Geranium sibiricum
Geranium sibiricum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Geranium sibiricum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2322
Corilagin23094-69-1
Instructions
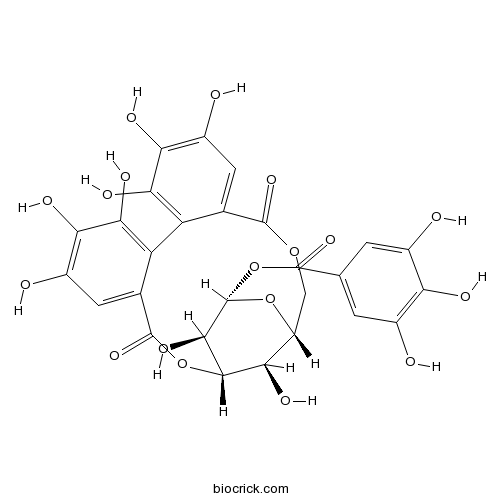
-
BCN2402
Geraniin60976-49-0
Instructions

-
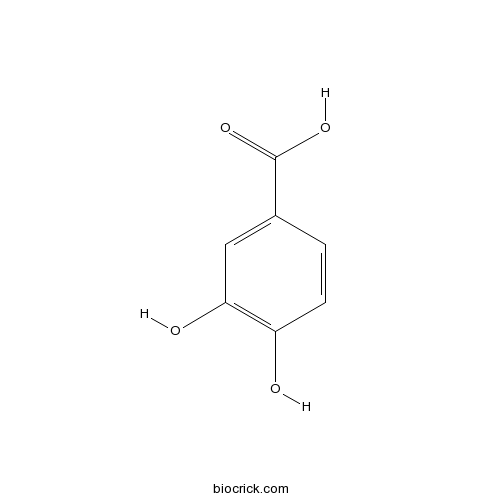
BCN4537
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
Geraniin inhibits migration and invasion of human osteosarcoma cancer cells through regulation of PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways.[Pubmed: 28704237]
Geraniin, an active compound isolated from Geranium sibiricum, was found to inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis of tumor cells. However, the antimetastatic effects of geraniin remain elusive. Our study found the potential antitumor mechanisms of geraniin through inhibiting the migration and invasion of human osteosarcoma U2OS cells. The western blot, gelatin zymography, and reversed transcription-PCR analysis showed that geraniin suppressed matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) expression in a concentration-dependent manner. Geraniin potently suppressed the phosphorylation of extracellular signal regulating kinase (ERK)1/2, phosphatidylinositide-3-kinase (PI3K), and Akt, but did not affect phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Furthermore, when transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) was used as an agonist, geraniin inhibited TGF-β1-mediated cell invasion and upregulation of MMP-9. These results suggested that geraniin inhibited U2OS cell migration and invasion by reducing the expression of MMP-9 through the PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways.
Geraniin suppresses tumor cell growth and triggers apoptosis in human glioma via inhibition of STAT3 signaling.[Pubmed: 28374108]
Natural phytochemicals are attracting increasing interest as anticancer agents. The aim of this study is to evaluate the therapeutic potential of geraniin, a major ellagitannin extracted from Geranium sibiricum L., in human glioma. Human U87 and LN229 glioma cells were treated with different concentrations of geraniin, and cell viability, apoptosis, and gene expression were assessed. The involvement of STAT3 signaling in the action of geraniin was examined. We found that geraniin treatment for 48 h significantly (P < 0.05) impaired the phosphorylation of STAT3 and reduced the expression of downstream target genes Bcl-xL, Mcl-1, Bcl-2, and cyclin D1. Exposure to geraniin led to a concentration-dependent decline in cell viability and increase in apoptosis in glioma cells, but had no significant impact on the viability of normal human astrocytes. Measurement of caspase-3 activity showed that geraniin-treated U87 and LN229 cells showed a 1.8-2.5-fold higher caspase-3 activity than control cells. Overexpression of constitutively active STAT3 significantly (P < 0.05) reversed geraniin-mediated growth suppression and apoptosis, which was accompanied by restoration of Bcl-xL, Mcl-1, Bcl-2, and cyclin D1 expression. In an xenograft tumor mouse model, geraniin treatment significantly retarded tumor growth and induced apoptosis. Western blot analysis confirmed the suppression of STAT3 phosphorylation in glioma xenograft tumors by geraniin. Taken together, these data suggest that geraniin exerts growth-suppressive and pro-apoptotic effects on glioma cells via inhibition of STAT3 signaling and may have therapeutic benefits in malignant gliomas.
Hair growth-promoting effect of Geranium sibiricum extract in human dermal papilla cells and C57BL/6 mice.[Pubmed: 28193226]
Geranium sibiricum L. has been used as a medicinal plant to treat diarrhea, bacterial infection, and cancer in Bulgaria, Peru, and Korea. However, its hair growth-promoting effect was not investigated so far. This study examined the effects of Geranium sibiricum L. extract (GSE) on hair growth, using in vitro and in vivo models.
Inhibitory effects of geraniin on LPS-induced inflammation via regulating NF-κB and Nrf2 pathways in RAW 264.7 cells.[Pubmed: 27181634]
Geraniin, a major polyphenolic compound of Geranium sibiricum L, has long been used as an important Chinese herbal medicine for the treatment of a variety of inflammatory pathologies. However, the underlying anti-inflammatory molecular mechanisms of this compound are not clear. The aim of the present study was to investigate the anti-inflammatory activities of geraniin and elucidate the underlying mechanisms. The anti-inflammatory effects of geraniin were studied by using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Geraniin suppressed the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression, and inhibited reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Subsequent studies demonstrated that geraniin effectively reduced production of NO and pro-inflammatory cytokines. These effects were mediated by impaired translocation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB and inhibition of the phosphorylation of Akt in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Furthermore, geraniin induced heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression via activation of transcription factor Nrf2. This study gives scientific evidence that geraniin inhibits the LPS-induced expression of inflammatory mediators via suppression of Akt-mediated NF-κB pathway as well as up-regulation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, indicating that geraniin has a potential application in inflammatory conditions.
Geraniin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice.[Pubmed: 27043748]
Geraniin, an active compound isolated from Geranium sibiricum, has been reported to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. The aim of this study was to investigate the protective effects of geraniin against cisplatin (CP)-induced kidney injury in mice. Geraniin was administrated for three consecutive days following CP (20 mg/kg) injection. The results showed that geraniin inhibited CP-induced kidney histopathologic changes, MDA, inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) production in kidney tissues. Geraniin also inhibited CP-induced blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine production. Meanwhile, the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX) decreased by CP were reversed by the treatment of geraniin. In addition, geraniin significantly inhibited CP-induced NF-κB activation in kidney tissues. Treatment of geraniin dosedependently upregulated the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1. The anticancer effects of CP were not affected by the treatment of geraniin. In conclusion, these results indicated that geraniin protected against CP-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammatory response.
Geraniin exerts cytoprotective effect against cellular oxidative stress by upregulation of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant enzyme expression via PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2 pathway.[Pubmed: 25917210]
Geraniin, an active compound with remarkable antioxidant activity, was isolated from Geranium sibiricum. The present study aimed to investigate whether geraniin has the ability to activate Nrf2, induce antioxidant enzyme expression and protect cells from oxidative damage.
Antioxidant activities and xanthine oxidase inhibitory effects of extracts and main polyphenolic compounds obtained from Geranium sibiricum L.[Pubmed: 20205393]
The antioxidant capacity and xanthine oxidase inhibitory effects of extracts and main polyphenolic compounds of Geranium sibiricum were studied in the present work. The antioxidant capacity was evaluated by ferric reducing antioxidant power, 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging, superoxide radical scavenging, nitric oxide scavenging, beta-carotene-linoleic acid bleaching, and reducing power assays. Among the extracts and four fractions, the ethyl acetate fraction showed the highest phenolic content (425.36 +/- 9.70 mg of gallic acid equivalent/g extracts) and the best antioxidant activity. The IC(50) values of the ethyl acetate fraction were 0.93, 3.32, 2.06, 2.66, and 1.64 microg/mL in the DPPH radical scavenging, superoxide radical scavenging, nitric oxide scavenging, beta-carotene-linoleic acid bleaching, and reducing power assays, respectively. Of the polyphenolic compounds separated from the ethyl acetate fraction, geraniin showed a higher activity than corilagin and gallic acid. The IC(50) values ranged from 0.87 to 2.53 microM, which were even lower than the positive control (except for allopurinol). All test samples except for the petroleum ether fraction showed xanthine oxidase inhibitory effects. We conclude that G. sibiricum represents a valuable natural antioxidant source and is potentially applicable in the healthy food industry.
Anti-inflammatory activity of ethanol extract from Geranium sibiricum Linne.[Pubmed: 19683044]
Geranium sibiricum (Geraniaceae) Linne (GSL) is used to heal various disorders of the diarrhea and the intestinal inflammation as an herbal agent in East Asia.
Antioxidative activity of glycoprotein isolated from Geranium sibiricum Linne.[Pubmed: 19296378]
Glycoprotein from Geranium sibiricum Linne (GSL) with 18 kDa was isolated and it consists of carbohydrate moiety (10.45%) and protein moiety (89.55%). The GSL glycoprotein was characterised by its radical scavenging activity under various experimental conditions. When GSL glycoprotein was treated with deactivation agents (pronase E or NaIO(4)), its scavenging activity decreased in both cases. It has optimal and maximal activity in acidic, neutral pH (up to pH 9), and up to 85 degrees C. Also, its activity reduced in the case of Ca(2+) and Mn(2+), with the exception of the Mg(2+) case. Its activity in the presence of Mn(2+) declined more than in the case of the Ca(2+). Also, GSL glycoprotein (500 microg mL(-1)) has antioxidative effects on hydroxyl and superoxide anion radicals in cell-free systems, and GSL glycoprotein (200 microg mL(-1)) significantly protected from cytotoxicity in the GO (100 mU mL(-1))-treated Chang liver cells for 4 h.


