AfzelinCAS# 482-39-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 482-39-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5316673 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
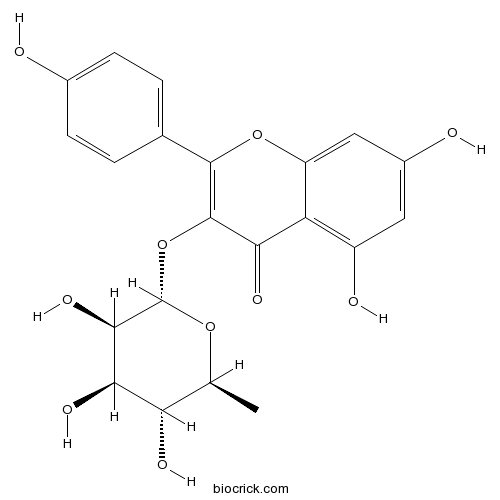
| Formula | C21H20O10 | M.Wt | 432.4 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Afzelin; Afzeloside; Kaempferin; 3,4',5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone 3-rhamnoside | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in methan | ||
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2=C(OC3=CC(=CC(=C3C2=O)O)O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SOSLMHZOJATCCP-AEIZVZFYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Afzelin has several cellular activities such as DNA-protective, antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory as well as UV-absorbing activity and may protect human skin from UVB-induced damage by a combination of UV-absorbing and cellular activities. Afzelin has potenial anti-cancer activity against prostate cancer, the activity is due to inhibition of LIM domain kinase 021 expression, it can inhibit the proliferation of LNCaP and PC302cells, and block the cell cycle in the G002phase. Afzelin can attenuate asthma phenotypes is based on reduction of Th2 cytokine via inhibition of GATA-binding protein 3 transcription factor, which is the master regulator of Th2 cytokine differentiation and production. |
| Targets | TNF-α | PGE | p38MAPK | cAMP | PKA |
| In vitro | Antagonizing effects and mechanisms of afzelin against UVB-induced cell damage.[Pubmed: 23626759]PLoS One. 2013 Apr 23;8(4):e61971.Ultraviolet (UV) radiation induces DNA damage, oxidative stress, and inflammatory processes in human keratinocytes, resulting in skin inflammation, photoaging, and photocarcinogenesis. Adequate protection of skin against the harmful effects of UV irradiation is essential. Antibacterial effects of afzelin isolated from Cornus macrophylla on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a leading cause of illness in immunocompromised individuals.[Pubmed: 24642906]Molecules. 2014 Mar 17;19(3):3173-80.The crude ethyl acetate extract of the leaves of Cornus macrophylla showed antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a leading cause of illness in immunocompromised individuals. Bioactivity-guided separation led to the isolation of kaempferol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (Afzelin). Preliminary in vitro and ex vivo evaluation of afzelin, kaempferitrin and pterogynoside action over free radicals and reactive oxygen species.[Pubmed: 25315635]Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Jun;38(6):1168-77.Biological activities of flavonoids have been extensively reviewed in literature. The biochemical profile of Afzelin, kaempferitrin, and pterogynoside acting on reactive oxygen species was investigated in this paper. |
| In vivo | Afzelin attenuates asthma phenotypes by downregulation of GATA3 in a murine model of asthma.[Pubmed: 25738969]Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jul;12(1):71-6.Asthma is a serious health problem causing significant mortality and morbidity globally. Persistent airway inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness, increased immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels and mucus hypersecretion are key characteristics of the condition. Asthma is mediated via a dominant T-helper 2 (Th2) immune response, causing enhanced expression of Th2 cytokines. These cytokines are responsible for the various pathological changes associated with allergic asthma. To investigate the anti-asthmatic potential of Afzelin, as well as the underlying mechanisms involved, its anti-asthmatic potential were investigated in a murine model of asthma. |
| Kinase Assay | Afzelin positively regulates melanogenesis through the p38 MAPK pathway.[Pubmed: 27287415]Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Jul 25;254:167-72.Melanogenesis refers to synthesis of the skin pigment melanin, which plays a critical role in the protection of skin against ultraviolet irradiation and oxidative stressors. We investigated the effects of Afzelin on melanogenesis and its mechanisms of action in human epidermal melanocytes. |
| Cell Research | Afzelin exhibits anti-cancer activity against androgen-sensitive LNCaP and androgen-independent PC-3 prostate cancer cells through the inhibition of LIM domain kinase 1.[Pubmed: 26622852 ]Oncol Lett. 2015 Oct;10(4):2359-2365.Prostate cancer presents high occurrence worldwide. Medicinal plants are a major source of novel and potentially therapeutic molecules; therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the possible anti-prostate cancer activity of Afzelin, a flavonol glycoside that was previously isolated from Nymphaea odorata. |

Afzelin Dilution Calculator

Afzelin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3127 mL | 11.5634 mL | 23.1267 mL | 46.2535 mL | 57.8168 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4625 mL | 2.3127 mL | 4.6253 mL | 9.2507 mL | 11.5634 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2313 mL | 1.1563 mL | 2.3127 mL | 4.6253 mL | 5.7817 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0463 mL | 0.2313 mL | 0.4625 mL | 0.9251 mL | 1.1563 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0231 mL | 0.1156 mL | 0.2313 mL | 0.4625 mL | 0.5782 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Kaempferitrin
Catalog No.:BCN5572
CAS No.:482-38-2
- Hyperoside
Catalog No.:BCN5570
CAS No.:482-36-0
- Isoquercitrin
Catalog No.:BCN5569
CAS No.:482-35-9
- Isopimpinellin
Catalog No.:BCN5568
CAS No.:482-27-9
- Byakangelicin 2'-O-Isovalerate
Catalog No.:BCC8899
CAS No.:108006-56-0
- Homoferreirin
Catalog No.:BCN4765
CAS No.:482-01-9
- Estriol 3-sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2236
CAS No.:481-95-8
- Chrysophanol
Catalog No.:BCN5567
CAS No.:481-74-3
- Citreorosein
Catalog No.:BCN5566
CAS No.:481-73-2
- Aloeemodin
Catalog No.:BCN5565
CAS No.:481-72-1
- Tangeretin
Catalog No.:BCN2386
CAS No.:481-53-8
- Cepharanthine
Catalog No.:BCN5393
CAS No.:481-49-2
- Imperatorin
Catalog No.:BCN5574
CAS No.:482-44-0
- Isoimperatorin
Catalog No.:BCN5897
CAS No.:482-45-1
- Isobergapten
Catalog No.:BCN2377
CAS No.:482-48-4
- Osajin
Catalog No.:BCN4789
CAS No.:482-53-1
- Sarpagine
Catalog No.:BCN5575
CAS No.:482-68-8
- Nordalbergin
Catalog No.:BCC8344
CAS No.:482-82-6
- Dalbergin
Catalog No.:BCN7452
CAS No.:482-83-7
- Indigo
Catalog No.:BCN1091
CAS No.:482-89-3
- Aricine
Catalog No.:BCN5576
CAS No.:482-91-7
- RG 108
Catalog No.:BCC1134
CAS No.:48208-26-0
- Tetrahydroamentoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN5571
CAS No.:48236-96-0
- 14-Dehydrobrowniine
Catalog No.:BCN8109
CAS No.:4829-56-5
Antibacterial effects of afzelin isolated from Cornus macrophylla on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a leading cause of illness in immunocompromised individuals.[Pubmed:24642906]
Molecules. 2014 Mar 17;19(3):3173-80.
The crude ethyl acetate extract of the leaves of Cornus macrophylla showed antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a leading cause of illness in immunocompromised individuals. Bioactivity-guided separation led to the isolation of kaempferol 3-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside (Afzelin). The structure was determined based on evaluation of its spectroscopic (UV, MS, and NMR) data. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of Afzelin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa was found to be 31 microg/mL. In addition, the results indicated that a hydroxyl group at C3 of the C-ring of the flavone skeleton and the rhamnose group may act as a negative factor and an enhancing factor, respectively, in the antibacterial activities of Afzelin.
Antagonizing effects and mechanisms of afzelin against UVB-induced cell damage.[Pubmed:23626759]
PLoS One. 2013 Apr 23;8(4):e61971.
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation induces DNA damage, oxidative stress, and inflammatory processes in human keratinocytes, resulting in skin inflammation, photoaging, and photocarcinogenesis. Adequate protection of skin against the harmful effects of UV irradiation is essential. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the protective effects of Afzelin, one of the flavonoids, against UV irradiation in human keratinocytes and epidermal equivalent models. Spectrophotometric measurements revealed that the Afzelin extinction maxima were in the UVB and UVA range, and UV transmission below 376 nm was <10%, indicating UV-absorbing activity of Afzelin. In the phototoxicity assay using the 3T3 NRU phototoxicity test (3T3-NRU-PT), Afzelin presented a tendency to no phototoxic potential. In addition, in order to investigate cellular functions of Afzelin itself, cells were treated with Afzelin after UVB irradiation. In human keratinocyte, Afzelin effectively inhibited the UVB-mediated increase in lipid peroxidation and the formation of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers. Afzelin also inhibited UVB-induced cell death in human keratinocytes by inhibiting intrinsic apoptotic signaling. Furthermore, Afzelin showed inhibitory effects on UVB-induced release of pro-inflammatory mediators such as interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and prostaglandin-E2 in human keratinocytes by interfering with the p38 kinase pathway. Using an epidermal equivalent model exposed to UVB radiation, anti-apoptotic activity of Afzelin was also confirmed together with a photoprotective effect at the morphological level. Taken together, our results suggest that Afzelin has several cellular activities such as DNA-protective, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory as well as UV-absorbing activity and may protect human skin from UVB-induced damage by a combination of UV-absorbing and cellular activities.
Afzelin exhibits anti-cancer activity against androgen-sensitive LNCaP and androgen-independent PC-3 prostate cancer cells through the inhibition of LIM domain kinase 1.[Pubmed:26622852]
Oncol Lett. 2015 Oct;10(4):2359-2365.
Prostate cancer presents high occurrence worldwide. Medicinal plants are a major source of novel and potentially therapeutic molecules; therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the possible anti-prostate cancer activity of Afzelin, a flavonol glycoside that was previously isolated from Nymphaea odorata. The effect of Afzelin on the proliferation of androgen-sensitive LNCaP and androgen-independent PC-3 cells was evaluated by performing a water soluble tetrazolium salt-1 assay. In addition, the effect of Afzelin on the cell cycle of the LNCaP and PC-3 prostate cancer cell lines was evaluated. Western blot analysis was performed to evaluate the effect of Afzelin on the kinases responsible for the regulation of actin organization. Afzelin was identified to inhibit the proliferation of LNCaP and PC3 cells, and block the cell cycle in the G0 phase. The anticancer activity of Afzelin in these cells was determined to be due to inhibition of LIM domain kinase 1 expression. Thus, the in vitro efficacy of Afzelin against prostate cancer is promising; however, additional studies on different animal models are required to substantiate its anticancer potential.
Afzelin positively regulates melanogenesis through the p38 MAPK pathway.[Pubmed:27287415]
Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Jul 25;254:167-72.
Melanogenesis refers to synthesis of the skin pigment melanin, which plays a critical role in the protection of skin against ultraviolet irradiation and oxidative stressors. We investigated the effects of Afzelin on melanogenesis and its mechanisms of action in human epidermal melanocytes. In this study, we found that Afzelin increased both melanin content and tyrosinase activity in a concentration-dependent manner. While the mRNA levels of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF), tyrosinase, and tyrosinase-related protein (TRP)-1 increased following Afzelin treatment, the mRNA levels of TRP-2 were not affected by Afzelin. Likewise, Afzelin increased the protein levels of MITF, TRP-1, and tyrosinase but not TRP-2. Mechanistically, we found that Afzelin regulated melanogenesis by upregulating MITF through phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), independent of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-protein kinase A (PKA) signaling. Taken together, these findings indicate that the promotion of melanogenesis by Afzelin occurs through increased MITF gene expression, which is mediated by activation of p38 MAPK, and suggest that Afzelin may be useful as a protective agent against ultraviolet irradiation.
Preliminary in vitro and ex vivo evaluation of afzelin, kaempferitrin and pterogynoside action over free radicals and reactive oxygen species.[Pubmed:25315635]
Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Jun;38(6):1168-77.
Biological activities of flavonoids have been extensively reviewed in literature. The biochemical profile of Afzelin, kaempferitrin, and pterogynoside acting on reactive oxygen species was investigated in this paper. The flavonoids were able to act as scavengers of the superoxide anion, hypochlorous acid and taurine chloramine. Although flavonoids are naturally occurring substances in plants which antioxidant activities have been widely advertised as beneficial, Afzelin, kaempferitrin, and pterogynoside were able to promote cytotoxic effect. In red blood cells this toxicity was enhanced, depending on flavonoids concentration, in the presence of hypochlorous acid, but reduced in the presence of 2,2'-azo-bis(2-amidinopropane) free radical. These flavonoids had also promoted the death of neutrophils, which was exacerbated when the oxidative burst was initiated by phorbol miristate acetate. Therefore, despite their well-known scavenging action toward free radicals and oxidants, these compounds could be very harmful to living organisms through their action over erythrocytes and neutrophils.
Afzelin attenuates asthma phenotypes by downregulation of GATA3 in a murine model of asthma.[Pubmed:25738969]
Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jul;12(1):71-6.
Asthma is a serious health problem causing significant mortality and morbidity globally. Persistent airway inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness, increased immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels and mucus hypersecretion are key characteristics of the condition. Asthma is mediated via a dominant T-helper 2 (Th2) immune response, causing enhanced expression of Th2 cytokines. These cytokines are responsible for the various pathological changes associated with allergic asthma. To investigate the anti-asthmatic potential of Afzelin, as well as the underlying mechanisms involved, its anti-asthmatic potential were investigated in a murine model of asthma. In the present study, BALB/c mice were systemically sensitized using ovalbumin (OVA) followed by aerosol allergen challenges. The effect of Afzelin on airway hyperresponsiveness, eosinophilic infiltration, Th2 cytokine and OVAspecific IgE production in a mouse model of asthma were investigated. It was found that Afzelintreated groups suppressed eosinophil infiltration, allergic airway inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness, OVA-specific IgE and Th2 cytokine secretion. The results of the present study suggested that the therapeutic mechanism by which Afzelin effectively treats asthma is based on reduction of Th2 cytokine via inhibition of GATA-binding protein 3 transcription factor, which is the master regulator of Th2 cytokine differentiation and production.


