Glechoma longituba
Glechoma longituba
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Glechoma longituba
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
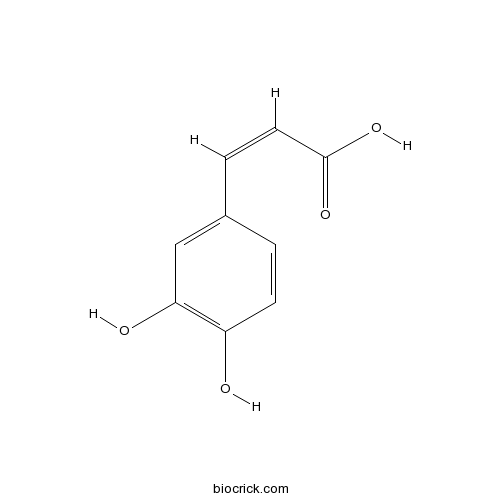
BCN5979
Caffeic acid331-39-5
Instructions
-
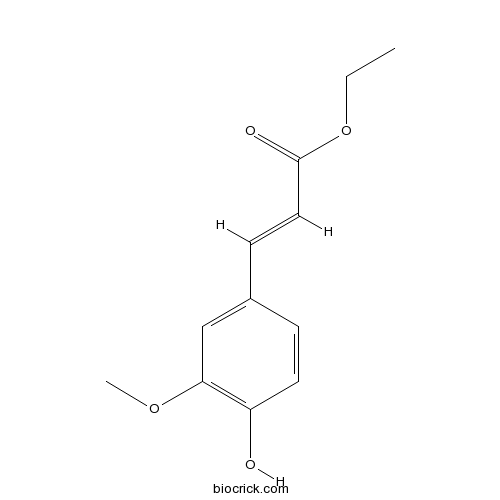
BCN1257
Ethyl ferulate4046-02-0
Instructions
-
BCN5488
Genkwanin437-64-9
Instructions

-
BCN5567
Chrysophanol481-74-3
Instructions

-
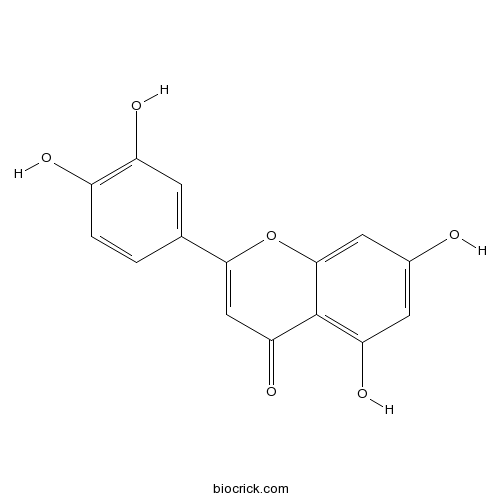
BCN5600
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
-
BCN8390
Myristic acid544-63-8
Instructions

Apigenin-7-diglucuronide protects retinas against bright light-induced photoreceptor degeneration through the inhibition of retinal oxidative stress and inflammation.[Pubmed: 28336272]
Vision impairment in retinal degenerative diseases such as age-related macular degeneration is primarily associated with photoreceptor degeneration, in which oxidative stress and inflammatory responses are mechanistically involved as central players. Therapies with photoreceptor protective properties remain to be developed. Apigenin-7-diglucuronide (A7DG), a flavonoid glycoside, is present in an assortment of medicinal plants with anti-inflammatory or ant-oxidant activities. However, the pharmacological significance of A7DG remains unknown in vivo. The current study isolated A7DG from Glechoma longituba (Nakai) Kuprian and investigated the retinal protective effect A7DG in mice characterized by bright light-induced photoreceptor degeneration. The results showed that A7DG treatment led to remarkable photoreceptor protection in bright light-exposed BALB/c mice. Moreover, A7DG treatment alleviated photoreceptor apoptosis, mitigated oxidative stress, suppressed reactive gliosis and microglial activation and attenuated the expression of proinflammatory genes in bright light-exposed retinas. The results demonstrated for the first time remarkable photoreceptor protective activities of A7DG in vivo. Inhibition of bright light-induced retinal oxidative stress and retinal inflammatory responses was associated with the retinal protection conferred by A7DG. The work here warrants further evaluation of A7DG as a pharmacological candidate for the treatment of vision-threatening retinal degenerative disorders. Moreover, given the general implication of oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of neurodegeneration, A7DG could be further tested for the treatment of other neurodegenerative disorders.
Clonal integration ameliorates the carbon accumulation capacity of a stoloniferous herb, Glechoma longituba, growing in heterogenous light conditions by facilitating nitrogen assimilation in the rhizosphere.[Pubmed: 25429006]
Enhanced availability of photosynthates increases nitrogen (N) mineralization and nitrification in the rhizosphere via rhizodeposition from plant roots. Under heterogeneous light conditions, photosynthates supplied by exposed ramets may promote N assimilation in the rhizosphere of shaded, connected ramets. This study was conducted to test this hypothesis.
Effects of clonal integration on microbial community composition and processes in the rhizosphere of the stoloniferous herb Glechoma longituba (Nakai) Kuprian.[Pubmed: 25243590]
The effects of rhizodeposition on soil C and N availabilities lead to substantial changes of microbial community composition and processes in the rhizosphere of plants. Under heterogeneous light, photosynthates can be translocated or shared between exposed and shaded ramets by clonal integration. Clonal integration may enhance the rhizodeposition of the shaded ramets, which further influences nutrient recycling in their rhizosphere. To test the hypothesis, we conducted a pot experiment by the stoloniferous herb Glechoma longituba subjected to heterogeneous light. Microbial biomass and community composition in the rhizosphere of shaded offspring ramets, assessed by phospholipid fatty acids (PLFAs) analysis, were markedly altered by clonal integration. Clonal integration positively affected C, N availabilities, invertase and urease activities, N mineralization (Nmin) and nitrification rates (Nnitri) in the rhizosphere of shaded offspring ramets. However, an opposite pattern was also observed in phenoloxidase (POXase) and peroxidase (PODase) activities. Our results demonstrated that clonal integration facilitated N assimilation and uptake in the rhizosphere of shaded offspring ramets. The experiment provides insights into the mechanism of nutrient recycling mediated by clonal integration.
[Chemical constituents from Glechoma longituba].[Pubmed: 25204149]
Fourteen compounds were obtained from Glechoma longituba by the chromatographic methods of silica gel, ODS, Sephadex LH-20 and preparative of HPLC. According to physicochemical properties and spectral data, these compounds were identified as stilbostemin B (1), trilepisiumic acid (2), 3, 4-dihydroxyphenyl ethanol ketone (3), bergeninmonohydrate (4), oresbiusin A (5), norbergenin (6), stilbostemin D (7), ehretioside B (8), ethyl ferulate (9), E-p-hydroxy-cinnamic acid (10), methyl gallate (11), protocatechuic acid (12), 4'-Hydroxyacetophenone (13), and E-3-2,4-dihydroxyphenyl-2-acrylic acid (14). Among them, compounds 1-10, 13 and 14 were isolated from this plant for the first time.
Simultaneous determination of four bioactive compounds in Glechoma longituba extracts by high performance liquid chromatography.[Pubmed: 23930004]
Glechoma longituba, one of the long-practiced traditional Chinese medicines in history, is still commonly used nowadays in oriental countries. Previous study indicates that phenolic acid and flavonoids have considerable bioactivities, thus, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, apigenin-7-O-glucoside and rosmarinic acid were chosen as the marker components for the simultaneous determination to evaluate the intrinsic quality of G. longituba, and related high performance liquid chromatographic method was urgent to established.
[Study on preparation of total flavones in Glechoma longituba sustained-release tablets and its in vitro release].[Pubmed: 23750420]
To study the preparation of total flavones in Glechoma longituba sustained-release tablets and evaluate its releasing features in vitro.


