Kadsura longipedunculata
Kadsura longipedunculata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Kadsura longipedunculata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN8166
Heteroclitin D140369-76-2
Instructions
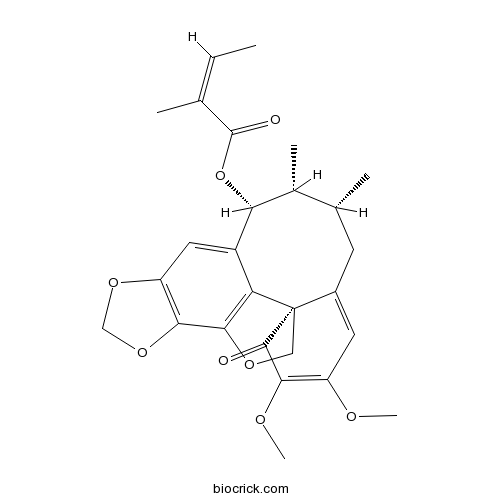
-
BCN6316
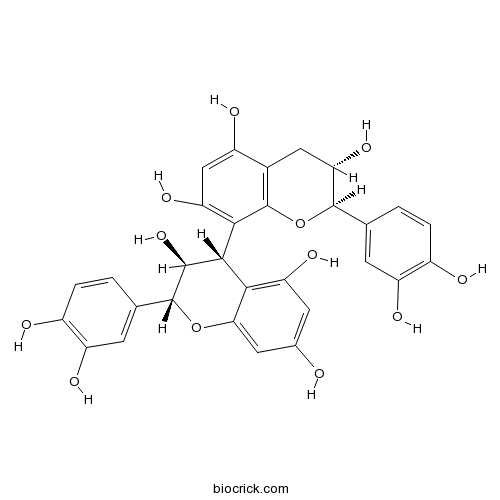
Procyanidin B323567-23-9
Instructions
Hepatoprotective Dibenzocyclooctadiene and Tetrahydrobenzocyclooctabenzofuranone Lignans from Kadsura longipedunculata.[Pubmed: 29595972]
Five new dibenzocyclooctadiene lignans, longipedlignans A-E (1-5), five new tetrahydrobenzocyclooctabenzofuranones (6-10), and 18 known analogues (11-28) were isolated from the roots of Kadsura longipedunculata. Compounds 6-10 are new spirobenzofuranoid-dibenzocyclooctadiene-type lignans. Their structures and absolute configurations were established using a combination of MS, NMR, and electronic circular dichroism data. Spirobenzofuranoids 6 and 15 showed moderate hepatoprotective activity against N-acetyl- p-aminophenol-induced toxicity in HepG2 cells with cell survival rates at 10 μM of 52.2% and 50.2%, respectively.
Assignment of the absolute configuration of hepatoprotective highly oxygenated triterpenoids using X-ray, ECD, NMR J-based configurational analysis and HSQC overlay experiments.[Pubmed: 28919469]
The plants of the genus Kadsura are widely distributed in China, South Korea, and Japan. Their roots and stems are traditionally used to treat blood diseases and pain. The main bioactive constituents of Kadsura longipedunculata comprise highly oxygenated triterpenoids. Schiartane-type nortriterpenoids showed anti-HIV, anti-HBV, and cytotoxic bioactivities. For such compounds, the absolute configuration influences the bioactivities, and hence its unambiguous determination is essential. In this work, the absolute configurations of three highly oxygenated schiartane-type nortriterpenoids were unequivocally assigned using X-ray, ECD, and J-based configuration analysis and HSQC overlay data.
Isolation of α-Amylase Inhibitors from Kadsura longipedunculata Using a High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography Target Guided by Centrifugal Ultrafiltration with LC-MS.[Pubmed: 27617987]
In this study, a high-speed counter-current chromatography (HSCCC) separation method target guided by centrifugal ultrafiltration with high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (CU-LC-MS) was proposed. This method was used to analyze α-amylase inhibitors from Kadsura longipedunculata extract. According to previous screening with CU-LC-MS, two screened potential α-amylase inhibitors was successfully isolated from Kadsura longipedunculata extract using HSCCC under the optimized experimental conditions. The isolated two target compounds (with purities of 92.3% and 94.6%) were, respectively, identified as quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (1) and protocatechuic acid (2) based on the MS, UV, and ¹H-NMR spectrometry data. To verify the inhibition of screened compounds, the inhibitory activities of quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (1) and protocatechuic acid (2) on α-amylase were tested, and it demonstrated that the experimental IC50 values of quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (1) and protocatechuic acid (2) were 28.8 and 12.5 μmol/L. These results proved that the hyphenated technique using CU-LC-MS and HSCCC was a rapid, competent, and reproductive method to screen and separate potential active compounds, like enzyme inhibitors from the extract of herbal medicines.
In silico Analysis and Experimental Validation of Lignan Extracts from Kadsura longipedunculata for Potential 5-HT1AR Agonists.[Pubmed: 26076134]
Kadsura longipedunculata (KL) has been widely used for the treatment of insomnia in traditional Chinese medicine. The aim of this study was to explore the mechanism of the sedative and hypnotic effects of KL.
[Molecular identification of aucklandiae radix, vladimiriae radix, inulae radix, aristolochiae radix and kadsurae radix using ITS2 barcode].[Pubmed: 25244738]
In order to identify Aucklandiae Radix, Vladimiriae Radix, Inulae Radix, Aristolochiae Radix and Kadsurae Radix using ITS2 barcodes, genomic DNA from sixty samples was extracted and the ITS2 (internal transcribed spacer) regions were amplified and sequenced. The genetic distances were computed using MEGA 5.0 in accordance with the kimura 2-parameter (K2P) model and the neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogenetic tree was constructed. The results indicated that for Aucklandiae Radix (Aucklandia lappa), Vladimiriae Radix (Vladimiria souliei and V. souliei var. cinerea), Inulae Radix (Inula helenium), Aristolochiae Radix (Aristolochia debilis) and Kadsurae Radix (Kadsura longipedunculata), the intra-specific variation was smaller than inter-specific one. There are 162 variable sites among 272 bp after alignment of all ITS2 sequence haplotypes. For each species, the intra-specific genetic distances were also smaller than inter-specific one. Furthermore, the NJ tree strongly supported that Aucklandiae Radix, Vladimiriae Radix, Inulae Radix, Aristolochiae Radix and Kadsurae Radix can be differentiated. At the same time, V. souliei (Dolomiaea souliei) and V. souliei var. cinerea( D. souliei var. cinerea) belonging to Vladimiriae Radix were clearly identified. In conclusion, ITS2 barcode could be used to identify Aucklandiae Radix, Vladimiriae Radix, Inulae Radix, Aristolochiae Radix and Kadsurae Radix. Our study may provide a scientific foundation for clinical safe use of the traditional Chinese medicines.
Identification of GABA A receptor modulators in Kadsura longipedunculata and assignment of absolute configurations by quantum-chemical ECD calculations.[Pubmed: 21889177]
A petroleum ether extract of Kadsura longipedunculata enhanced the GABA-induced chloride current (I(GABA)) by 122.5±0.3% (n=2) when tested at 100 μg/ml in Xenopuslaevis oocytes expressing GABA A receptors (α(1)β(2)γ(2S) subtype) in two-microelectrode voltage clamp measurements. Thirteen compounds were subsequently identified by HPLC-based activity profiling as responsible for GABA A receptor activity and purified in preparative scale. 6-Cinnamoyl-6,7-dihydro-7-myrceneol and 5,6-dihydrocuparenic acid were thereby isolated for the first time. The determination of the absolute stereochemistry of these compounds was achieved by comparison of experimental and calculated ECD spectra. All but one of the 13 isolated compounds from K. longipedunculata potentiated I(GABA) through GABA A receptors composed of α(1)β(2)γ(2S) subunits in a concentration-dependent manner. Potencies ranged from 12.8±3.1 to 135.6±85.7 μM, and efficiencies ranged from 129.7±36.8% to 885.8±291.2%. The phytochemical profiles of petroleum ether extracts of Kadsura japonica fruits (114.1±2.6% potentiation of I(GABA) at 100 μg/ml, n=2), and Schisandra chinensis fruits (inactive at 100 μg/ml) were compared by HPLC-PDA-ESIMS with that of K. longipedunculata.
Biological activity of the essential oil of Kadsura longipedunculata (Schisandraceae) and its major components.[Pubmed: 20663038]
The aim was to determine the chemical composition of the essential oil of Kadsura longipedunculata and the biological activity of the oil and its major components.
Three new compounds from Kadsura longipedunculata.[Pubmed: 18670115]
Two new tetrahydrofuran lignans, kadlongirins A and B (1, 2), a new cadinane-type sesquiterpenoid, 2,7-dihydroxy-11,12-dehydrocalamenene (3), together with seven known lignans, grandisin, fragransin B1, vladirol F, kadsuralignan C, otobaphenol, isoanwulignan, and 4-[4-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2,3-dimethylbutyl]-2-methoxy-phenol, were isolated from the leaves and stems of Kadsura longipedunculata. The structures of these new compounds were elucidated by spectroscopic methods. Compound 2 exhibited weak anti-human immunodeficiency virus-1 activity with an EC50 value of 16.0 microg/ml, and therapeutic index (TI) value of 6.7.
Isolation and structure elucidation of kadlongilactones C-F from Kadsura longipedunculata by NMR spectroscopy and DFT computational methods.[Pubmed: 17970593]
Four new triterpenoids, kadlongilactones C-F (2-5), containing a consecutive hexacyclic [7,7,5,6,6,6] ring system, were isolated from the leaves and stems of Kadsura longipedunculata. In comparison with the NMR data of kadlongilactones A (1) and D (3), a significant phenomena was discovered that ring D of 3 inverted from a half-chair in 1 to a half-boat conformation when the HO-16 group changed from alpha- to beta-orientation. The structures of 2-5 were established on the basis of detailed spectroscopic analysis, and DFT computational methods were applied in the structural validation of compounds 3 and 5. Compounds 1-4 showed significant cytotoxicity against A549, HT-29, and K562 cell lines with IC50 values of 0.49-3.61 microM in vitro.


