Hypericum ascyron
Hypericum ascyron
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Hypericum ascyron
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
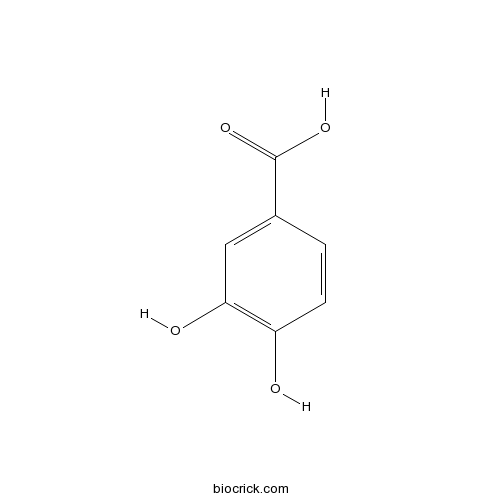
BCN0310
trans-p-Coumaric acid501-98-4
Instructions

-
BCN4537
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
[Chemical Constituents of Ethyl Acetate Fraction from Hypericum ascyron].[Pubmed: 30080367]
To study the chemical consituents of Hypericum ascyron.
Extractive from Hypericum ascyron L promotes serotonergic neuronal differentiation in vitro.[Pubmed: 30015171]
Plant natural products have many different biological activities but the precise mechanisms underlying these activities remain largely unknown. Hypericum longistylum has long been recorded in Chinese medicine as a cure for depression and related disorders, but how it repairs neural lineages has not been addressed.
Difference in protective effects of three structurally similar flavonoid glycosides from Hypericum ascyron against H₂O₂-induced injury in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts.[Pubmed: 26177564]
According to previous studies, hyperoside possesses myocardial protective effects. To investigate whether isoquercitrin and isohyperoside have similar functions, the protective effects of isoquercitrin and isohyperoside against H2O2‑induced injury in H9c2 rat cardiomyoblasts were evaluated using a 3‑(4,5‑dimethylthiazol‑2‑yl)‑2,5‑diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. The mechanism of action was investigated by assessing the leakage of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) of hyperoside and isoquercitrin‑pretreated H9c2 cardiomyocytes following H2O2‑induced injury, and examining their effects on the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. The isolation of two flavonoid glycosides from H. ascyron was performed, following extraction, using semi‑preparative high performance liquid chromatography. Using the spectral characteristics, the structures of these compounds were identified as isoquercitrin and isohyperoside. This was the first time, to the best of our knowledge, that isohyperoside has been identified from H. ascyron. The results revealed that isoquercitrin and isohyperoside possessed similar protective effects to hyperoside against H2O2‑induced injury in H9c2 cells. The half maximal inhibitory concentration values of hyperoside, isoquercitrin and isohyperoside were 0.0008, 0.0017 and 0.0002 µM, respectively. Based on these results, isohyperoside possessed more marked protective effects against H2O2‑induced injury in the H9c2 cardiomyoblasts. The significant reduction in LDH leakage, decrease in MDA level and increase in SOD activity also provided evidence of the cardioprotective effects of isoquercitrin and isohyperoside. The present study reported for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, the myocardial protective effects of isoquercitrin and isohyperoside. The mechanism of action may involve protection of the cell membrane from oxidative damage.
Antibacterial active compounds from Hypericum ascyron L. induce bacterial cell death through apoptosis pathway.[Pubmed: 25916905]
Hypericum ascyron L. has been used as a traditional medicine for the treatment of wounds, swelling, headache, nausea and abscesses in China for thousands of years. However, modern pharmacological studies are still necessary to provide a scientific basis to substantiate their traditional use. In this study, the mechanism underlying the antimicrobial effect of the antibacterial activity compounds from H. ascyron L. was investigated. Bioguided fractionation of the extract from H. ascyron L. afforded antibacterial activity fraction 8. The results of cup plate analysis and MTT assay showed that the MIC and MBC of fraction 8 is 5 mg/mL. Furthermore, using Annexin V-FITC/PI, TUNEL labeling and DNA gel electrophoresis, we found that cell death with apoptosis features similar to those in eucaryon could be induced in bacteria strains after exposure to the antibacterial activity compounds from H. ascyron L. at moderate concentration. In addition, we further found fraction 8 could disrupt the cell membrane potential indicate that fraction 8 exerts pro-apoptotic effects through a membrane-mediated apoptosis pathway. Finally, quercetin and kaempferol 3-O-β-(2″-acetyl)-galactopyranoside, were identified from fraction 8 by means of Mass spectrometry and Nuclear magnetic resonance. To our best knowledge, this study is the first to show that Kaempferol 3-O-β-(2″-acetyl)-galactopyranoside coupled with quercetin had significant antibacterial activity via apoptosis pathway, and it is also the first report that Kaempferol 3-O-β-(2″-acetyl)-galactopyranoside was found in clusiacea. Our data might provide a rational base for the use of H. ascyron L. in clinical, and throw light on the development of novel antibacterial drugs.
A new 3,4-seco-oleanane-type triterpenoid with an unusual enedione moiety from Hypericum ascyron.[Pubmed: 25870936]
A novel 3,4-seco-oleanane-type triterpenoid named 3,4-seco-olean-13(18)-ene-12,19-dione-3-oic acid (1), bearing an unusual enedione moiety, was isolated from the aerial parts of Hypericum ascyron, together with a known feiedelane-type triterpenoid friedelin (2). The structure of 1 with absolute configuration was elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic methods and a single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis.
Hyperascyrones A-H, polyprenylated spirocyclic acylphloroglucinol derivatives from Hypericum ascyron Linn.[Pubmed: 25800107]
Eight polyprenylated spirocyclic acylphloroglucinol derivatives (PSAPs), hyperascyrones A-H, were isolated from the aerial parts of Hypericum ascyron Linn., together with six known analogs. Their structures were established by spectroscopic analyses including HRESIMS, 1D and 2D NMR, and their absolute configurations were determined by electronic circular dichroism calculations (ECD, Gaussian 09). Structures of previously reported tomoeones C, D, G, and H were revised. Hyperascyrones A-H were evaluated for their cytotoxic and anti-HIV-1 activities, with hyperascyrones C and G exhibiting significant cytotoxicities against HL-60 cell lines with IC50 values of 4.22 and 8.36 μM, respectively. In addition, the chemotaxonomic significance of these compounds was also discussed.
The extract of Hypericum ascyron L. induces bacterial cell death through apoptosis pathway.[Pubmed: 25796407]
Hypericum ascyron L. (H. ascyron L.) has been used as a traditional medicine for the treatment of wounds, swelling, headache, nausea, stomach ache, abscesses, dysentery and chronic bronchitis. Pharmacological studies are necessary to provide a scientific basis to substantiate their traditional use. In this study, antimicrobial effect and its mechanism of the H. ascyron L. extract was investigated.
Quality evaluation of Hypericum ascyron extract by two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with the colorimetric 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide method.[Pubmed: 25521967]
In this paper, a heart-cutting two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) method was established for controlling the quality of different batches of Hypericum ascyron extract for the first time. In comparison with the common one-dimensional fingerprint, the second-dimensional fingerprint compiled additional spectral data and was hence more informative. The quality of H. ascyron extract was further evaluated by similarity measures and the same results were achieved, the correlation coefficients of the similarity of ten batches of H. ascyron extract were >0.99. Furthermore, we also evaluated the quality of the ten batches of H. ascyron extract by antibacterial activity. The result demonstrated that the quality of the ten batches of H. ascyron extract was not significantly different by MTT. Finally, we demonstrated that the second-dimensional fingerprint coupled with the MTT method was a more powerful tool to characterize the quality of samples of batch to batch. Therefore the proposed method could be used to comprehensively conduct the quality control of traditional Chinese medicines.
Quality and antitumour activity evaluation of extract of Hypericum ascyron.[Pubmed: 24638934]
Similarity assessment of complex chromatographic profiles is a potential tool for the identification and quality control of herbal medicinal products to guarantee the expected biological activity. In this paper, a high-performance liquid chromatography method was established for controlling the quality of extract of Hypericum ascyron for the first time. With this method, the correlation coefficients of similarity of 10 batches extract of H. ascyron were >0.97. The extract of H. ascyron displayed steadily inhibitorty activities on the growth of human cervical cancer Hela cell lines. Therefore, the present study successfully set up a sensitive efficient method which might confirm stable biological activity of the extract of H. ascyron.


