Kaempferia rotunda
Kaempferia rotunda
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Kaempferia rotunda
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
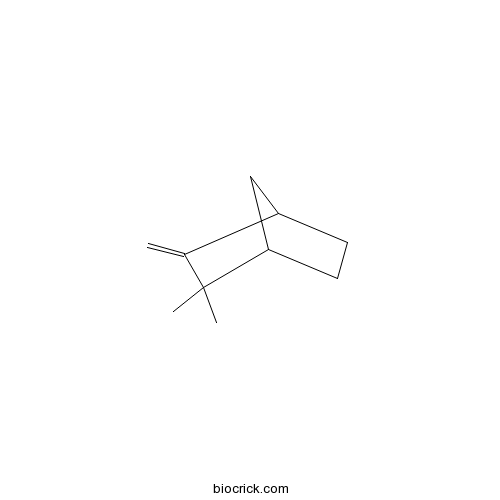
BCC9217
Camphene79-92-5
Instructions
Antitumor properties of a methyl-β-d-galactopyranoside specific lectin from Kaempferia rotunda against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells.[Pubmed: 28461165]
A lectin was isolated from the tuberous rhizome of Keampferia rotunda by using different chromatographic methods with the molecular weight of 21±1kDa. The lectin contained highest percentage of leucine and lowest percentage of tryptophan residues as determined by LC-MS. The lectin agglutinated mice and human erythrocytes and the hemagglutination activity was inhibited by Methyl-β-d-galactopyranoside. The lectin did not lose its activity in the presence of urea but the activity abolished completely when treated with EDTA. The lectin exhibited its activity at the pH ranging from 6.0 to 9.0 and in a temperature range of 30-80°C. Antiproliferative activity was studied against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma (EAC) and U87 cell lines. No inhibitory effect was observed against U87 cell line whereas 43.7% cell growth inhibition was observed in vitro against EAC cells at 160μg/ml. The lectin was injected (i.p.) in EAC bearing Swiss albino mice at the doses of 3.0 and 6.0mg/kg/day for five consecutive days and 41 and 59% of EAC cell growth inhibition was observed, respectively. The cell growth inhibition was due to the induction of apoptosis in the EAC cells which was confirmed by cell morphological study, caspase-3 inhibitor and apoptosis-related gene expression.


