine
Catalog No.:BCC1892
CAS No.:656820-32-5
- AZD1152
Catalog No.:BCC1393
CAS No.:722543-31-9
- XL228
Catalog No.:BCC2058
CAS No.:898280-07-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1158838-45-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44139710 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C31H31ClFN7O2 | M.Wt | 588.07 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
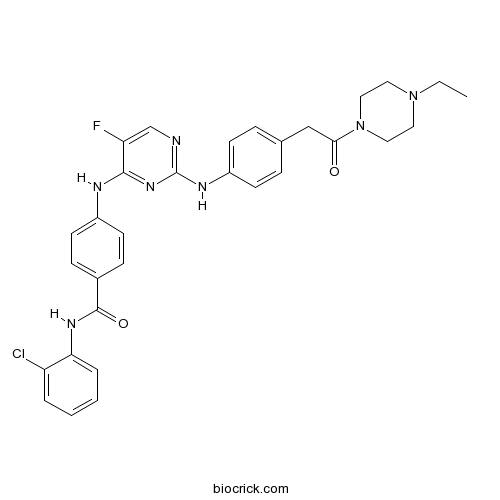
| Chemical Name | N-(2-chlorophenyl)-4-[[2-[4-[2-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl]anilino]-5-fluoropyrimidin-4-yl]amino]benzamide | ||
| SMILES | CCN1CCN(CC1)C(=O)CC2=CC=C(C=C2)NC3=NC=C(C(=N3)NC4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)NC5=CC=CC=C5Cl)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AKSIZPIFQAYJGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C31H31ClFN7O2/c1-2-39-15-17-40(18-16-39)28(41)19-21-7-11-24(12-8-21)36-31-34-20-26(33)29(38-31)35-23-13-9-22(10-14-23)30(42)37-27-6-4-3-5-25(27)32/h3-14,20H,2,15-19H2,1H3,(H,37,42)(H2,34,35,36,38) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and selective inhibitor of Aurora kinase A (IC50 = 3.4 nM); exhibits 1000-fold selectivity for Aurora kinase A over Aurora kinase B. Displays antiproliferative activity in HCT116 and HT29 cells (IC50 values are 0.19 and 2.9 μM respectively). |

Aurora A Inhibitor I Dilution Calculator

Aurora A Inhibitor I Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7005 mL | 8.5024 mL | 17.0048 mL | 34.0096 mL | 42.5119 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3401 mL | 1.7005 mL | 3.401 mL | 6.8019 mL | 8.5024 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.17 mL | 0.8502 mL | 1.7005 mL | 3.401 mL | 4.2512 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.034 mL | 0.17 mL | 0.3401 mL | 0.6802 mL | 0.8502 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.017 mL | 0.085 mL | 0.17 mL | 0.3401 mL | 0.4251 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 3.4 nM.
Aurora A Inhibitor I is a novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of Aurora A .
Aurora kinases are reported to be required for mitosis and to complete cell division. Because of this, Aurora kinase inhibitors have been investigated extensively as potential anticancer therapeutic agents. The two major Aurora kinases (Aurora A and Aurora B) are closely related in kinase domain sequence (71% identical).
In vitro: Aurora A Inhibitor I was tested against wild-type kinase and two mutants (Aurora A (T217E) and Aurora B (E161T)). The inhibitory potencies of Aurora A Inhibitor I was strongly affected by the single amino acid substitutions. For either Aurora kinase, the presence of threonine allowed potent inhibition, while for glutamic acid variants, there was a approximately 100-fold shift in IC50, which supported the “gating” role for this residue. The Aurora B binding pocket was enlarged by the E161T mutation, while the pocket in Aurora A was closed by the T217E mutation. Aurora A Inhibitor I was exceptionally selective Aurora A inhibitors, as shown by no inhibition on Aurora B or CDKs was observed in cellular assays [1].
In vivo: So far, there is no animal in vivo study reported.
Clinical trial: N/A
Reference:
[1] Aliagas-Martin I,Burdick D,Corson L,Dotson J,Drummond J,Fields C,Huang OW,Hunsaker T,Kleinheinz T,Krueger E,Liang J,Moffat J,Phillips G,Pulk R,Rawson TE,Ultsch M,Walker L,Wiesmann C,Zhang B,Zhu BY,Cochran AG. A class of 2,4-bisanilinopyrimidine Aurora A inhibitors with unusually high selectivity against Aurora B. J Med Chem.2009 May 28;52(10):3300-7.
- Salvianolic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN5376
CAS No.:115841-09-3
- 2,7-Dideacetoxytaxinine J
Catalog No.:BCN7281
CAS No.:115810-14-5
- Tubeimoside III
Catalog No.:BCN2956
CAS No.:115810-13-4
- Tubeimoside II
Catalog No.:BCN2955
CAS No.:115810-12-3
- ent-Atisane-3beta,16alpha,17-triol
Catalog No.:BCN6626
CAS No.:115783-44-3
- 15,16-Dihydro-15-methoxy-16-oxohardwickiic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1612
CAS No.:115783-35-2
- Galanolactone
Catalog No.:BCN6037
CAS No.:115753-79-2
- 1-O-galloyl-6-O-cinnamoylglucose
Catalog No.:BCN8264
CAS No.:115746-69-5
- 6'-O-beta-D-Glucosylgentiopicroside
Catalog No.:BCN2814
CAS No.:115713-06-9
- Adonifoline
Catalog No.:BCN2056
CAS No.:115712-88-4
- Daidzein dimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN6761
CAS No.:1157-39-7
- B2
Catalog No.:BCC7505
CAS No.:115687-05-3
- N1-Methoxymethyl picrinine
Catalog No.:BCN6038
CAS No.:1158845-78-3
- Tos-Arg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2873
CAS No.:1159-15-5
- Angoroside C
Catalog No.:BCN4997
CAS No.:115909-22-3
- Tarafenacin D-tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4148
CAS No.:1159101-48-0
- Salvianolic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN6106
CAS No.:115939-25-8
- Alstonic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN6039
CAS No.:1159579-44-8
- Alstonic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN6040
CAS No.:1159579-45-9
- Poricoic acid AE
Catalog No.:BCN7282
CAS No.:1159753-88-4
- CZC24832
Catalog No.:BCC1507
CAS No.:1159824-67-5
- Abiesadine N
Catalog No.:BCN6041
CAS No.:1159913-80-0
- Caulophine
Catalog No.:BCN7990
CAS No.:1159989-19-1
- TC-I 2000
Catalog No.:BCC6244
CAS No.:1159996-20-9
Association of an aurora kinase a (AURKA) gene polymorphism with progression-free survival in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma treated with the selective aurora kinase a inhibitor alisertib.[Pubmed:28155045]
Invest New Drugs. 2017 Aug;35(4):524-528.
Background and purpose Salvage therapies for urothelial carcinoma are needed. A single-arm trial in patients with advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma refractive to other therapies found that alisertib, a selective inhibitor of aurora kinase A, maintained stable disease in a few cases, despite a low objective response rate. To better understand why some patients benefited from alisertib, we genotyped the 22 patients of this pilot trial for two single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs2273535 and rs1047972) in AURKA, the gene encoding aurora kinase A, and looked for associations with survival and treatment response. Results Carrier status for the minor allele of rs2273535 (T91A, p. F31I) was a favorable prognostic factor for progression-free survival (HR = 0.18; 95% CI, 0.039-0.81; P = 0.026) but not for overall survival (HR = 0.88; 95% CI, 0.26-2.9; P = 0.83). These results were confirmed in multivariable analyses, adjusting for sex, age and hemoglobin, for both progression-free survival (HR = 0.11; 95% CI, 0.018-0.69; P = 0.018) and overall survival. No association was found between rs1047972 and survival. Moreover, neither SNP was associated with treatment response. Conclusion In patients who received alisertib for advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, longer progression-free survival was observed in carriers of the minor allele A of rs2273535 in AURKA than in patients who were homozygous for the major allele T. This finding, based on a small pilot trial, warrants further investigation.
A phase 1 study of AMG 900, an orally administered pan-aurora kinase inhibitor, in adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia.[Pubmed:28370201]
Am J Hematol. 2017 Jul;92(7):660-667.
Aurora kinases are involved in the pathophysiology of several cancers including acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In this phase 1 study, we investigated the safety and efficacy of AMG 900, an orally administered, highly potent, selective, small-molecule inhibitor of both Aurora kinase A and B, in patients with AML . Patients with pathologically documented AML who either declined standard treatments or had relapsed from or were refractory to previous therapies were enrolled. Two every-2-week dose-escalation schedules using a modified 3 + 3 + 3 design were evaluated AMG 900 given daily for 4 days with 10 days off (4/10 schedule), and AMG 900 given daily for 7 days with 7 days off (7/7 schedule). Thirty-five patients were enrolled at 9 different dose levels: 22 patients on the 4/10 schedule (doses from 15 to 100 mg daily), and 13 patients on the 7/7 schedule (doses from 30 to 50 mg daily). Both schedules were tolerated; nausea (31%), diarrhea (29%), febrile neutropenia (29%), and fatigue (23%) were the most common treatment-related adverse events. Three patients (9%) achieved complete response with incomplete count recovery. Patients with higher baseline expression of a set of specific pathway-related genes (BIRC5, AURKA, TTK, CDC2, and CCNB1) were more likely to respond in an exploratory biomarker analysis. AMG 900 was tolerated in a general AML population, and pathway-specific biomarkers identified a potential target population. Future research efforts will be directed toward further exploration of biomarkers of response and combination of AMG 900 with other anticancer agents.
Aurora B Inhibitor TAK-901 Synergizes with BCL-xL Inhibition by Inducing Active BAX in Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:28179288]
Anticancer Res. 2017 Feb;37(2):437-444.
BACKGROUND: Aurora B kinase plays an essential role in chromosome segregation and cytokinesis, and is dysregulated in many cancer types, making it an attractive therapeutic target. TAK-901 is a potent aurora B inhibitor that showed efficacy in both in vitro and in vivo oncology models. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We conducted a synthetic lethal siRNA screening to identify the genes that, when silenced, can potentiate the cell growth-inhibitory effect of TAK-901. RESULTS: B-cell lymphoma-extra large (BCL-xL) depletion by siRNA or chemical inhibition synergized with TAK-901 in cancer cell lines. As a mechanism of synthetic lethality, active BCL2 associated X, apoptosis regulator (BAX) was induced by TAK-901. BCL-xL protected cells from BAX-dependent apoptosis induction. Therefore, TAK-901 sensitizes cancer cells to BCL-xL inhibition. CONCLUSION: Polyploid cells induced by TAK-901 are vulnerable to BCL-xL inhibition. Our findings may have an impact on combination strategies with aurora B inhibitors in clinical studies.
SMARCA4-inactivating mutations increase sensitivity to Aurora kinase A inhibitor VX-680 in non-small cell lung cancers.[Pubmed:28102363]
Nat Commun. 2017 Jan 19;8:14098.
Mutations in the SMARCA4/BRG1 gene resulting in complete loss of its protein (BRG1) occur frequently in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. Currently, no single therapeutic agent has been identified as synthetically lethal with SMARCA4/BRG1 loss. We identify AURKA activity as essential in NSCLC cells lacking SMARCA4/BRG1. In these cells, RNAi-mediated depletion or chemical inhibition of AURKA induces apoptosis and cell death in vitro and in xenograft mouse models. Disc large homologue-associated protein 5 (HURP/DLGAP5), required for AURKA-dependent, centrosome-independent mitotic spindle assembly is essential for the survival and proliferation of SMARCA4/BRG1 mutant but not of SMARCA4/BRG1 wild-type cells. AURKA inhibitors may provide a therapeutic strategy for biomarker-driven clinical studies to treat the NSCLCs harbouring SMARCA4/BRG1-inactivating mutations.
Overcoming CML acquired resistance by specific inhibition of Aurora A kinase in the KCL-22 cell model.[Pubmed:22116466]
Carcinogenesis. 2012 Feb;33(2):285-93.
Serine/threonine kinase Aurora A is essential for regulating mammalian cell division and is overexpressed in many types of human cancer. However, the role of Aurora A in chemoresistance of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is not well understood. Using the KCL-22 cell culture model we have recently developed for studying mechanisms of CML acquired resistance, we found that Aurora A expression was partially reduced in these cells upon treatment with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib, which accompanied the acquisition of BCR-ABL mutation for imatinib resistance. Gene knockdown of BCR-ABL also reduced Aurora A expression, and conversely, Aurora A expression increased in hematopoietic progenitor cells after BCR-ABL expression. Inhibition of Aurora A induced apoptosis of CML cells with or without T315I BCR-ABL mutation and suppressed CML cell growth. Inhibition of Aurora A by gene knockdown or a highly specific small molecule inhibitor sensitized CML cells to imatinib treatment and effectively blocked acquisition of BCR-ABL mutations and KCL-22 cell relapse on imatinib, nilotinib or dasatinib. Our results show that Aurora A plays an important role for facilitating acquisition of BCR-ABL mutation and acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the culture model and suggest that inhibition of Aurora A may provide an alternative strategy to improve CML treatment to overcome resistance.
A class of 2,4-bisanilinopyrimidine Aurora A inhibitors with unusually high selectivity against Aurora B.[Pubmed:19402633]
J Med Chem. 2009 May 28;52(10):3300-7.
The two major Aurora kinases carry out critical functions at distinct mitotic stages. Selective inhibitors of these kinases, as well as pan-Aurora inhibitors, show antitumor efficacy and are now under clinical investigation. However, the ATP-binding sites of Aurora A and Aurora B are virtually identical, and the structural basis for selective inhibition has therefore not been clear. We report here a class of bisanilinopyrimidine Aurora A inhibitors with excellent selectivity for Aurora A over Aurora B, both in enzymatic assays and in cellular phenotypic assays. Crystal structures of two of the inhibitors in complex with Aurora A implicate a single amino acid difference in Aurora B as responsible for poor inhibitory activity against this enzyme. Mutation of this residue in Aurora B (E161T) or Aurora A (T217E) is sufficient to swap the inhibition profile, suggesting that this difference might be exploited more generally to achieve high selectivity for Aurora A.


