Gynura bicolor
Gynura bicolor
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Gynura bicolor
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
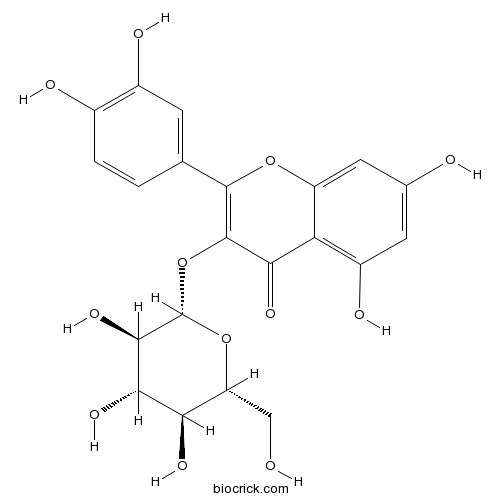
BCN5569
Isoquercitrin482-35-9
Instructions
Variation of cassiicolin genes among Chinese isolates of Corynespora cassiicola.[Pubmed: 30054815]
Corynespora cassiicola is a species of fungus that is a plant pathogen of many agricultural crop plants, including severe target spot disease on cucumber. Cassiicolin is an important effector of pathogenicity of this fungus. In this study, we collected 141 Corynespora isolates from eighteen hosts, and the casscolin gene was detected in 82 C. cassiicola strains. The deduced protein sequences revealed that 72 isolates contained the Cas2 gene, two strains from Gynura bicolor harboured the Cas2.2 gene, and 59 isolates without a cassiicolin gene were classified as Cas0. Phylogenetic analyses was performed for the 141 isolates using four loci (ITS, ga4, caa5, and act1) and revealed two genetic clusters. Cluster A is composed of four subclades: subcluster A1 includes all Cas2 isolates plus 18 Cas0 strains, subcluster A2 includes the eight Cas5 isolates and one Cas0 isolate, and subclusters A3 and A4 contain Cas0 strains. Cluster B consists of 21 Cas0 isolates. Twenty-two C. cassiicola strains from different toxin classes showed varying degrees of virulence against cucumber. Cas0 or Cas2 strains induced diverse responses on cucumber, from no symptoms to symptoms of moderate or severe infection, but all Cas5 isolates exhibited avirulence on cucumber.
[Effects of light quality on growth, secondary metabolites, and oxidative stress tolerance of Gynura bicolor.][Pubmed: 29696855]
None
Detection and Toxicity Evaluation of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Medicinal Plants Gynura bicolor and Gynura divaricata Collected from Different Chinese Locations.[Pubmed: 27623358]
Two edible plants in Southeast Asia, Gynura bicolor and G. divaricata, are not only known to be nutritive but also useful as medicinal herbs. Previous phytochemical investigation of Gynura species showed the presence of hepatotoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs), indicating the toxic risk of using these two plants. The present study was designed to analyze the distribution of PA components and tried to evaluate the preliminary toxicity of these two Gynura species. Eight samples of G. bicolor and G. divaricata from five different Chinese locations were collected and their specific PAs were qualitatively characterized by applying an UPLC/MS/MS spectrometry method. Using a pre-column derivatization HPLC method, the total retronecine ester-type PAs in their alkaloids extracts were quantitatively estimated as well. Finally, their genotoxicity was investigated with an effective high-throughput screening method referred to as Vitotox™ test and their potential cytotoxicity was tested on HepG2 cells. It was found that different types of PAs were widely present in Gynura species collected from south of China. Among them, no significant genotoxic effects were detected with serial concentrations through the present in vitro assay. However, the cytotoxicity assay of Gynura plants collected from Jiangsu displayed weak activity at the concentration of 100 mg/ml. It is important to note that this research validates in part the indication that the use of Gynura species requires caution.
Chemical composition, aroma evaluation, and inhibitory activity towards acetylcholinesterase of essential oils from Gynura bicolor DC.[Pubmed: 26758617]
The compositions of the essential oils obtained from leaves and stems of Gynura bicolor DC. were analyzed by GC-MS. One hundred eight components of these oils were identified. (E)-β-caryophyllene (31.42 %), α-pinene (17.11 %), and bicyclogermacrene (8.09 %) were found to be the main components of the leaf oil, while α-pinene (61.42 %), β-pinene (14.39 %), and myrcene (5.10 %) were the major constituents of the stem oil. We found 73 previously unidentified components in these oils from G. bicolor. The oils were also subjected to odor evaluation. Eleven and 12 aroma-active compounds were detected in the leaf and stem oils, respectively. The abilities of these oils to inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity were determined. The sesquiterpenoids in the oils were found to inhibit AChE activity more strongly than the monoterpenoids in the oils did. It was suggested that the three main components in each essential oil act synergistically against AChE activity. These results show that the essential oils obtained from G. bicolor are a good dietary source of AChE activity inhibition.
Elevated CO2 enhances photosynthetic efficiency, ion uptake and antioxidant activity of Gynura bicolor DC. grown in a porous-tube nutrient delivery system under simulated microgravity.[Pubmed: 26669703]
It is well known that plants can grow under space conditions, however, perturbations of many biological phenomena have been highlighted due to the effect of altered gravity and its possible interaction with other factors (e.g., CO2 , ion radiation, etc. Our aim was to test whether elevated CO2 could provide 'protection' to Gynura bicolor against the damaging effects of simulated microgravity (SM) on photosynthesis, ion uptake and antioxidant activity. As compared to G. bicolor grown in ambient CO2 with no SM (ACO2 ), growth and yield of the plants increased under elevated ambient CO2 with no SM (ECO2 ) and decreased under ACO2 +SM, whereas there was no significant effect on ECO2 +SM. Reductions in the content of Chl a, carotenoids and Chl a+b were 17.9%, 20.7% and 17.9% under ACO2 +SM, respectively, but under ECO2 there was a significant effect on all photosynthetic pigments except Chl b, compared to ACO2 . Photosynthesis was improved under ECO2 with SM and such an improvement was associated with improved water use efficiency and instantaneous carboxylation efficiency. Furthermore, SM caused a reduction in ion absorption rate, except for Ca(2+) , while ECO2 increased the uptake rate. Finally, the activity of SOD, POD and the content of MDA and H2 O2 were enhanced under SM treatments and were highest in ACO2 +SM. In contrast, T-AOC activity and GSH content significantly declined in ACO2 +SM compared to other treatments. These results suggest that ACO2 is not sufficient to counteract SM impact, but the increase is usually caused by improvement in CO2 nutrition in ECO2 +SM in comparison with ACO2 +SM.
Antioxidant Potential in Different Parts and Callus of Gynura procumbens and Different Parts of Gynura bicolor.[Pubmed: 26491654]
Plants from Gynura family was used in this study, namely, Gynura procumbens and Gynura bicolor. Gynura procumbens is well known for its various medicinal properties such as antihyperglycaemic, antihyperlipidaemic, and antiulcerogenic; meanwhile, G. bicolor remains unexploited. Several nonenzymatic antioxidants methods were utilized to study the antioxidant capacity, which include ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging assay, total flavonoid content, total phenolic content, and ascorbic acid content determination. DPPH assay reveals G. procumbens shoot as the lowest (66.885%) and G. procumbens root as the highest (93.499%) DPPH radical inhibitor. In FRAP assay, reducing power was not detected in G. procumbens leaf callus (0.000 TEAC mg/g FW) whereby G. procumbens root exhibits the highest (1.103 TEAC mg/g FW) ferric reducing power. Total phenolic content and total flavonoid content exhibited similar trend for both the intact plants analysed. In all antioxidant assays, G. procumbens callus culture exhibits very low antioxidant activity. However, G. procumbens root exhibited highest phenolic content, flavonoid content, and ascorbic acid content with 4.957 TEAC mg/g FW, 543.529 QE µg/g FW, and 54.723 µg/g FW, respectively. This study reveals that G. procumbens root extract is a good source of natural antioxidant.
Effects of extracts from Gynura bicolor (Roxb. & Willd.) DC. on iron bioavailability in rats.[Pubmed: 28911699]
Gynura bicolor (Roxb. & Willd.) DC. is widely distributed in certain areas of Asia and is very popular in vegetarian cuisine in Taiwan. This study investigates the effects of G. bicolor extracts with different polarities of 80 mg/kg body weight (BW) G. bicolor alcohol extract, 80 mg/kg BW G. bicolor water extract, and 80 mg/kg BW G. bicolor ether extract on Fe bioavailability using the hemoglobin repletion efficiency assay. Wistar rats were assigned to five groups: a group receiving an iron-deficient (ID) diet; a group receiving an ID diet supplemented with ferrous sulfate (20 mg Fe/kg BW); and three groups receiving ID diets supplemented with ferrous sulfate and one of G. bicolor alcohol extract, G. bicolor water extract, or G. bicolor water extract. The results indicated that the levels of hemoglobin, serum iron, serum ferritin, liver ferritin, hemoglobin regeneration efficiency, relative biological value, and hepcidin all were significantly higher than those of the ID diet group. Besides, the iron transporter divalent metal transporter-1 was significantly reduced, but iron release protein expression of ferroportin was significantly increased. It was concluded that G. bicolor extracts may promote iron bioavailability and regulate the expressions of divalent metal transporter-1 and ferroportin.
Phytochemical investigation of Gynura bicolor leaves and cytotoxicity evaluation of the chemical constituents against HCT 116 cells.[Pubmed: 25738869]
Gynura bicolor (Compositae) is a popular vegetable in Asia and believed to confer a wide range of benefits including anti-cancer. Our previous findings showed that the ethyl acetate extract of G. bicolor possessed cytotoxicity and induced apoptotic and necrotic cell death in human colon carcinoma cells (HCT 116). A combination of column chromatography had been used to purify chemical constituents from the ethyl acetate and water extract of G. bicolor leaves. Eight chemical constituents 5-p-trans-coumaroylquinic acid (I), 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (II), rutin (III), kampferol-3-O-rutinoside (IV), 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (V), kampferol-3-O-glucoside (VI), guanosine (VII) and chlorogenic acid (VIII) were isolated from G. bicolor grown in Malaysia. To our best knowledge, all chemical constituents were isolated for the first time from G. bicolor leaves except rutin (III). 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (V), guanosine (VII) and chlorogenic acid (VIII) demonstrated selective cytotoxicity (selective index>3) against HCT 116 cancer cells compared to CCD-18Co human normal colon cells.


