Libanotis buchtormensis
Libanotis buchtormensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Libanotis buchtormensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
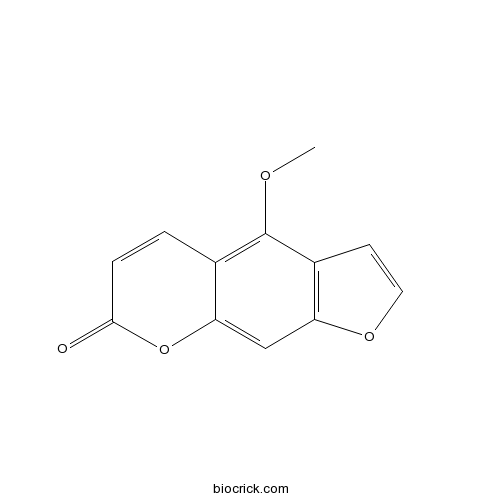
BCN2698
Oxypeucedanin hydrate2643-85-8
Instructions

-
BCN5582
Bergapten484-20-8
Instructions
Phylogeography of Libanotis buchtormensis (Umbelliferae) in Disjunct Populations along the Deserts in Northwest China.[Pubmed: 27442136]
In Northwest China, aridification and desert expansion play significant roles in promoting desert plant diversification and speciation. However, to date, little is known about the effects of the desert barrier on the population structure of montane, non-desert species in the area. In this study, we sequenced chloroplast DNA regions (trnL-trnF and trnS-trnG) and a nuclear gene (rpb2) to investigate the population differentiation and phylogeographical history of Libanotis buchtormensis, a perennial montane species possessing a disjunct distribution at the periphery of the central desert. In total, 23 chloroplast haplotypes and 24 nuclear haplotypes were recovered from the 21 natural populations and six hebarium specimens. Phylogenetic analysis based on the combined plastid and nuclear dataset revealed two distinct lineages of L. buchtormensis, which inhabit the disjunct areas on both sides of the desert zone. The molecular dating analysis indicated that the divergence between the southeastern and the northwestern populations occurred in the middle Pleistocene, concomitantly with the desert expansion. The geographical vicariance likely contributed to the present disjunct distribution of L. buchtormensis across the deserts in Northwest China. Populations in the southeastern region may have migrated from the northwestern region, and seem to be a peripheral distribution of L. buchtormensis.
Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of essential oils from Acantholippia deserticola, Artemisia proceriformis, Achillea micrantha and Libanotis buchtormensis against phytopathogenic bacteria and fungi.[Pubmed: 26404704]
Essential oils from aerial parts of Acantholippia deserticola, Artemisia proceriformis, Achillea micrantha and Libanotis buchtormensis were analysed by GC-MS. The major compounds identified were β-thujone (66.5 ± 0.2%), and trans-sabinyl acetate (12.1 ± 0.2%) in A. deserticola; α-thujone (66.9 ± 0.4%) in A. proceriformis; 1,8-cineole (26.9 ± 0.5%), and camphor (17.7 ± 0.3%) in A. micrantha and cis-β-ocimene (23.3 ± 0.3%), and trans-β-ocimene (18.4 ± 0.2%) in L. buchtormensis. The oils showed a weak antimicrobial effect (MIC100 > 1.5 mg/ml) on most phytopathogens tested. A moderate antimicrobial activity (MIC100 between 0.5 and 1.5 mg/ml) was displayed by the oils of A. deserticola, A. micrantha and L. buchtormensis on Septoria tritici and by the oil of A. deserticola on Septoria glycine. The antimicrobial activity was associated to the contents of β-thujone, trans-sabinyl acetate and trans-sabinol. Our results indicate that the tested essential oils have little inhibitory potency not suitable for use as plant protection products against the phytopathogens assayed.
Comparative study of pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of osthole in rats after oral administration of pure osthole and Libanotis buchtormensis supercritical extract.[Pubmed: 23142197]
Libanotis buchtormensis is the source of an important traditional medicine from Shaanxi province of China used in the treatment of many illnesses. Libanotis buchtormensis supercritical extract (LBSE) has analgesic, sedative and anti-inflammatory qualities. Osthole is one of the major bioactive components of LBSE; it is known for its significant anti-tumor, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory properties, it also alleviates hyperglycemia.


