Cinnamyl caffeateCAS# 115610-32-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 115610-32-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11380911 | Appearance | Powder |
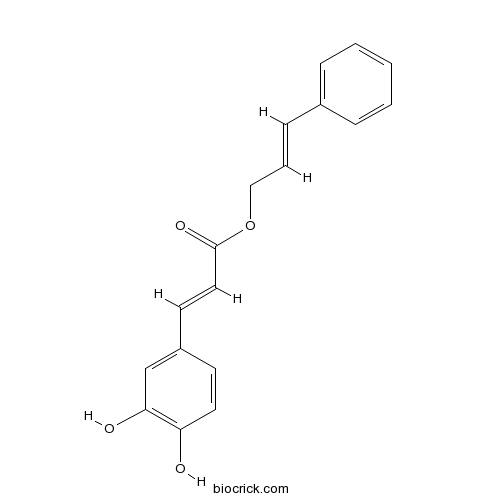
| Formula | C18H16O4 | M.Wt | 296.31 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(E)-3-phenylprop-2-enyl] (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C=CCOC(=O)C=CC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GRZQNEYQRVPNRY-WUZDHUPESA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H16O4/c19-16-10-8-15(13-17(16)20)9-11-18(21)22-12-4-7-14-5-2-1-3-6-14/h1-11,13,19-20H,12H2/b7-4+,11-9+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Cinnamyl caffeate has cardiovascular protective effects, it can increase H9c2 cellular antioxidant potential, decrease intracellular calcium ion ([Ca2+]i) level, and prevent cell apoptosis. 2. Cinnamyl caffeate possesses potent NO inhibitory activity with the IC(50) value of 9.53 microM. 3. Cinnamyl caffeate possesses potent antiproliferative activity with the EC(50) value of 0.114 microM, toward colon 26-L5 carcinoma. |
| Targets | Calcium Channel | NO |

Cinnamyl caffeate Dilution Calculator

Cinnamyl caffeate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3748 mL | 16.8742 mL | 33.7484 mL | 67.4969 mL | 84.3711 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.675 mL | 3.3748 mL | 6.7497 mL | 13.4994 mL | 16.8742 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3375 mL | 1.6874 mL | 3.3748 mL | 6.7497 mL | 8.4371 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0675 mL | 0.3375 mL | 0.675 mL | 1.3499 mL | 1.6874 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0337 mL | 0.1687 mL | 0.3375 mL | 0.675 mL | 0.8437 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Cinnamyl isoferulate
Catalog No.:BCN7718
CAS No.:115610-31-6
- Cinnamyl coumarate
Catalog No.:BCN7739
CAS No.:115610-30-5
- 4-Androstenediol
Catalog No.:BCC8692
CAS No.:1156-92-9
- 2'-Hydroxygenistein
Catalog No.:BCN6036
CAS No.:1156-78-1
- Marbofloxacin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4250
CAS No.:115551-26-3
- Marbofloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC2510
CAS No.:115550-35-1
- BI 224436
Catalog No.:BCC5531
CAS No.:1155419-89-8
- Fmoc-Cys(Trt)-Opfp
Catalog No.:BCC3480
CAS No.:115520-21-3
- (2-Amino-1-hydroxyethyl)phosphonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1613
CAS No.:115511-00-7
- H-Lys(Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2986
CAS No.:1155-64-2
- Z-Glu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2781
CAS No.:1155-62-0
- 5,6,7,7a-Tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-2(4H)-one hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8721
CAS No.:115473-15-9
- H-DL-Pro-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC3027
CAS No.:115630-49-4
- B2
Catalog No.:BCC7505
CAS No.:115687-05-3
- Daidzein dimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN6761
CAS No.:1157-39-7
- Adonifoline
Catalog No.:BCN2056
CAS No.:115712-88-4
- 6'-O-beta-D-Glucosylgentiopicroside
Catalog No.:BCN2814
CAS No.:115713-06-9
- 1-O-galloyl-6-O-cinnamoylglucose
Catalog No.:BCN8264
CAS No.:115746-69-5
- Galanolactone
Catalog No.:BCN6037
CAS No.:115753-79-2
- 15,16-Dihydro-15-methoxy-16-oxohardwickiic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1612
CAS No.:115783-35-2
- ent-Atisane-3beta,16alpha,17-triol
Catalog No.:BCN6626
CAS No.:115783-44-3
- Tubeimoside II
Catalog No.:BCN2955
CAS No.:115810-12-3
- Tubeimoside III
Catalog No.:BCN2956
CAS No.:115810-13-4
- 2,7-Dideacetoxytaxinine J
Catalog No.:BCN7281
CAS No.:115810-14-5
Potential Protective Effects of Bioactive Constituents from Chinese Propolis against Acute Oxidative Stress Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide in Cardiac H9c2 Cells.[Pubmed:28337227]
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:7074147.
Chinese propolis (CP) is known as a health food but its beneficial effects in protecting cardiomyocytes remain elusive. Here, we investigated the effects of CP and its active compounds on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) induced rats cardiomyocytes (H9c2) oxidative injury. Cell viability decreases induced by H2O2 were mitigated by different CP extracts using various solvents. From these active fractions, six active compounds were separated and identified. Among tested isolated compound, the cytoprotective activities of three caffeates, caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), benzyl caffeate (BZC), and Cinnamyl caffeate (CNC), exerted stronger effects than chrysin, pinobanksin, and 3,4-dimethoxycinnamic acid (DMCA). These three caffeates also increased H9c2 cellular antioxidant potential, decreased intracellular calcium ion ([Ca(2+)]i) level, and prevented cell apoptosis. Overall, the cardiovascular protective effects of the CP might be attributed to its caffeates constituents (CAPE, BZC, and CNC) and provide evidence for its usage in complementary and alternative medicine.
Antiproliferative activity of the Netherlands propolis and its active principles in cancer cell lines.[Pubmed:11891088]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2002 Apr;80(1):67-73.
The MeOH extract of the Netherlands propolis showed promising antiproliferative activity toward highly liver-metastatic murine colon 26-L5 carcinoma with an EC(50) value of 3.5 microg/ml. Further, antiproliferative activity-guided purification of the MeOH extract led us to isolate four flavonoids (1-4), seven cinnamic acid derivatives (5-11) and two new glycerol derivatives (12, 13), whose structures were elucidated on the basis of spectral analysis. The isolated compounds were tested for their antiproliferative activity against murine colon 26-L5, murine B16-BL6 melanoma, human HT-1080 fibrosarcoma and human lung A549 adenocarcinoma cell lines. The benzyl (9), phenethyl (10) and Cinnamyl caffeates (11) possessed potent antiproliferative activities with EC(50) values of 0.288, 1.76 and 0.114 microM, respectively, toward colon 26-L5 carcinoma. These caffeates were considered to be active constituents of the Netherlands propolis in their antiproliferative activity. The antioxidative activity of these caffeates may play an important role in their antiproliferative activities.
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) analogues: potent nitric oxide inhibitors from the Netherlands propolis.[Pubmed:12673030]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2003 Apr;26(4):487-91.
The MeOH and water extracts of the Netherlands propolis were tested for their inhibitory activity toward nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated murine macrophage-like J774.1 cells. Both of the extract possessed significant NO inhibitory activity with IC(50) values of 23.8 and 51.5 microg/ml, respectively. Then 13 phenolic compounds obtained from the MeOH extract showing stronger NO inhibition were examined on their NO inhibitory activities. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) analogues, i.e., benzyl caffeate, CAPE and Cinnamyl caffeate, possessed most potent NO inhibitory activities with IC(50) values of 13.8, 7.64 and 9.53 microM, respectively, which were two- to four-fold stronger than the positive control N(G)-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA; IC(50), 32.9 microM). Further study on the synthetic analogues of CAPE revealed that both of 3-phenylpropyl caffeate (18; IC(50), 7.34 microM) and 4-phenylbutyl caffeate (19; IC(50), 6.77 microM) possessed stronger NO inhibitory activity than CAPE (10) and that elongation of alkyl side chain of alcoholic parts of caffeic acid esters enhance the NO inhibitory activity. In addition, it was found that CAPE analogues having longer carbon chain (>C(5)) in alcoholic part showed toxic effects toward J774.1 cells. This NO inhibitory effect may directly correlate with antiinflammatory properties of the Netherlands propolis.


