AdonifolineCAS# 115712-88-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 115712-88-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 15736564 | Appearance | Cryst. |
| Formula | C18H23NO7 | M.Wt | 365.38 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
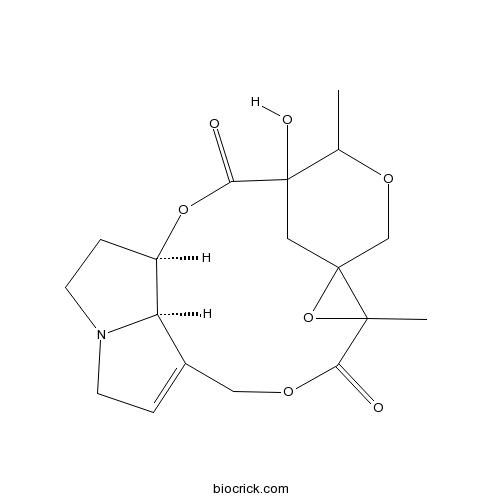
| Chemical Name | (1R,20R)-4-hydroxy-5,10-dimethyl-2,6,9,12-tetraoxa-17-azapentacyclo[12.5.1.14,8.08,10.017,20]henicos-14-ene-3,11-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC1C2(CC3(CO1)C(O3)(C(=O)OCC4=CCN5C4C(CC5)OC2=O)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MYOFCWPLRKBPJD-AQYQBICXSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H23NO7/c1-10-18(22)8-17(9-24-10)16(2,26-17)14(20)23-7-11-3-5-19-6-4-12(13(11)19)25-15(18)21/h3,10,12-13,22H,4-9H2,1-2H3/t10?,12-,13-,16?,17?,18?/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Adonifoline is a hepatotoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloid. |

Adonifoline Dilution Calculator

Adonifoline Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7369 mL | 13.6844 mL | 27.3688 mL | 54.7375 mL | 68.4219 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5474 mL | 2.7369 mL | 5.4738 mL | 10.9475 mL | 13.6844 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2737 mL | 1.3684 mL | 2.7369 mL | 5.4738 mL | 6.8422 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0547 mL | 0.2737 mL | 0.5474 mL | 1.0948 mL | 1.3684 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0274 mL | 0.1368 mL | 0.2737 mL | 0.5474 mL | 0.6842 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Daidzein dimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN6761
CAS No.:1157-39-7
- B2
Catalog No.:BCC7505
CAS No.:115687-05-3
- H-DL-Pro-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC3027
CAS No.:115630-49-4
- Cinnamyl caffeate
Catalog No.:BCN7721
CAS No.:115610-32-7
- Cinnamyl isoferulate
Catalog No.:BCN7718
CAS No.:115610-31-6
- Cinnamyl coumarate
Catalog No.:BCN7739
CAS No.:115610-30-5
- 4-Androstenediol
Catalog No.:BCC8692
CAS No.:1156-92-9
- 2'-Hydroxygenistein
Catalog No.:BCN6036
CAS No.:1156-78-1
- Marbofloxacin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4250
CAS No.:115551-26-3
- Marbofloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC2510
CAS No.:115550-35-1
- BI 224436
Catalog No.:BCC5531
CAS No.:1155419-89-8
- Fmoc-Cys(Trt)-Opfp
Catalog No.:BCC3480
CAS No.:115520-21-3
- 6'-O-beta-D-Glucosylgentiopicroside
Catalog No.:BCN2814
CAS No.:115713-06-9
- 1-O-galloyl-6-O-cinnamoylglucose
Catalog No.:BCN8264
CAS No.:115746-69-5
- Galanolactone
Catalog No.:BCN6037
CAS No.:115753-79-2
- 15,16-Dihydro-15-methoxy-16-oxohardwickiic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1612
CAS No.:115783-35-2
- ent-Atisane-3beta,16alpha,17-triol
Catalog No.:BCN6626
CAS No.:115783-44-3
- Tubeimoside II
Catalog No.:BCN2955
CAS No.:115810-12-3
- Tubeimoside III
Catalog No.:BCN2956
CAS No.:115810-13-4
- 2,7-Dideacetoxytaxinine J
Catalog No.:BCN7281
CAS No.:115810-14-5
- Salvianolic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN5376
CAS No.:115841-09-3
- Aurora A Inhibitor I
Catalog No.:BCC2182
CAS No.:1158838-45-9
- N1-Methoxymethyl picrinine
Catalog No.:BCN6038
CAS No.:1158845-78-3
- Tos-Arg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2873
CAS No.:1159-15-5
Glucuronidation, a new metabolic pathway for pyrrolizidine alkaloids.[Pubmed:20092275]
Chem Res Toxicol. 2010 Mar 15;23(3):591-9.
Pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) possess significant hepatotoxicity to humans and animals after metabolic activation by liver P450 enzymes. Metabolism pathways of PAs have been studied for several decades, including metabolic activation, hydroxylation, N-oxidation, and hydrolysis. However, the glucuronidation of intact PAs has not been investigated, although glucuronidation plays an important role in the elimination and detoxication of xenobiotics. In this study, PAs glucuronidation was investigated, and three important points were found. First, we demonstrated that senecionine (SEN)-a representative hepatotoxic PA-could be conjugated by glucuronic acid via an N-glucuronidation reaction catalyzed by uridine diphosphate glucuronosyl transferase in human liver microsomes. Second, glucuronidation of SEN was catalyzed not only by human but also other animal species and showed significant species differences. Rabbits, cattle, sheep, pigs, and humans showed the significantly higher glucuronidation activity than mice, rats, dogs, and guinea pigs on SEN. Kinetics of SEN glucuronidation in humans, pigs, and rabbits followed the one-site binding model of the Michaelis-Menten equation, while cattle and sheep followed the two-sites binding model of the Michaelis-Menten equation. Third, besides SEN, other hepatotoxic PAs including monocrotaline, Adonifoline, and isoline also underwent N-glucuronidation in humans and several animal species such as rabbits, cattle, sheep, and pigs.
Identification of metabolites of adonifoline, a hepatotoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloid, by liquid chromatography/tandem and high-resolution mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:19918941]
Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2009 Dec;23(24):3907-16.
Hepatotoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloid (HPA)-containing plants have always been a threat to human and livestock health worldwide. Adonifoline, a main HPA in Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don (Qianli guang), was used officially as an infusion in cases of oral and pharyngeal infections in China. In this study in vivo metabolism of Adonifoline was studied for the first time by identifying the metabolites of Adonifoline present in bile, urine and feces of rats using liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC/ESI-MS(n)) (ion trap) as well as liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC/ESI-HRMS) (quadrupole-time of flight). In total 19 metabolites were identified and, among them, retronecine-N-oxides were confirmed by matching their fragmentation patterns with their fully characterized synthetic compounds. These metabolites are all involved in both phase I and phase II metabolic processes and the principal in vivo metabolism pathways of Adonifoline were proposed.
The comparative pharmacokinetics of two pyrrolizidine alkaloids, senecionine and adonifoline, and their main metabolites in rats after intravenous and oral administration by UPLC/ESIMS.[Pubmed:21573843]
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011 Jul;401(1):275-87.
Pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) are considered to be one of the most hepatotoxic groups of compounds of plant origin and are present in about 3% of the world's flowering plants. Most PAs represent a considerable health hazard to both livestock and humans through the consumption of plants and PA-contaminated products such as milk, honey, herbal teas, and medicines. This study determined the differences in the in vivo pharmacokinetic behavior of senecionine (SEN), Adonifoline (ADO), and their main metabolites in rats after intravenous administration and oral administration by ultraperformance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Upon intravenous administration and oral administration of SEN and ADO, significant differences in pharmacokinetics were observed, with the SEN and ADO being absorbed fast with lower bioavailability and being quickly metabolized to PA N-oxides and hydroxylation products of PAs or their N-oxides. It could be seen that the plasma concentration ratio of senecionine N-oxide (SEN-NO) to SEN (C (SEN-NO)/C (SEN)) was significantly larger than that for Adonifoline N-oxide (ADO-NO) and ADO (C (ADO-NO)/C (ADO)) (P < 0.001) for both dosing routes in rats. The high N-oxygenation activity and extensive toxicity of SEN, compared with ADO, in rats raised the question of whether or not the higher metabolic rate of SEN in rats in vivo was related to its potent toxicity. The toxicity of SEN-NO and ADO-NO needs to be evaluated further and compared in vitro/in vivo. This study was most helpful for interpreting the metabolism of metabolic bioactivation and detoxication, and toxicity differences among SEN, ADO and other PAs.


