Hosta plantaginea
Hosta plantaginea
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Hosta plantaginea
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
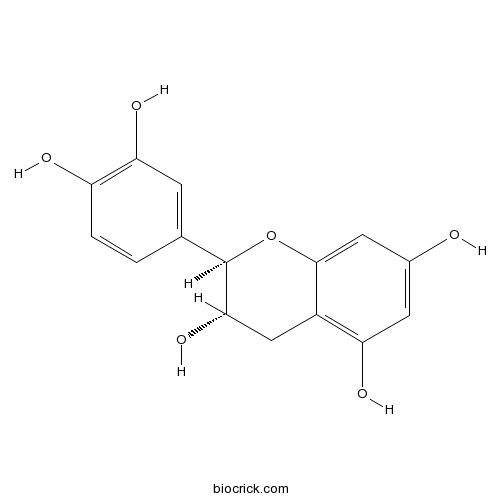
BCN1688
Catechin154-23-4
Instructions
-
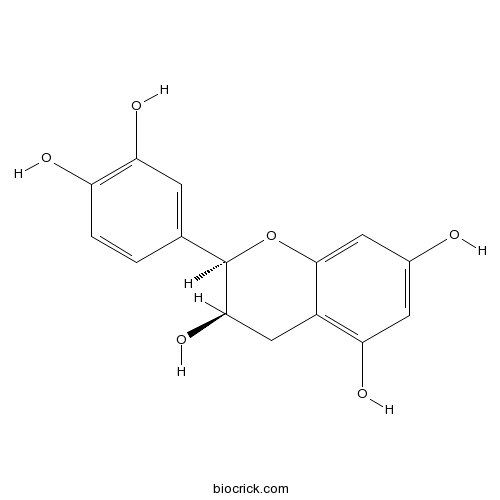
BCN5597
Epicatechin490-46-0
Instructions
-
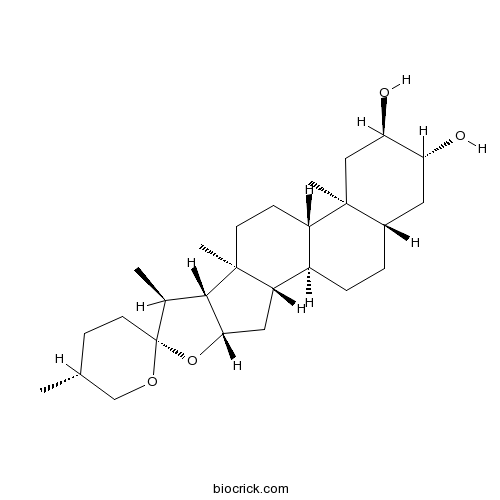
BCN3886
Gitogenin511-96-6
Instructions
A new flavonol glycoside from the flowers of Hosta plantaginea with cyclooxygenases-1/2 inhibitory and antioxidant activities.[Pubmed: 29390913]
Hosta plantaginea was a traditional Chinese medicinal plants used to treat inflammatory and painful diseases with partial scientific validation. Solvent extractions followed by repeated chromatographic purification of the H. plantaginea flowers led to the isolation of one new flavonoid glycoside, hostaflavone A (1), together with one related known compound, kaempferol-3-O-sophoroside-7-O-glucoside (2), and their structures were elucidated on the basis of chemical and spectral evidence, as well as by comparison with literature data. Compounds 1 and 2 were evaluated for the anti-inflammatory activites against cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2) and DPPH free radical-scavenging activities in vitro. The results revealed that 1 and 2 exhibited significant COX-1 inhibition and moderate COX-2 inhibition compared to the reference celecoxib. Additionally, 1 and 2 displayed insignificant antioxidant activities compared to the positive control L-ascorbic acid.
Chemical Constituents from the Flower of Hosta plantaginea with Cyclooxygenases Inhibition and Antioxidant Activities and Their Chemotaxonomic Significance.[Pubmed: 29072626]
None
The bioassay-guided isolation of antifungal saponins from Hosta plantaginea leaves.[Pubmed: 28534424]
Four new steroidal saponins hostaside Ⅰ (1), hostaside Ⅱ (2), hostaside Ⅲ (3), and hostaside Ⅳ (4), together with five known steroidal saponins (5-9), were isolated by the bioassay-guided fractionation from the leaves of Hosta plantaginea (Lam.) Aschers, a worldwide well-known ornamental plant. Hostasides Ⅰ and Ⅱ showed significant antifungal activities, and they could inhibit the growth of Candida albicans and Fusarium oxysporium with MIC values as low as 4 μg/ml.
New steroidal glycosides from Hosta plantaginea (Lam.) Aschers.[Pubmed: 25559690]
Four new furostanol glycosides were isolated from the flowers of Hosta plantaginea (Lam.) Aschers. On the basis of spectroscopic methods including 1D and 2D NMR experiments, their structures were elucidated as 26-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(25R)-22-O-methyl-5α-furostan-2α,3β,22ξ,26-tetrol 3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 → 4)-O-β-d-xylopyranosyl-(1 → 3)-[O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 2)]-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 4)-β-d-galactopyranoside (hostaplantagineoside A, 1), 26-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(25R)-5α-furostan-20(22)-ene-2α,3β,26-triol-3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 2)-[O-β-d-xylopyranosyl-(1 → 3)]-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 4)-β-d-galactopyranoside (hostaplantagineoside B, 2), 26-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(25R)-5α-furostan-22(23)-ene-2α,3β,20α,26-tetraol-3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 2)-[O-β-d-xylopyranosyl-(1 → 3)]-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 4)-O-β-d-galactopyranoside (hostaplantagineoside C, 3), 26-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(25R)-5α-furostan-20(22)-ene-2α,3β,26-triol-3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 → 4)-O-β-d-xylopyranosyl-(1 → 3)-[O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 2)]-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 4)-β-d-galactopyranoside (hostaplantagineoside D, 4).
Polyphasic characterisation of three new Phyllosticta spp.[Pubmed: 23105155]
Three new species of Phyllosticta, P. hostae on Hosta plantaginea (China), P. schimae on Schima superba (China), and P. ilicis-aquifolii on Ilex aquifolium (UK), are described and illustrated in this study. They are compared with morphologically similar and phylogenetically closely related species. A polyphasic approach using phylogeny, host association, disease symptoms, colony and morphological characteristics, is employed to justify the introduction of the new taxa. Phylogenetic relationships of the new species with other Phyllosticta species are revealed by DNA sequence analyses based on the nrDNA-internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions and a combined multilocus alignment of the ITS, partial translation elongation factor 1-alpha (TEF1), actin (ACT), and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPDH) gene regions.
Isolation and characterisation of an HpSHP gene from Hosta plantaginea.[Pubmed: 22311025]
Based on genetic and molecular analyses, the ABC model has been proposed to explain the genetic control of floral development. C-class MADS-box genes play crucial roles in Arabidopsis thaliana development by regulating the organ identities of stamens and gynoecium. The present research reports for the first time the cloning of an HpSHP gene from Hosta plantaginea (Lam.) Aschers. Phylogenetic analysis shows that HpSHP is a member of the C-class MADS-box genes that is closely related to C-lineage SHP homologues from monocot species. Semi-quantitative and real-time polymerase chain reaction analyses show that HpSHP expression is stamen and gynoecium specific. HpSHP also has spatial and temporal expression patterns in the reproductive organs of H. plantaginea. A functional analysis is carried out in Arabidopsis by overexpression of HpSHP. Homeotic transformations of sepals into carpelloid organs, bent ovaries, and prematurely shattering fruits are observed in 35S::HpSHP transgenic plants. All these results show that HpSHP plays a crucial role in gynoecium development.
Isolation and characterization of an AGAMOUS-like gene from Hosta plantaginea.[Pubmed: 21667245]
Based on genetic and molecular analyses, the ABC model was proposed to explain the genetic control of floral development. The C-class MADS box gene AGAMOUS (AG) plays crucial roles in Arabidopsis thaliana development through regulation of the organ identity of stamens and gynoecium. The present research reports for the first time the cloning of an AG homologue (HpAG) from Hosta plantaginea Aschers. Phylogenetic analysis shows HpAG is a homologue of AG that is closely related to C-lineage AG homologues from monocot species. Semi-quantitative PCR and real-time PCR analyses show that HpAG is stamen- and gynoecium-specific in expression and has spatial and temporal expression patterns in the reproductive organs of H. plantaginea. The transcriptional activation property of HpAG is also verified by a yeast one-hybrid. Functional analysis is carried out in Arabidopsis by overexpression of HpAG. The homeotic transformations of petals into staminoid organs are observed in 35S::HpAG transgenic plants. All these results show that HpAG1 plays a crucial role in stamen specification and gynoecium development.
Structure elucidation and biomimetic synthesis of hostasinine A, a new benzylphenethylamine alkaloid from Hosta plantaginea.[Pubmed: 17994756]
Hostasinine A (1), a benzylphenethylamine alkaloid with an unprecedented skeleton featuring a C-4-C-6 linkage and a nitrone moiety, was isolated from Hosta plantaginea. Its structure was established on the basis of spectroscopic data, and was further confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The alkaloid was postulated biogenetically from haemanthidine via N-oxidation and aza-aldol-type condensation and was synthesized biomimetically. The inhibitory activities of 1 on acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and two tumor cell lines (K562 and A549) were also evaluated.
Benzylphenethylamine alkaloids from Hosta plantaginea with inhibitory activity against tobacco mosaic virus and acetylcholinesterase.[Pubmed: 17822295]
Five new benzylphenethylamine alkaloids, hostasine (1), 8-demethoxyhostasine, 8-demethoxy-10-O-methylhostasine, 10-O-methylhostasine, and 9-O-demethyl-7-O-methyllycorenine, along with 12 known compounds, were isolated from Hosta plantaginea by bioassay-guided fractionation. The structures of the new alkaloids were established by means of extensive spectroscopic methods, and the relative configuration of 1 was further confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. 7-Deoxy-trans-dihydronarciclasine (IC(50) = 1.80 microM), a known alkaloid, showed strong activity against tobacco mosaic virus by the half-leaf method. Some of these alkaloids were also evaluated for their inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase. 8-Demethoxy-10-O-methylhostasine was found to possess significant activity, with an IC(50) of 2.32 microM.


