Incarvillea younghusbandii
Incarvillea younghusbandii
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Incarvillea younghusbandii
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
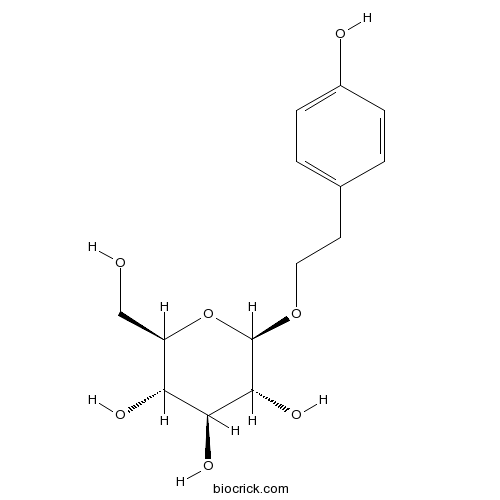
BCN5966
Salidroside10338-51-9
Instructions
-
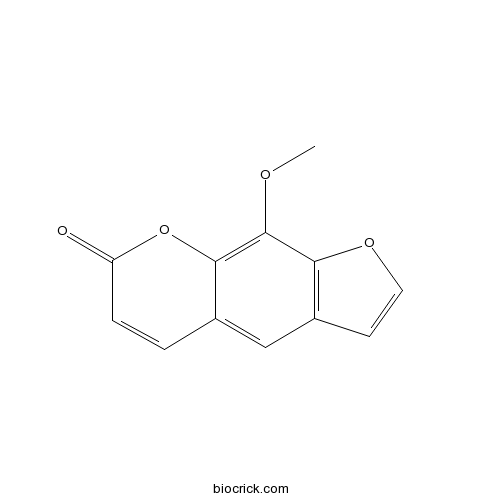
BCN5205
Xanthotoxin298-81-7
Instructions
-
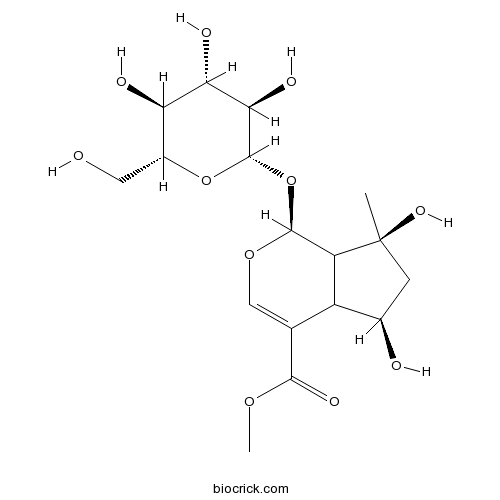
BCN4187
Shanzhiside methylester64421-28-9
Instructions
-
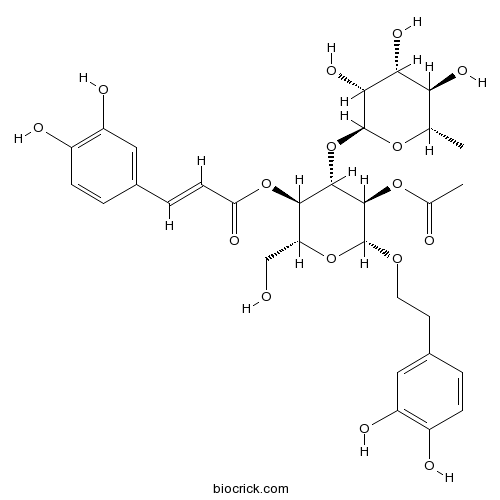
BCN3409
2'-Acetylacteoside94492-24-7
Instructions
Extracts from the roots of Incarvillea younghusbandii on antioxidant effects and life span prolonging in Drosophila melanogaster.[Pubmed: 23302531]
To investigate antioxidant activities and life span prolonging effects of the extracts from the roots of Incarvillea younghusbandii Sprague, and to study the correlations between these activities and the polar intensity of the extracts.
Incarvilleatone, a new cyclohexylethanoid dimer from Incarvillea younghusbandii and its inhibition against nitric oxide (NO) release.[Pubmed: 22483266]
Incarvilleatone (1), an unprecedented dimeric cyclohexylethanoid analog with a racemic nature, was isolated from the whole plant of Incarvillea younghusbandii. HPLC chiral separation of 1 gave two enantiomers (-)-incarvilleatone and (+)-incarvilleatone. The structure of 1 was established by spectroscopic methods and single crystal X-ray diffraction. The absolute configurations of enantiomers were determined by quantum mechanical calculation. (-)-Incarvilleatone exhibited a potent inhibitory effect against NO production in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages.
Isolation, purification and structure identification of two phenolic glycosides from the roots of Incarvillea younghusbandii Sprague and their antioxidant activities.[Pubmed: 21748972]
Using a bioassay-guided fractionation technique, two compounds were isolated from the roots of Incarvillea younghusbandii Sprague through silica gel, reverse-phase C18 column chromatography and reverse-phase HPLC. Their structures were identified as acteoside (1) and isoacteoside (2) by ESI-MS, GC-MS, 1D- and 2D-NMR. 1 and 2 showed *OH scavenging capacity similar with benzoic acid, higher O2*- (or *OH) scavenging capacity than ascorbic acid, far higher hepatic LPO inhibitory activities than 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol (BHT) or ascorbic acid, and more powerful effect on protecting erythrocytes from oxidative damage than ascorbic acid. The *OH scavenging capacity was positively proportional to the concentrations of 1 and 2 ranging from 0.015 6 to 0.500 0 mg x mL(-1). The hepatic LPO inhibitory activities increased with the increasing concentrations of 1 and 2 from 0.001 9 to 0.250 0 mg x mL(-1), but decreased slightly with the increasing concentration from 0.250 0 to 1.0000 mg x L(-1).
[Chemical constituents of Incarvillea younghusbandii].[Pubmed: 20349717]
To study the chemical constituents of Incarvillea younghusbandii.
Isolation, purification and structure identification of antioxidant compound from the roots of Incarvillea younghusbandii Sprague and its life span prolonging effect in Drosophila melanogaster.[Pubmed: 18569713]
For the purpose of preventative treatment for oxidative stress-mediated diseases and anti-aging, a high-antioxidant compound was isolated from the roots of Incarvillea younghusbandii Sprague for the first time through silica gel column chromatography, reverse-phase C18 column chromatography and reverse-phase semi-preparative HPLC using a bioassay-guided fractionation technique, and was identified as acteoside by ESI-MS, GC-MS, 1D- and 2D-NMR. Feeding Drosophila melanogaster with acteoside, significant life span prolonging effect were achieved at the dosage range from 0.64 to 2.56 mg mL(-1). Positive relationships existed between the dosage and the life span prolonging effect. Otherwise, acteoside possess better life span prolonging effect in females than in males.


