Leontopodium leontopodioides
Leontopodium leontopodioides
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Leontopodium leontopodioides
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5906
Chlorogenic acid327-97-9
Instructions
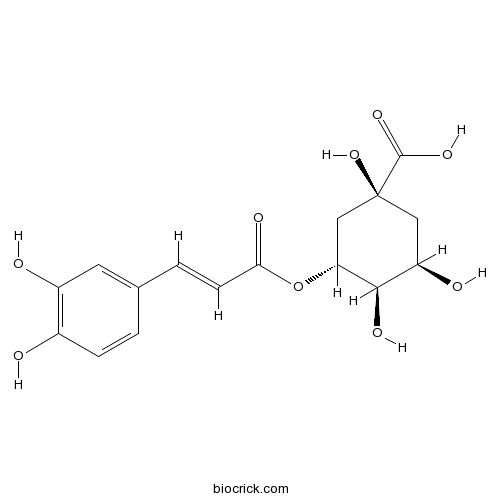
-
BCN5600
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
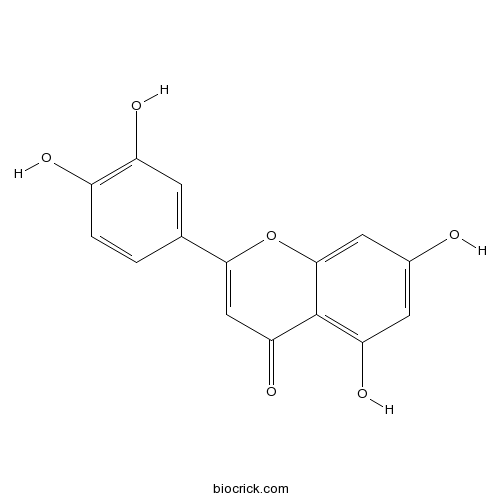
-
BCN5653
Kaempferol520-18-3
Instructions
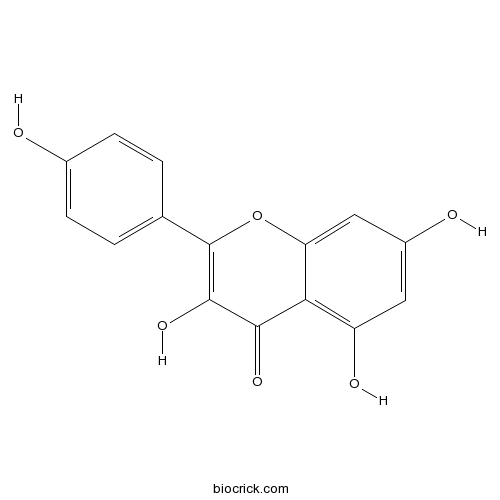
-
BCN4537
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
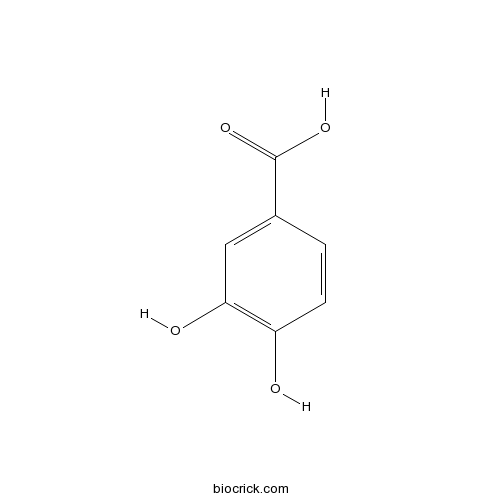
Chemical composition, antioxidant, antibacterial and cytotoxic activities of essential oil of Leontopodium leontopodioides (Willd.) Beauverd.[Pubmed: 29149803]
None
Isobenzofuranones from the aerial parts of Leontopodium leontopodioides (Wild.) Beauv.[Pubmed: 29074227]
A phytochemical investigation to obtain new triglyceride (TG) accumulation inhibitors resulted in the isolation of six new isobenzofuranones, leontopodiols A (1), B (2), leontopodiosides C (3), D (4), E (5), F (6), together with three known ones (7-9) from the aerial parts of Leontopodium leontopodioides (Willd.) Beauv. The structures of these isolates were identified by routine NMR experiments, optical rotation determination, electronic circular dichroism (ECD) calculation, along with chemical reaction. Moreover, compounds 1, 2, 5, and 7-9 displayed TG accumulation inhibitory effects on HepG2 cells.
Bioactive constituents from the whole plants of Leontopodium leontopodioides (Wild.) Beauv.[Pubmed: 28936642]
Five new compounds, leontoaerialosides A (1), B (2), C (3), D (4), and E (5) were obtained from the 70% EtOH extract of the whole plants of Leontopodium leontopodioides (Wild.) Beauv. Their structures were elucidated by chemical and spectroscopic methods. Moreover, compounds 4 and 5 showed significant effects on stimulating the hepatic glucose uptake in HepG2 cells.
Antagonistic effects of extracts from Artemisia rupetris L. and Leontopodium leontopodioides to CC chemokine receptor 2b (CCR2b).[Pubmed: 27478099]
The present study was designed to establish a suitable assay to explore CCR2b receptor antagonists from the natural products of Artemisia rupetris and Leontopodium leontopodioides. An aequorin assay was developed as a cell-based assay suitable for 384-well microplate and used for screening CCR2b receptor antagonists from natural products. Through establishing suitable conditions, the assay was shown to be suitable for screening of CCR2b receptor antagonists. Seven compounds were identified in preliminary screening. Five of them showed evident dose-response relationship in secondary screening. The structure-activity relationship study suggested that 7-position hydroxyl group of flavonoids was necessary, a polar group should be introduced on the 3-position, and the substituents on 2-position benzene ring of flavonoids have little influence on the potentency of the inhibition activity on CCR2b receptor. The ortho-position dihydroxyl structure in quinic acid compounds may be important. In conclusion, Compounds HR-1, 5, 7, and AR-20, 35 showed activity as antagonist of CCR2b receptor, which shed lights on the development of novel drugs as CCR2b receptor antagonists for preventing inflammation related diseases.
Phenolics from Leontopodium leontopodioides inhibiting nitric oxide production.[Pubmed: 22484093]
Two new compounds, a neolignan (1), and a benzofuran derivative (2), along with 6 known compounds (3-8), were isolated from the aerial parts of Leontopodium leontopodioides. The structures of the new compounds were elucidated as (7R,8S)-3,5'-dimethoxy-4',7-epoxy-8,3'-neolignane-5,9,9'-triol (1) and (2R)-12-hydoxy-4-methoxy-tremeton (2) on the basis of their spectroscopic data, respectively. All of the isolates were evaluated for their effects on the inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW264.7 macrophages and compounds 1 and 8 exhibited inhibitory activity with IC(50) values of 35.80 and 24.41 μM, respectively.
[Effect of Leontopodium leontopodioides (Willd.) Beauv. on inflammation induced by animal reversed passive arthus (RPA)].[Pubmed: 7945846]
The extract from Leontopodium leontopodioides 50-100mg/kg ip has been proved able to suppress the swelling of normal or adrenalectomised rat hind paws induced by RPA, and strongly inhibit the cutaneous hemorrhage of animals induced by RPA, lysosome or lysosome of broken membrane. It has also been shown that the extract 100 mg/kg ip can markedly inhibit the migration of leukocytes. These suggest that the anti-inflammatory properties of the extract are not dependent on the pituitary-adrenal system or membrane of lysosome.


