AZD1152Aurora B kinase inhibitor,highly potent and selective CAS# 722543-31-9 |
- Ro 31-8220 Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4999
CAS No.:138489-18-6
- CHIR-99021 (CT99021)
Catalog No.:BCC1275
CAS No.:252917-06-9
- CHIR-98014
Catalog No.:BCC3751
CAS No.:252935-94-7
- TWS119
Catalog No.:BCC4512
CAS No.:601514-19-6
- GSK-3 inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4126
CAS No.:603272-51-1
- GSK-3 Inhibitor IX (BIO)
Catalog No.:BCC4510
CAS No.:667463-62-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 722543-31-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11497983 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H31FN7O6P | M.Wt | 587.54 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Barasertib | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 33 mg/mL (56.17 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
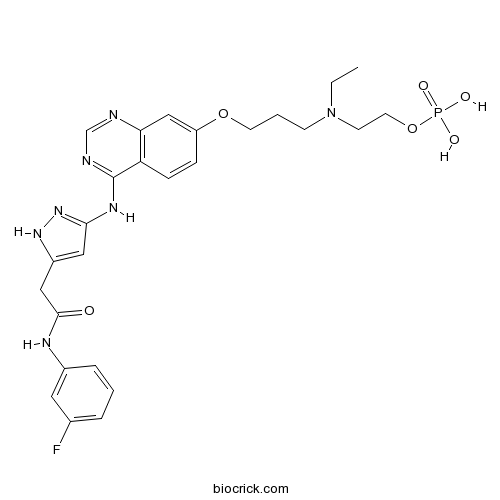
| Chemical Name | 2-[ethyl-[3-[4-[[5-[2-(3-fluoroanilino)-2-oxoethyl]-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]amino]quinazolin-7-yl]oxypropyl]amino]ethyl dihydrogen phosphate | ||
| SMILES | CCN(CCCOC1=CC2=C(C=C1)C(=NC=N2)NC3=NNC(=C3)CC(=O)NC4=CC(=CC=C4)F)CCOP(=O)(O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GBJVVSCPOBPEIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H31FN7O6P/c1-2-34(10-12-40-41(36,37)38)9-4-11-39-21-7-8-22-23(16-21)28-17-29-26(22)31-24-14-20(32-33-24)15-25(35)30-19-6-3-5-18(27)13-19/h3,5-8,13-14,16-17H,2,4,9-12,15H2,1H3,(H,30,35)(H2,36,37,38)(H2,28,29,31,32,33) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AZD1152 is a pro-drug of Barasertib-hQPA, which is a highly selective Aurora B inhibitor with IC50 of 0.37 nM in a cell-free assay.In Vitro:AZD1152 displays >3000-fold selectivity for Aurora B as compared with Aurora A which has an IC50 of 1.368 μM. AZD1152 has even less activity against 50 other serine-threonine and tyrosine kinases including FLT3, JAK2, and Abl. AZD1152 inhibits the proliferation of hematopoietic malignant cells such as HL-60, NB4, MOLM13, PALL-1, PALL-2, MV4-11, EOL-1, THP-1, and K562 cells with IC50 of 3-40 nM, displaying appr 100-fold potency than another Aurora kinase inhibitor ZM334739 which has IC50 of 3-30 μM. AZD1152 inhibits the clonogenic growth of MOLM13 and MV4-11 cells with IC50 of 1 nM and 2.8 nM, respectively, as well as the freshly isolated imatinib-resistant leukemia cells with IC50 values of 1-3 nM, more significantly compared with bone marrow mononuclear cells with IC50 values of >10 nM. AZD1152 induces accumulation of cells with 4N/8N DNA content, followed by apoptosis in a dose- and time-dependent manner[1]. AZD1152 causes significant accumulation of cells with 4N/8N DNA content in KMS12 and U266 and induces apoptosis in KMS18 and U266. AZD1152 in combination with DEX, has negative effects on cell viability in comparison with single agent in PMI8226, KMS11 and U266[3].In Vivo:Administration of AZD1152 (25 mg/kg) alone markedly suppresses the growth of MOLM13 xenografts, confirmed by the observation of necrotic tissue with infiltration of phagocytic cells[1]. In addition, AZD1152 (10-150 mg/kg/day) significantly inhibits the growth of a variety of human solid tumor xenografts, including colon, breast, and lung cancers, in a dose-dependent manner[2]. AZD1152 (25 mg/kg/day) treatment reduces xenograft levels such that they are slightly lower levels than after the first round of treatment, but this is not statistically significant indicating that residual cells might be more resistant to a second cycle of AZD1152[4]. References: | |||||

AZD1152 Dilution Calculator

AZD1152 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.702 mL | 8.5101 mL | 17.0201 mL | 34.0402 mL | 42.5503 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3404 mL | 1.702 mL | 3.404 mL | 6.808 mL | 8.5101 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1702 mL | 0.851 mL | 1.702 mL | 3.404 mL | 4.255 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.034 mL | 0.1702 mL | 0.3404 mL | 0.6808 mL | 0.851 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.017 mL | 0.0851 mL | 0.1702 mL | 0.3404 mL | 0.4255 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AZD1152 is a highly selective inhibitor of Aurora kinases with IC50 values of 1.37 μM and 0.37 nM for Aurora A and Aurora B, respectively [1].
AZD1152 is a dihydrogen phosphate pro-drug of HQPA which is a highly potent and specific inhibitor of the serine/threonine kinase Aurora kinases. The expression of Aurora kinase A and B are found to be related with the development of various cancers such as ovarian, pancreatic, breast and colon. Since that, the Aurora family is regarded as attractive target for anticancer treatment. As a selective Aurora kinase inhibitor, AZD1152 showed no significant effect on other kinases including JAK2, FLT3 and Abl. Besides that, AZD1152 exerted potent antitumor activities through inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis [1].
AZD1152 treatment potently inhibited cell growth in various leukemic cells including ALL PALL-2, MV4-11 and MOLM13 with IC50 values of 5, 1and 2.8 nM, respectively. AZD1152 also inhibited clone formation of freshly isolated leukemia cells with IC50 values of less than 3 nM. For the colon cancer HCT-116 cells, incubation of AZD1152 at dose of 30 nM for one day resulted in 80% cell number reduction after 4 days drug wash out. In prostate cancer DU145 and PC3 cells, AZD1152 caused decrease of G0/G1-phase cells and induced G2/M cell cycle arrest. Moreover, AZD1152 treatment enhanced the radio sensitivity of prostate cancer cells which were androgen-insensitive [1, 2 and 3].
In mice model with human MOLM13 cell xenografts, administration of AZD1152 at dose of 25 mg/kg significantly inhibited tumor growth. The combination treatment of AZD1152 at dose of 5 mg/kg and vincristine at dose of 0.2 mg/kg resulted in almost 100% inhibition of tumor growth of MOLM13 xenografts. In mice injected with MiaPaCa-2cells, the combination of AZD1152 and gemcitabine showed more than double effective than the single treatment [1 and 2].
References:
[1] Yang J, Ikezoe T, Nishioka C, Tasaka T, Taniguchi A, Kuwayama Y, Komatsu N, Bandobashi K, Togitani K, Koeffler HP, Taguchi H, Yokoyama A. AZD1152, a novel and selective aurora B kinase inhibitor, induces growth arrest, apoptosis, and sensitization for tubulin depolymerizing agent or topoisomerase II inhibitor in human acute leukemia cells in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 2007 Sep 15;110(6):2034-40.
[2] Azzariti A, Bocci G, Porcelli L, Fioravanti A, Sini P, Simone GM, Quatrale AE, Chiarappa P, Mangia A, Sebastian S, Del Bufalo D, Del Tacca M, Paradiso A. Aurora B kinase inhibitor AZD1152: determinants of action and ability to enhance chemotherapeutics effectiveness in pancreatic and colon cancer. Br J Cancer. 2011 Mar 1;104(5):769-80.
[3] Niermann KJ, Moretti L, Giacalone NJ, Sun Y, Schleicher SM, Kopsombut P, Mitchell LR, Kim KW, Lu B. Enhanced radiosensitivity of androgen-resistant prostate cancer: AZD1152-mediated Aurora kinase B inhibition. Radiat Res. 2011 Apr;175(4):444-51.
- Org 24598 lithium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7845
CAS No.:722456-08-8
- Laurifoline
Catalog No.:BCN4278
CAS No.:7224-61-5
- 2alpha-Hydroxyeupatolide 8-O-angelate
Catalog No.:BCN7340
CAS No.:72229-39-1
- 2-Hydroxyeupatolide
Catalog No.:BCN2490
CAS No.:72229-33-5
- Echitovenidine
Catalog No.:BCN7482
CAS No.:7222-35-7
- Parsonsine
Catalog No.:BCN2111
CAS No.:72213-98-0
- Calcitetrol
Catalog No.:BCC1446
CAS No.:72203-93-1
- Aflatoxin B2
Catalog No.:BCC9213
CAS No.:7220-81-7
- 2-Hydroxyplatyphyllide
Catalog No.:BCN7119
CAS No.:72145-19-8
- b-Casomorphin (1-3)
Catalog No.:BCC1007
CAS No.:72122-59-9
- Nerolidol
Catalog No.:BCN5459
CAS No.:7212-44-4
- Prilocaine
Catalog No.:BCC4929
CAS No.:721-50-6
- Barasertib (AZD1152-HQPA)
Catalog No.:BCC2168
CAS No.:722544-51-6
- Malvidin-3-O-glucoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3031
CAS No.:7228-78-6
- Streptolydigin
Catalog No.:BCN1858
CAS No.:7229-50-7
- Sulfamethoxazole
Catalog No.:BCC4857
CAS No.:723-46-6
- 9-AC
Catalog No.:BCC6867
CAS No.:723-62-6
- Rivularine
Catalog No.:BCN2038
CAS No.:723-78-4
- ZLN024
Catalog No.:BCC5527
CAS No.:723249-01-2
- ZJ 43
Catalog No.:BCC2355
CAS No.:723331-20-2
- Beta-Carotene
Catalog No.:BCN4965
CAS No.:7235-40-7
- Licoflavone C
Catalog No.:BCN3256
CAS No.:72357-31-4
- Isobellendine
Catalog No.:BCN1916
CAS No.:72362-45-9
- 2,3-Dihydrobellendine
Catalog No.:BCN1896
CAS No.:72362-47-1
Significance of AZD1152 as a potential treatment against Aurora B overexpression in acute promyelocytic leukemia.[Pubmed:27091351]
Ann Hematol. 2016 Jun;95(7):1031-42.
Aurora B kinase as a chromosomal passenger protein plays multiple roles in regulating mitosis and cytokinesis. The function of Aurora B in leukemic cells has made it an important treatment target. In this study, we explored the expressions of Aurora (A, B, and C) kinases in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) patients. In addition, we investigated the effects of AZD1152 as a specific inhibitor of Aurora B on cell survival, DNA synthesis, nuclear morphology, apoptosis induction, cell cycle distribution, and gene expression in an APL-derived NB4 cell line. Our results showed that Aurora B was overexpressed in 88 % of APL patients. AZD1152 treatment of NB4 cells led to viability reduction and G2/M arrest followed by an increase in cell size and polyploidy induction. These giant cells showed morphological evidence of mitotic catastrophe. AZD1152 treatment induced activation of G2/M checkpoint which in turn led to transient G2/M arrest in a p21-independent manner. Lack of functional p53 in NB4 cells might provide an opportunity to escape from G2/M block and to endure repeated rounds of replication and polyploidy. Treated cells were probably eliminated via p73-mediated overexpression of BAX, PUMA, and APAF1 and downregulation of survivin and MCL-1. In summary, AZD1152 treatment led to endomitosis and polyploidy in TP53-mutated NB4 cells. These giant polyploid cells might undergo mitotic catastrophe and p73-mediated apoptosis. It seems that induction of polyploidy via AZD1152 could be a novel form of anti-cancer therapy for APL that may be clinically accessible in the near future.
Inhibitor of Aurora Kinase B Induces Differentially Cell Death and Polyploidy via DNA Damage Response Pathways in Neurological Malignancy: Shedding New Light on the Challenge of Resistance to AZD1152-HQPA.[Pubmed:25752998]
Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Apr;53(3):1808-1823.
Aurora kinase B (AURKB), a crucial regulator of malignant mitosis, is involved in chromosome segregation and cytokinesis. AZD1152-HQPA is a selective inhibitor for AURKB activity and currently bears clinical assessment for several malignancies. However, the effect of this drug still needs to be elucidated in neurological malignancies. In this study, we investigated the restrictive potentials of AZD1152-HQPA in U87MG and SK-N-MC. AZD1152-HQPA treatment resulted in growth arrest, modification of cell cycle, and inhibition of colony formation in both cell lines. Furthermore, lower concentrations of AZD1152-HQPA profoundly induced apoptosis in U87GM (p53/p73 wild type) cells in parallel with an upregulation of p53 and its target genes BAX, BAD, APAF1, and PUMA. But remarkably, SK-N-MC (p53/p73 double null) responded to AZD1152-HQPA at much higher concentrations with an upregulation of genes involved in cell cycle progression, induction of excessive endoreduplication, and polyploidy rather than apoptosis. Although SK-N-MC was resistant to AZD1152-HQPA, we did not find a mutation in the coding sequence of Aurora B gene or overexpressions of ABCG2 and ABCB1 as reported previously to be resistance mechanisms. However, our results suggest that p53/p73 status could be an important mechanism for the type of response and resistance of the tumor cells to AZD1152-HQPA. Collectively, inhibition of Aurora kinase B differentially induced cell death and polyploidy via DNA damage response pathways, depending on the status of p53/p73. We suggest p53/p73 could be a key regulator of sensitivity to AZD1152-HQPA and their status should be explored in clinical response to this ongoing drug in clinical trials.
[(14) C]-AZD1152 drug substance manufacture: challenges of an IV-infusion dosed human mass balance study in patients.[Pubmed:27169761]
J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2016 May 30;59(6):250-4.
[(14) C]-AZD1152 (barasertib) drug substance was prepared in order to support a hADME study that was to be dosed as an intravenous infusion to patients with acute myeloid leukaemia. A long patient recruitment time (1-2 years) was expected, and because of its limited stability several batches of [(14) C]-AZD1152 drug substance needed to be prepared in order to maintain a supply of [(14) C]-AZD1152 in the clinic over this period. A method was developed to purify the [(14) C]-AZD1152 to a GMP-like standard at high specific activity to provide material for each of these batches. This approach to the delivery of the drug substance was successful in supplying the study with radiolabelled drug for over 1 year until all patients had been recruited.
Barasertib (AZD1152), a Small Molecule Aurora B Inhibitor, Inhibits the Growth of SCLC Cell Lines In Vitro and In Vivo.[Pubmed:27496133]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Oct;15(10):2314-2322.
Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) cells have rapid proliferation, universal Rb inactivation, and high rates of MYC family amplification, making aurora kinase inhibition a natural target. Preclinical studies have demonstrated activity for Aurora A and pan-Aurora inhibitors with some relationship to MYC family expression. A clinical trial showed activity for an Aurora kinase A inhibitor, but no biomarkers were evaluated. We screened a panel of 23 SCLC lines with and without MYC family gene amplification or high MYC family gene expression for growth inhibition by the highly potent, selective aurora kinase B inhibitor barasertib. Nine of the SCLC lines were very sensitive to growth inhibition by barasertib, with IC50 values of <50 nmol/L and >75% growth inhibition at 100 nmol/L. Growth inhibition correlated with cMYC amplification (P = 0.018) and cMYC gene expression (P = 0.026). Sensitive cell lines were also enriched in a published MYC gene signature (P = 0.042). In vivo, barasertib inhibited the growth of xenografts established from an SCLC line that had high cMYC gene expression, no cMYC amplification, and was positive for the core MYC gene signature. Our studies suggest that SCLC tumors with cMYC amplification/high gene expression will frequently respond to Aurora B inhibitors and that clinical studies coupled with predictive biomarkers are indicated. Mol Cancer Ther; 15(10); 2314-22. (c)2016 AACR.


