Salvianolic acid BCAS# 115939-25-8 |
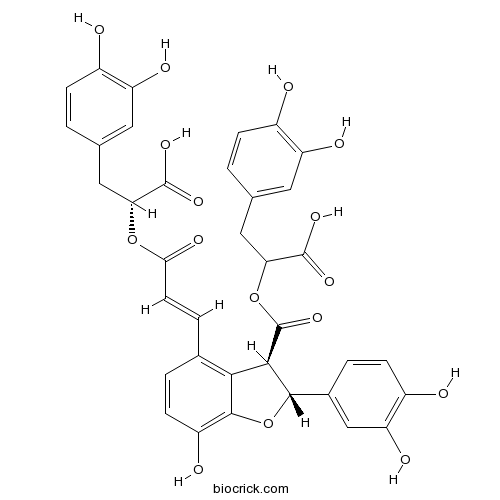
- Salvianolic acid B; Lithospermic acid B; Danfensuan B
Catalog No.:BCC8249
CAS No.:121521-90-2
- Salvianolic acid Y
Catalog No.:BCN8123
CAS No.:1638738-76-7
- Isosalvianolic Acid B
Catalog No.:BCC8330
CAS No.:930573-88-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 115939-25-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6441188 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C36H30O16 | M.Wt | 718.62 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-[(E)-3-[(2R,3R)-3-[1-carboxy-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]carbonyl-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-4-yl]prop-2-enoyl]oxy-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1CC(C(=O)O)OC(=O)C=CC2=C3C(C(OC3=C(C=C2)O)C4=CC(=C(C=C4)O)O)C(=O)OC(CC5=CC(=C(C=C5)O)O)C(=O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SNKFFCBZYFGCQN-RDHSGEKBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C36H30O16/c37-20-6-1-16(11-24(20)41)13-27(34(45)46)50-29(44)10-5-18-3-9-23(40)33-30(18)31(32(52-33)19-4-8-22(39)26(43)15-19)36(49)51-28(35(47)48)14-17-2-7-21(38)25(42)12-17/h1-12,15,27-28,31-32,37-43H,13-14H2,(H,45,46)(H,47,48)/b10-5+/t27-,28?,31-,32+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Salvianolic acid B is a bioactive compound isolated from the Chinese medicinal herb Danshen, which is used for treating neoplastic and chronic inflammatory diseases in China, it shows a protective action against the ischemia-reperfusion induced injury in rat brain. It inhibited the expression of COX,ERK,TNF-α, NO. |
| Targets | COX | ERK | TNF-α | NO |
| In vitro | Salvianolic acid B possesses vasodilation potential through NO and its related signals in rabbit thoracic aortic rings.[Pubmed: 23051676]Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Dec 15;697(1-3):81-7.Salviae miltiorrhizae, a traditional Chinese medicine, is widely used in the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Salvianolic acid B is identified as one of the most important water-soluble active ingredients in Salviae miltiorrhizae and associated with the activation of Ca(2+) channel of cytomembrane. But the further mechanism of action was not very clearly.
|
| In vivo | Effect and mechanism of salvianolic acid B on the myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.[Pubmed: 24507676]Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014 Apr;7(4):280-4.To investigate the effect of Salvianolic acid B on rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Salvianolic acid B promotes osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells through activating ERK signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 24657587]Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Jun;51:1-9.Salvianolic acid B, a major bioactive component of Chinese medicine herb, Salvia miltiorrhiza, is widely used for treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Our recent studies have shown that Salvianolic acid B can prevent development of osteoporosis. However, the underlying mechanisms are still not clarified clearly.
|
| Cell Research | Salvianolic acid B inhibits growth of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo via cyclooxygenase-2 and apoptotic pathways.[Pubmed: 19123475]Int J Cancer. 2009 May 1;124(9):2200-9.Salvianolic acid B (Sal-B) is a leading bioactive component of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge, which is used for treating neoplastic and chronic inflammatory diseases in China.
|
| Animal Research | Antagonism by salvianolic acid B of lipopolysaccharide-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation in rabbits.[Pubmed: 24739088]Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014 Jul;41(7):502-8.Animal Models: DIC model in rabbits |

Salvianolic acid B Dilution Calculator

Salvianolic acid B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3916 mL | 6.9578 mL | 13.9156 mL | 27.8311 mL | 34.7889 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2783 mL | 1.3916 mL | 2.7831 mL | 5.5662 mL | 6.9578 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1392 mL | 0.6958 mL | 1.3916 mL | 2.7831 mL | 3.4789 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0278 mL | 0.1392 mL | 0.2783 mL | 0.5566 mL | 0.6958 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0139 mL | 0.0696 mL | 0.1392 mL | 0.2783 mL | 0.3479 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Tarafenacin D-tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4148
CAS No.:1159101-48-0
- Angoroside C
Catalog No.:BCN4997
CAS No.:115909-22-3
- Tos-Arg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2873
CAS No.:1159-15-5
- N1-Methoxymethyl picrinine
Catalog No.:BCN6038
CAS No.:1158845-78-3
- Aurora A Inhibitor I
Catalog No.:BCC2182
CAS No.:1158838-45-9
- Salvianolic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN5376
CAS No.:115841-09-3
- 2,7-Dideacetoxytaxinine J
Catalog No.:BCN7281
CAS No.:115810-14-5
- Tubeimoside III
Catalog No.:BCN2956
CAS No.:115810-13-4
- Tubeimoside II
Catalog No.:BCN2955
CAS No.:115810-12-3
- ent-Atisane-3beta,16alpha,17-triol
Catalog No.:BCN6626
CAS No.:115783-44-3
- 15,16-Dihydro-15-methoxy-16-oxohardwickiic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1612
CAS No.:115783-35-2
- Galanolactone
Catalog No.:BCN6037
CAS No.:115753-79-2
- Alstonic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN6039
CAS No.:1159579-44-8
- Alstonic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN6040
CAS No.:1159579-45-9
- Poricoic acid AE
Catalog No.:BCN7282
CAS No.:1159753-88-4
- CZC24832
Catalog No.:BCC1507
CAS No.:1159824-67-5
- Abiesadine N
Catalog No.:BCN6041
CAS No.:1159913-80-0
- Caulophine
Catalog No.:BCN7990
CAS No.:1159989-19-1
- TC-I 2000
Catalog No.:BCC6244
CAS No.:1159996-20-9
- Aldicarb
Catalog No.:BCC5475
CAS No.:116-06-3
- 4-Amino-3-hydroxy-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8680
CAS No.:116-63-2
- 1-Amino-4-hydroxyanthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCC8452
CAS No.:116-85-8
- VU 0238429
Catalog No.:BCC7729
CAS No.:1160247-92-6
- MLN4924 HCl salt
Catalog No.:BCC1773
CAS No.:1160295-21-5
Salvianolic acid B promotes osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells through activating ERK signaling pathway.[Pubmed:24657587]
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Jun;51:1-9.
Salvianolic acid B, a major bioactive component of Chinese medicine herb, Salvia miltiorrhiza, is widely used for treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Our recent studies have shown that Salvianolic acid B can prevent development of osteoporosis. However, the underlying mechanisms are still not clarified clearly. In the present study, we aim to investigate the effects of Salvianolic acid B on viability and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). The results showed Salvianolic acid B (Sal B) had no obvious toxic effects on hMSCs, whereas Sal B supplementation (5muM) increased the alkaline phosphatase activity, osteopontin, Runx2 and osterix expression in hMSCs. Under osteogenic induction condition, Sal B (5muM) significantly promoted mineralization; and when the extracellular-signal-regulated kinases signaling (ERK) pathway was blocked, the anabolic effects of Sal B were diminished, indicating that Sal B promoted osteogenesis of hMSCs through activating ERK signaling pathway. The current study confirms that Sal B promotes osteogenesis of hMSCs with no cytotoxicity, and it may be used as a potential therapeutic agent for the management of osteoporosis.
Salvianolic acid B possesses vasodilation potential through NO and its related signals in rabbit thoracic aortic rings.[Pubmed:23051676]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Dec 15;697(1-3):81-7.
Salviae miltiorrhizae, a traditional Chinese medicine, is widely used in the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Salvianolic acid B is identified as one of the most important water-soluble active ingredients in Salviae miltiorrhizae and associated with the activation of Ca(2+) channel of cytomembrane. But the further mechanism of action was not very clearly. In our study, we investigated the vasodilation activity of Salvianolic acid B using the isolated thoracic aortic rings from Japanese white rabbit. Salvianolic acid B significantly released the contraction of the isolated thoracic aortic rings induced by phenylephrine and CaCl(2) while had no effects on the aortic rings with KCl stimulated. Different with Di-ao-xin-xue-kang capsule, Salvianolic acid B caused an increase of Ca(2+) in cytoplasm from not only activation of Ca(2+) channel in cytomembrane but also release of endogenous Ca(2+). Then, a series of endogenous Ca(2+) inhibitors were pretreated to explore the mechanism of Salvianolic acid B, and the results provided further evidences that Salvianolic acid B causes intracellular calcium release in ryanodine receptors-dependent manners. Moreover, combining l-arginine (l-Arg) with Salvianolic acid B promoted the vasodilation activity suggesting a relationship with nitric oxide (NO). To further investigated its mechanism, both guanylate cyclase (GC) inhibitor and NO Synthase inhibitor were used and demonstrated to block vasodilation activity of the aortic rings. Our findings reveal a NO-sGC-cGMP signals dependence mechanism of Salvianolic acid B on its vasodilation activity which provide an evidence for its subsequent application in clinic.
Antagonism by salvianolic acid B of lipopolysaccharide-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation in rabbits.[Pubmed:24739088]
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014 Jul;41(7):502-8.
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of Salvianolic acid B on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) in rabbits. Continuous infusion of LPS was used to induce a DIC model in rabbits. Treatment with Salvianolic acid B (1, 3 or 6 mg/kg) was started simultaneously with LPS infusion (0.5 mg/kg LPS in 60 mL saline; 10 mL/h over a period of 6 h) through the contralateral marginal ear vein. Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), prothrombin time (PT), platelet count and fibrinogen concentration were determined, as were plasma levels of fibrin-fibrinogen degradation products (FDP), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), protein C activity, antithrombin III (ATIII) and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha concentration. The gradual impairment of haemostatic parameters was induced by continuous infusion of LPS. There were marked increases in APTT, PT, BUN, ALT and plasma TNF-alpha and marked decreases in the platelet count, fibrinogen, FDP, protein C and ATIII. The intravenous administration of 1, 3 or 6 mg/kg Salvianolic acid B attenuated the increases in APTT, PT, BUN, ALT and plasma TNF-alpha and the decreases in fibrinogen, platelet, FDP, protein C and ATIII induced by LPS infusion. These observations indicate that Salvianolic acid B has an effect against LPS-induced DIC in rabbits.
Effect and mechanism of salvianolic acid B on the myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.[Pubmed:24507676]
Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014 Apr;7(4):280-4.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the effect of Salvianolic acid B on rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. METHODS: SD rats were randomly divided into five groups (n=10 in each group): A sham operation group, B ischemic reperfusion group model group, C low dose Salvianolic acid B group, D median dose Salvianolic acid B group, E high dose Salvianolic acid B group. One hour after establishment of the myocardial ischemia-reperfusion model, the concentration and the apoptotic index of the plasma level of myocardial enzymes (CTn I, CK-MB), SOD, MDA, NO, ET were measured. Heart tissues were obtained and micro-structural changes were observed. RESULTS: Compared the model group, the plasma CTn, CK-MB, MDA and ET contents were significantly increased, NO, T-SOD contents were decreased in the treatment group (group C, D, and E) (P<0.05); compared with group E, the plasma CTn I, CK-MB, MDA and ET levels were increased, the NO, T-SOD levels were decreased in groups C and D (P<0.05). Infarct size was significantly reduced, and the myocardial ultrastructural changes were improved significantly in treatment group. CONCLUSIONS: Salvianolic acid B has a significant protective effect on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. It can alleviate oxidative stress, reduce calcium overload, improve endothelial function and so on.


