IsoquercitrinCAS# 482-35-9 |
- Hyperoside
Catalog No.:BCN5570
CAS No.:482-36-0
Quality Control & MSDS
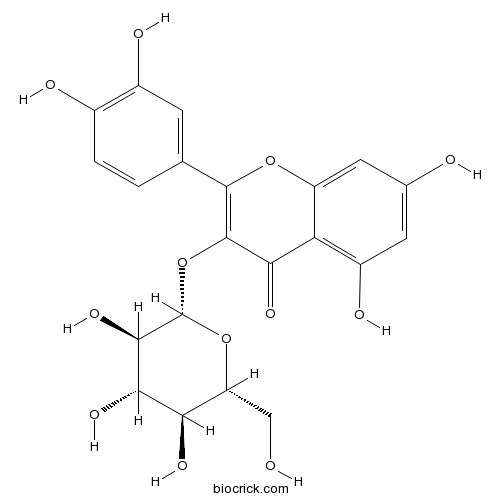
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 482-35-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5280804 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C21H20O12 | M.Wt | 464.4 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 21637-25-2;Quercitin-3'-O-glucofuranoside | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol and methanol; slightly soluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-3-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1C2=C(C(=O)C3=C(C=C(C=C3O2)O)O)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OVSQVDMCBVZWGM-QSOFNFLRSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H20O12/c22-6-13-15(27)17(29)18(30)21(32-13)33-20-16(28)14-11(26)4-8(23)5-12(14)31-19(20)7-1-2-9(24)10(25)3-7/h1-5,13,15,17-18,21-27,29-30H,6H2/t13-,15-,17+,18-,21+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Isoquercitrin has anti-tumoral, antihypertensive, anti-osteoporosis, anti-allergy, anti-inflammatory, and antiasthmatic activities, it also may be as a potential therapeutic agent against neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. Isoquercitrin is an inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin that acts downstream of the β-catenin nuclear translocation; it is also a potential stimulator of bone mineralization used for prophylaxis of osteoporotic disorders. Isoquercitrin inhibited carbachol and leukotriene D4 -induced contraction in guinea-pig airways, and it induced hypotension in rats is an event dependent on the inhibition of angiotensin II generation by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). |
| Targets | Caspase | ERK | JNK | p38MAPK | PKC | Wnt/β-catenin | RUNX2 | ATF6 | IL Receptor |
| In vitro | Isoquercitrin and polyphosphate co-enhance mineralization of human osteoblast-like SaOS-2 cells via separate activation of two RUNX2 cofactors AFT6 and Ets1.[Pubmed: 24726443]Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Jun 1;89(3):413-21.Isoquercitrin, a dietary phytoestrogen, is a potential stimulator of bone mineralization used for prophylaxis of osteoporotic disorders.
Isoquercitrin inhibits the progression of pancreatic cancer in vivo and in vitro by regulating opioid receptors and the mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathway.[Pubmed: 25434366]Oncol Rep. 2015 Feb;33(2):840-8.Pancreatic cancer is a common malignant tumour that affects individuals worldwide. In recent years, the incidence and mortality rates of pancreatic cancer have continuously increased. Currently, the primary clinical treatment methods for pancreatic cancer include surgical resection, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. However, these treatment methods rarely produce satisfactory therapeutic outcomes. Extensive research has also proven that the effective components of several traditional Chinese medicines, particularly flavonoids extracted from plants, have significant antitumour effects. Isoquercitrin, which is one of the flavonoids found in Bidens pilosa extracts, has a significant antitumour effect.
However, the antitumour effect of Isoquercitrin and its mechanism of action remain unclear.
|
| In vivo | Isoquercitrin from Argemone platyceras inhibits carbachol and leukotriene D4-induced contraction in guinea-pig airways.[Pubmed: 16202993]Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Oct 17;522(1-3):108-15.Argemone platyceras is used in Mexico as a remedy for cough, bronchitis and pneumonia. The present study was performed to investigate the pharmacological anti-asthmatic properties of Argemone platyceras on airways and to identify its active principles.
|
| Kinase Assay | Isoquercitrin suppresses colon cancer cell growth in vitro by targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 25359775]J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 19;289(51):35456-67.Flavonoids are plant-derived polyphenolic molecules that have potential biological effects including anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, and anti-tumoral effects.
These effects are related to the ability of flavonoids to modulate signaling pathways, such as the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. This pathway controls many aspects of embryonic development and tissue maintenance and has been found to be deregulated in a range of human cancers.
|
| Cell Research | Protective effects of flavonol isoquercitrin, against 6-hydroxy dopamine (6-OHDA)-induced toxicity in PC12 cells.[Pubmed: 24443837 ]BMC Res Notes. 2014 Jan 21;7:49.Free radicals-induced neurodegeneration is one of the many causes of Parkinson's disease (PD). This study investigated the neuroprotective effects of flavonol Isoquercitrin against toxicity induced by 6-hydroxy-dopamine (6-OHDA) in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells.
|
| Animal Research | Antihypertensive effects of isoquercitrin and extracts from Tropaeolum majus L.: evidence for the inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme.[Pubmed: 21185932 ]Anti-inflammatory activity of quercetin and isoquercitrin in experimental murine allergic asthma.[Pubmed: 18026696]Inflamm Res. 2007 Oct;56(10):402-8.Eosinophils and cytokines are implicated in the pathogenesis of allergic diseases. In the present study, we investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of quercetin and Isoquercitrin in a murine model of asthma.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Mar 24;134(2):363-72.Previous studies have shown that the extracts obtained from Tropaeolum majus L. exhibit pronounced diuretic properties. In the present study, we assessed whether the hypotensive and/or antihypertensive mechanism of hydroethanolic extract (HETM), semi-purified fraction (TMLR) obtained from T. majus and the flavonoids Isoquercitrin (ISQ) and kaempferol (KPF) can be mediated by their interaction with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE).
|

Isoquercitrin Dilution Calculator

Isoquercitrin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1533 mL | 10.7666 mL | 21.5332 mL | 43.0663 mL | 53.8329 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4307 mL | 2.1533 mL | 4.3066 mL | 8.6133 mL | 10.7666 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2153 mL | 1.0767 mL | 2.1533 mL | 4.3066 mL | 5.3833 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0431 mL | 0.2153 mL | 0.4307 mL | 0.8613 mL | 1.0767 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0215 mL | 0.1077 mL | 0.2153 mL | 0.4307 mL | 0.5383 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Isopimpinellin
Catalog No.:BCN5568
CAS No.:482-27-9
- Byakangelicin 2'-O-Isovalerate
Catalog No.:BCC8899
CAS No.:108006-56-0
- Homoferreirin
Catalog No.:BCN4765
CAS No.:482-01-9
- Estriol 3-sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2236
CAS No.:481-95-8
- Chrysophanol
Catalog No.:BCN5567
CAS No.:481-74-3
- Citreorosein
Catalog No.:BCN5566
CAS No.:481-73-2
- Aloeemodin
Catalog No.:BCN5565
CAS No.:481-72-1
- Tangeretin
Catalog No.:BCN2386
CAS No.:481-53-8
- Cepharanthine
Catalog No.:BCN5393
CAS No.:481-49-2
- Ginkgetin
Catalog No.:BCN2319
CAS No.:481-46-9
- Plumbagin
Catalog No.:BCN2586
CAS No.:481-42-5
- Juglone
Catalog No.:BCN2639
CAS No.:481-39-0
- Hyperoside
Catalog No.:BCN5570
CAS No.:482-36-0
- Kaempferitrin
Catalog No.:BCN5572
CAS No.:482-38-2
- Afzelin
Catalog No.:BCN5573
CAS No.:482-39-3
- Imperatorin
Catalog No.:BCN5574
CAS No.:482-44-0
- Isoimperatorin
Catalog No.:BCN5897
CAS No.:482-45-1
- Isobergapten
Catalog No.:BCN2377
CAS No.:482-48-4
- Osajin
Catalog No.:BCN4789
CAS No.:482-53-1
- Sarpagine
Catalog No.:BCN5575
CAS No.:482-68-8
- Nordalbergin
Catalog No.:BCC8344
CAS No.:482-82-6
- Dalbergin
Catalog No.:BCN7452
CAS No.:482-83-7
- Indigo
Catalog No.:BCN1091
CAS No.:482-89-3
- Aricine
Catalog No.:BCN5576
CAS No.:482-91-7
Isoquercitrin inhibits the progression of liver cancer in vivo and in vitro via the MAPK signalling pathway.[Pubmed:24676882]
Oncol Rep. 2014 May;31(5):2377-84.
Liver cancer is a malignant tumour with high morbidity and fatality rates that is common worldwide. At present, the clinical approaches to treating primary liver cancer include partial hepatectomy, systemic or local chemotherapy, radiotherapy, radiofrequency ablative surgery and liver transplantation. However, all of these approaches have shortcomings, including poor prognosis and numerous side-effects. A large number of studies have proven that many effective ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine, particularly the flavonoid compounds extracted from plants, have achieved breakthroughs in terms of enhancing the effects and reducing the toxicity of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, preventing tumour metastasis and relapse after surgery, alleviating the clinical symptoms of advanced tumours, improving the quality of life of the patient with tumours and extending patient longterm survival. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the impact of Isoquercitrin, the flavonoid from Bidens bipinnata L. extract, on the progression of liver cancer and to achieve a deeper understanding of the biological characteristics of Isoquercitrin's involvement in the progression of liver cancer. In the in vitro experiments, Isoquercitrin was found to strongly inhibit the proliferation of human liver cancer cells, promote the apoptosis of human liver cancer cells, and block the cell cycle in the G1 phase. Isoquercitrin activated caspase-3, -8 and -9, inhibited the expression level of ERK and p38MAPK protein phosphorylation, and promoted the phosphorylation of JNK. Additionally, Isoquercitrin reduced the expression level of PKC in human liver cancer cells. In the in vivo experiments, Isoquercitrin was also found to significantly inhibit the growth of transplanted tumours in nude mice. The present study confirmed that Isoquercitrin could inhibit the progression of human liver cancer in vivo and in vitro, and the molecular mechanism of Isoquercitrin may be closely associated with the MAPK and PKC signalling pathways.
Isoquercitrin promotes the osteogenic differentiation of osteoblasts and BMSCs via the RUNX2 or BMP pathway.[Pubmed:29852784]
Connect Tissue Res. 2019 Mar;60(2):189-199.
AIM: Isoquercitrin is widely present in fruits, vegetables and medicinal herbs. As a natural phytoestrogen, Isoquercitrin has been considered a possible osteoporosis prevention option to avoid the risk of hormone therapy. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The cell proliferation of osteoblasts and bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) was examined by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8). The osteogenic differentiation was evaluated by real-time qPCR, ALP staining and Alizarin Red S staining. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) was used to knockdown the expression of runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2). RESULTS: The cell proliferation of osteoblasts and BMSCs was promoted by Isoquercitrin at low concentrations. High concentrations of Isoquercitrin promoted the osteogenic differentiation via RUNX2 expression in osteoblasts and via the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) pathway in BMSCs. Inhibition of RUNX2 expression in osteoblasts by siRNA or addition of noggin to the culture medium of BMSCs reduced the effects of osteogenic differentiation induced by Isoquercitrin. CONCLUSIONS: These data suggest that Isoquercitrin is a natural potential osteoinductive compound and might be valuable for the prevention/treatment of bone disorders.
Anti-inflammatory activity of quercetin and isoquercitrin in experimental murine allergic asthma.[Pubmed:18026696]
Inflamm Res. 2007 Oct;56(10):402-8.
OBJECTIVE: Eosinophils and cytokines are implicated in the pathogenesis of allergic diseases. In the present study, we investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of quercetin and Isoquercitrin in a murine model of asthma. METHODS: BALB/c mice were immunized (ovalbumin/aluminum hydroxide, s. c.), followed by two intranasal ovalbumin challenges. From day 18 to day 22 after the first immunization, the mice received daily gavages of Isoquercitrin (15 mg/kg) or quercetin (10 mg/kg). Dexamethasone (1 mg/kg, s. c.) was administered as a positive control. Leucocytes were analyzed in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), blood and pulmonary parenchyma at 24 h after the last ovalbumin challenge. Interleukin-5 (IL-5) was analyzed in BALF and lung homogenates. RESULTS: In animals receiving Isoquercitrin or quercetin, eosinophil counts were lower in the BALF, blood and lung parenchyma. Neutrophil counts in blood and IL-5 levels in lung homogenate were lower only in Isoquercitrin-treated mice. No alterations in mononuclear cell numbers were observed. CONCLUSION: Quercetin and Isoquercitrin are effective eosinophilic inflammation suppressors, suggesting a potential for treating allergies.
Spironolactone in Combination with alpha-glycosyl Isoquercitrin Prevents Steatosis-related Early Hepatocarcinogenesis in Rats through the Observed NADPH Oxidase Modulation.[Pubmed:29843569]
Toxicol Pathol. 2018 Jul;46(5):530-539.
Administration of the diuretic, spironolactone (SR), can inhibit chronic liver diseases. We determined the effects of SR alone or in combination with the antioxidant alpha-glycosyl Isoquercitrin (AGIQ) on hyperlipidemia- and steatosis-related precancerous lesions in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed rats subjected to a two-stage hepatocarcinogenesis model. Rats were fed with control basal diet or HFD, which was administered with SR alone or in combination with an antioxidant AGIQ in drinking water. An HFD increased body weight, intra-abdominal fat (adipose) tissue weight, and plasma lipids, which were reduced by coadministration of SR and AGIQ. SR and AGIQ coadministration also reduced hepatic steatosis and preneoplastic glutathione S-transferase placental form-positive foci, in association with decrease in NADPH oxidase (NOX) subunit p22phox-positive cells and an increase in active-caspase-3-positive cells in the foci. Hepatic gene expression analysis revealed that the coadministration of SR and AGIQ altered mRNA levels of lipogenic enzymes ( Scd1 and Fasn), antioxidant-related enzymes ( Catalase), NOX component ( P67phox), and anti-inflammatory transcriptional factor ( Pparg). Our results indicated that SR in combination with AGIQ had the potential of suppressing hyperlipidemia- and steatosis-related early hepatocarcinogenesis through the reduced expression of NOX subunits.
Isoquercitrin inhibits the progression of pancreatic cancer in vivo and in vitro by regulating opioid receptors and the mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathway.[Pubmed:25434366]
Oncol Rep. 2015 Feb;33(2):840-8.
Pancreatic cancer is a common malignant tumour that affects individuals worldwide. In recent years, the incidence and mortality rates of pancreatic cancer have continuously increased. Currently, the primary clinical treatment methods for pancreatic cancer include surgical resection, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. However, these treatment methods rarely produce satisfactory therapeutic outcomes. Extensive research has also proven that the effective components of several traditional Chinese medicines, particularly flavonoids extracted from plants, have significant antitumour effects. Isoquercitrin, which is one of the flavonoids found in Bidens pilosa extracts, has a significant antitumour effect. However, the antitumour effect of Isoquercitrin and its mechanism of action remain unclear. The objective of the present study was to investigate the effect of Isoquercitrin on the progression of pancreatic cancer and to further understand the biological characteristics of the participation of Isoquercitrin in the progression of pancreatic cancer. In vitro, we found that a therapeutic dose of Isoquercitrin significantly inhibited proliferation, promoted apoptosis and induced cell cycle arrest within the G1 phase in pancreatic cancer cells. Isoquercitrin activated caspase-3, -8 and -9 and reduced the mitochondrial membrane potential. In addition, Isoquercitrin inhibited the expression level of the delta opioid receptor; however, Isoquercitrin had no effect on the kappa and micro opioid receptors. Furthermore, Isoquercitrin inhibited extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation and promoted c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) phosphorylation. In vivo, we found that a therapeutic dose of Isoquercitrin significantly inhibited xenograft growth in nude mice. In summary, the present study demonstrated that Isoquercitrin inhibits human pancreatic cancer progression in vivo and in vitro and that its molecular mechanism may be closely related to opioid receptors and to the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling pathway.
Antihypertensive effects of isoquercitrin and extracts from Tropaeolum majus L.: evidence for the inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme.[Pubmed:21185932]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Mar 24;134(2):363-72.
AIM OF THE STUDY: Previous studies have shown that the extracts obtained from Tropaeolum majus L. exhibit pronounced diuretic properties. In the present study, we assessed whether the hypotensive and/or antihypertensive mechanism of hydroethanolic extract (HETM), semi-purified fraction (TMLR) obtained from T. majus and the flavonoids Isoquercitrin (ISQ) and kaempferol (KPF) can be mediated by their interaction with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). METHODS AND METHODS: Firstly, to evaluate changes in mean arterial pressure (MAP), different groups of normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) were orally and intraduodenally treated with HETM (10-300 mg/kg) and TMLR (12.5-100mg/kg) and intravenously treated with ISQ and KPF being later anesthetized with ketamine (100mg/kg) and xylazine (20mg/kg). The left femoral vein and the right carotid artery were isolated, and polyethylene catheters were inserted for ISQ and KPF (0.5-4 mg/kg) administration and blood pressure recording, respectively. The plasmatic ACE activity was evaluated to indirect fluorimetry, in serum samples after orally treatment with HETM, TMLR, ISQ and KPF. RESULTS: The oral administration of the HETM and its TMLR significantly reduced, in a dose-dependent manner, the MAP in both normotensive and SHR. In addition, these preparations significantly decreased the MAP for up to 3h after the administration of the extract. Additionally, the intravenous administration of ISQ, but not KPF, decreased MAP in rats. Otherwise, neither the extracts nor ISQ affected the heart rate. The oral administration of the HETM, TMLR or ISQ reduced ACE activity in serum samples at 90 min after administration. Finally, the intravenous administration of ISQ caused a significant reduction in the hypertensive response to angiotensin I, but not angiotensin II in normotensive rats. CONCLUSION: Our results show that the hypotensive effects caused by the HETM, as well as by its TMLR, may be associated with the high levels of the flavonoid ISQ found in this plant. In addition, ISQ-induced hypotension in rats is an event dependent on the inhibition of angiotensin II generation by ACE.
Isoquercitrin from Argemone platyceras inhibits carbachol and leukotriene D4-induced contraction in guinea-pig airways.[Pubmed:16202993]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Oct 17;522(1-3):108-15.
Argemone platyceras is used in Mexico as a remedy for cough, bronchitis and pneumonia. The present study was performed to investigate the pharmacological anti-asthmatic properties of Argemone platyceras on airways and to identify its active principles. Methanol extracts of leaves and flowers, subsequent organic and aqueous extraction phases, and silica gel chromatography fractions were assayed on the carbachol-induced response, and/or on ovalbumin antigenic challenge, and on leukotriene D(4)-induced response of tracheae from sensitized and non-sensitized guinea-pigs. Methanol extracts, ethyl-acetate phase, and its fractions 6 and 7 inhibited the carbachol-induced contractile response. Isoquercitrin and rutin were the main compounds found in fractions 6 and 7 respectively. Isoquercitrin (fraction 6) abolished the response to ovalbumin, and decreased the contractile response to leukotriene D(4). Because of its effect on carbachol-induced contractile response, on the late-phase response to ovalbumin, and on leukotriene D(4)-induced contractile response, Isoquercitrin might be highly useful in treatment of asthma.
Isoquercitrin suppresses colon cancer cell growth in vitro by targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway.[Pubmed:25359775]
J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 19;289(51):35456-67.
Flavonoids are plant-derived polyphenolic molecules that have potential biological effects including anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, and anti-tumoral effects. These effects are related to the ability of flavonoids to modulate signaling pathways, such as the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. This pathway controls many aspects of embryonic development and tissue maintenance and has been found to be deregulated in a range of human cancers. We performed several in vivo assays in Xenopus embryos, a functional model of canonical Wnt signaling studies, and also used in vitro models, to investigate whether Isoquercitrin affects Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Our data provide strong support for an inhibitory effect of Isoquercitrin on Wnt/beta-catenin, where the flavonoid acts downstream of beta-catenin translocation to the nuclei. Isoquercitrin affects Xenopus axis establishment, reverses double axes and the LiCl hyperdorsalization phenotype, and reduces Xnr3 expression. In addition, this flavonoid shows anti-tumoral effects on colon cancer cells (SW480, DLD-1, and HCT116), whereas exerting no significant effect on non-tumor colon cell (IEC-18), suggesting a specific effect in tumor cells in vitro. Taken together, our data indicate that Isoquercitrin is an inhibitor of Wnt/beta-catenin and should be further investigated as a potential novel anti-tumoral agent.
Isoquercitrin and polyphosphate co-enhance mineralization of human osteoblast-like SaOS-2 cells via separate activation of two RUNX2 cofactors AFT6 and Ets1.[Pubmed:24726443]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Jun 1;89(3):413-21.
Isoquercitrin, a dietary phytoestrogen, is a potential stimulator of bone mineralization used for prophylaxis of osteoporotic disorders. Here we studied the combined effects of Isoquercitrin, a cell membrane permeable 3-O-glucoside of quercetin, and polyphosphate [polyP], a naturally occurring inorganic polymer inducing bone formation, on mineralization of human osteoblast-like SaOS-2 cells. Both compounds Isoquercitrin and polyP induce at non-toxic concentrations the mineralization process of SaOS-2 cells. Co-incubation experiments revealed that Isoquercitrin (at 0.1 and 0.3muM), if given simultaneously with polyP (as Ca(2+) salt; at 3, 10, 30 and 100muM) amplifies the mineralization-enhancing effect of the inorganic polymer. The biomineralization process induced by Isoquercitrin and polyP is based on two different modes of action. After incubation of the cells with Isoquercitrin or polyP the expression of the Runt-related transcription factor 2 [RUNX2] is significantly upregulated. In addition, Isoquercitrin causes a strong increase of the steady-state-levels of the two co-activators of RUNX2, the activating transcription factor 6 [ATF6] and the Ets oncogene homolog 1 [Ets1]. The activating effect of Isoquercitrin occurs via a signal transduction pathway involving ATF6, and by that, is independent from the induction cascade initiated by polyP. This conclusion is supported by the finding that Isoquercitrin upregulates the expression of the gene encoding for osteocalcin, while polyP strongly increases the expression of the Ets1 gene and of the alkaline phosphatase. We show that the two compounds, polyP and Isoquercitrin, have a co-enhancing effect on bone mineral formation and in turn might be of potential therapeutic value for prevention/treatment of osteoporosis.
Protective effects of flavonol isoquercitrin, against 6-hydroxy dopamine (6-OHDA)-induced toxicity in PC12 cells.[Pubmed:24443837]
BMC Res Notes. 2014 Jan 21;7:49.
BACKGROUND: Free radicals-induced neurodegeneration is one of the many causes of Parkinson's disease (PD). This study investigated the neuroprotective effects of flavonol Isoquercitrin against toxicity induced by 6-hydroxy-dopamine (6-OHDA) in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. METHODS: PC12 cells were pretreated with different concentrations of Isoquercitrin for 4, 8 and 12 hours and incubated with 6-OHDA for 24 hours to induce oxidative cell damage. RESULTS: A significant cytoprotective activity was observed in Isoquercitrin pre-treated cells in a dose-dependent manner. There was a significant increase (P < 0.01) in the antioxidant enzymes namely superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and glutathione in Isoquercitrin pretreated cells compared to cells incubated with 6-OHDA alone. Isoquercitrin significantly reduced (P < 0.01) lipid peroxidation in 6-OHDA treated cells. These results suggested that Isoquercitrin protects PC 12 cells against 6-OHDA-induced oxidative stress. CONCLUSIONS: The present study suggests the protective role of Isoquercitrin on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced toxicity by virtue of its antioxidant potential. Isoquercitrin could be a potential therapeutic agent against neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease.


