Livistona chinensis
Livistona chinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Livistona chinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
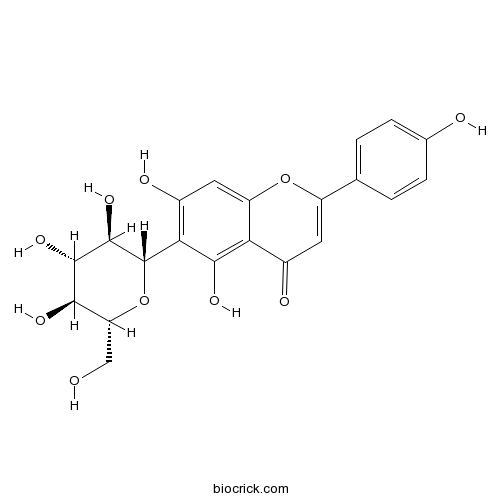
BCN5441
Isovitexin38953-85-4
Instructions
-
BCN4985
Luteolin-6-C-glucoside4261-42-1
Instructions

-
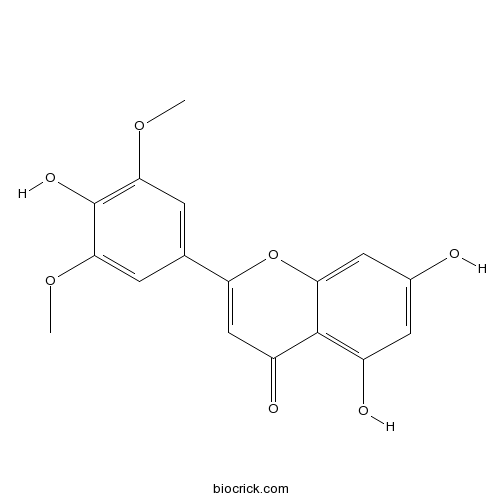
BCN5656
Tricin520-32-1
Instructions
A new arylbenzofuran derivative functions as an anti-tumour agent by inducing DNA damage and inhibiting PARP activity.[Pubmed: 26041102]
We previously reported that 7-hydroxy-5, 4'-dimethoxy-2-arylbenzofuran (HDAB) purified from Livistona chinensis is a key active agent. The present study investigated the function and molecular mechanism of HDAB. HDAB treatment of cervical cancer cells resulted in S phase arrest and apoptosis, together with cyclin A2 and CDK2 upregulation. Cyclin A2 siRNA and a CDK inhibitor efficiently relieved S phase arrest but increased the apoptosis rate. Mechanistic studies revealed that HDAB treatment significantly increased DNA strand breaks in an alkaline comet assay and induced ATM, CHK1, CHK2 and H2A.X phosphorylation. Wortmannin (a broad inhibitor of PIKKs) and CGK733 (a specific ATM inhibitor), but not LY294002 (a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor) or NU7026 (a DNA-PK specific inhibitor), prevented H2A.X phosphorylation and γH2A.X-positive foci formation in the nuclei, reversed S phase arrest and promoted the HDAB-induced apoptosis, suggesting that HDAB is a DNA damaging agent that can activate the ATM-dependent DNA repair response, thereby contributing to cell cycle arrest. In addition, molecular docking and in vitro activity assays revealed that HDAB can correctly dock into the hydrophobic pocket of PARP-1 and suppress PARP-1 ADP-ribosylation activity. Thus, the results indicated that HDAB can function as an anti-cancer agent by inducing DNA damage and inhibiting PARP activity.
Study on life parameters of the invasive species Octodonta nipae (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on different palm species, under laboratory conditions.[Pubmed: 25195440]
In southeastern China, the invasion of the nipa palm hispid Octodonta nipae (Maulik) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) results in devastating damage to palms. Host plants play an important role in the population increases and outbreaks of O. nipae. O. nipae could not complete its development on the Majestic palm (Ravenea rivularis Jumelle & Perrier), and females did not lay eggs on Chinese fan palm (Livistona chinensis R. Brown). However, this insect species both completed development and laid eggs on Chinese windmill palm (Trachycarpus fortunei (Hooker) H. Wendland), Canary Island date palm (Phoenix canariensis Chabaud), and pygmy date palm (Phoenix roebelenii O' Brien). The demographic characteristics of O. nipae reared on Chinese windmill palm, Canary Island date palm, and pygmy date palm were compared with an age-stage, two-sex life table. In this study, the developmental periods from egg to adult varied from 42.1 d on Chinese windmill palm to 49.8 d on pygmy date palm. The survivorship from egg to adult on Chinese windmill palm, Canary Island date palm, and pygmy date palm was 77.5, 79.4, and 66.7%, respectively. Although the adult longevity and the mean fecundity for individuals reared on Chinese windmill palm, Canary Island date palm, and pygmy date palm were not significantly different, there were significant differences in the intrinsic rate of increase, the finite rate, and the mean generation time among palm species, and the values of intrinsic rate of increase and finite rate were higher for populations reared on Chinese windmill palm and Canary Island date palm (0.0313 and 1.0318 d(-1) and 0.0278 and 1.0282 d(-1), respectively) and lower for populations reared on pygmy date palm (0.0192 and 1.0194 d(-1)). However, mean generation time was shorter on Chinese windmill palm (124.11 d) and Canary Island date palm (129.62 d) and longer on pygmy date palm (166.03 d). Our study indicated that different hosts affected life parameters of O. nipae, with the most preferred hosts being the Chinese windmill palm and Canary Island date palm. These results may be useful for the design of culture management strategies for O. nipae.
Livistona chinensis seeds inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma angiogenesis in vivo via suppression of the Notch pathway.[Pubmed: 24573440]
Livistona chinensis seeds have been used for centuries to clinically treat various types of cancer. Our published data suggest that Livistona chinensis seeds are able to inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) growth in vitro and in vivo via promotion of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. To further elucidate the molecular mechanisms of its antitumor activity, in the present study, we used an HCC xenograft mouse model to evaluate the effect of an ethanol extract of Livistona chinensis seeds (EELC) on tumor angiogenesis and on the activation of the Notch pathway. Intratumoral microvessel density (MVD) in HCC xenograft mouse tumors was evaluated via immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for CD31. The mRNA and protein expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A), VEGFR-2, Notch, Dll4 and Jagged1 was evaluated using RT-PCR and IHC, respectively. We found that EELC profoundly reduced MVD in the HCC mouse tumors, demonstrating the in vivo inhibitory effect of EELC on tumor angiogenesis. In addition, EELC treatment reduced the expression of VEGF-A and VEGFR-2 in tumor tissues. Furthermore, EELC treatment inhibited the expression of Notch, Dll4 and Jagged1. Our findings suggest that Livistona chinensis seeds inhibit tumor angiogenesis through suppression of the Notch pathway.
The phenolics from the roots of Livistona chinensis show antioxidative and obsteoblast differentiation promoting activity.[Pubmed: 24378966]
This study investigated the antioxidative and obsteoblast differentiation promoting activity of the phenolics isolated from the 70% ethanol extract of the roots of Livistona chinensis. Two new phenolics, (2R,3R)-3,5,6,7,3',4'-hexahydroxyflavane (1), and phenanthrene-2,4,9-triol (2), together with six known phenolics 3-8, were isolated and identified on the basis of extensive spectroscopic analysis. The antioxidative and obsteoblast differentiation promoting abilities of the compounds 1-3, 7-8 were tested, the phenolics 1-3, 7 showed effects on proliferation of osteoblastic cells and antioxidative activity of 3.125-50 µg/mL. In addition, the phenolics 1-3 observably increased alkaline phosphatase activity, osteocalcin content and hydroxyproline content in osteoblastic cells. Phenolic 1 at 12.5 µg/mL concentration significantly increased the area of nodules by about 9.35-fold. The antioxidative activity results indicated that the anti-osteoporosis effects of these phenolics may be linked to a reduction of oxidative stress. The observed effects of these phenolics on bone formation by rat osteoblastic cells suggest that these phenolics may have beneficial effects on bone health.
A new species of Callispa Baly (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae, Cassidinae, Callispini) infesting coconut palm ( Cocos nucifera L.) in India.[Pubmed: 23653522]
Callispa keram sp. n. infesting coconut palm (Cocos nucifera L.) in Kerala, India is described and illustrated. Livistona chinensis R.Br. and Syagrus romanzoffiana (Cham.) Glassman are reported as additional host plants.
Livistona chinensis seed suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth through promotion of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis.[Pubmed: 23467659]
The Livistona chinensis seed has been used for centuries to clinically treat various types of cancer. However, the precise mechanism of its anticancer activity remains to be elucidated. In the present study, we evaluated the efficacy of the ethanol extract of Livistona chinensis seed (EELC) against tumor growth using a hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) mouse xenograft model and an HCC cell line, HepG2, and investigated the molecular mechanisms mediating its biological activities. We found that EELC inhibited HCC growth both in vivo and in vitro, without apparent signs of toxicity. In addition, EELC treatment resulted in the induction of HCC cell apoptosis. Moreover, EELC-induced apoptosis was accompanied by the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3, and increase in the pro-apoptotic Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Our findings suggest that promotion of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in cancer cells may be one of the mechanisms by which the Livistona chinensis seed is effective in cancer treatment.
Screening and quantitative analysis of antioxidants in the fruits of Livistona chinensis R. Br using HPLC-DAD-ESI/MS coupled with pre-column DPPH assay.[Pubmed: 22980875]
In this study, a high performance liquid chromatography-photo diode array detection-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-DAD/ESI-MS) with pre-column DPPH assay is developed for screening the antioxidant components in the fruits of Livistona chinensis R. Br. Accordingly, six antioxidative flavonoids are identified as orientin, isoorientin, vitexin, isovitexin, isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside and tricin in methanolic extract of L. chinensis fruits, based on their mass spectra and fragmentation patterns. To the best of our knowledge, orientin, isoorientin, isovitexin and isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside were found firstly in this plant. The free radical scavenging activity of the six antioxidants found is further examined by off-line DPPH assay. The results indicated that the free radical scavenging activity of orientin and isoorientin are stronger than those of two antioxidative drugs, vitamin C and baicalin. In addition, an HPLC-DAD method is firstly established for simultaneous determination of the six antioxidants in L. chinensis fruits. Tricin was found to be the major component in L. chinensis fruits.
Cytotoxic ceramides and glycerides from the roots of Livistona chinensis.[Pubmed: 22305945]
A 70% ethanol extract of the roots of Livistona chinensis has been investigated, led to the isolation of 13 compounds, including a new ceramide, (2S,3S,4R,9Z)-2-[(2R)-2-hydroxytricosanoylamino]-9-octadecene-1,3,4-triol (2), a new glycosyl ceramide, 1-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(2S,3S,4R,9Z)-2-[(2R)-2-hydroxydocosanoylamino]-9-octadecene-1,3,4-triol (3), three new monoacylglycerols, 1-(34-hydroxytetratriacontanoyl)-sn-glycerol (9), 1-[nonadeca-(9Z,12Z)-dienoyl]-sn-glycerol (10), and 1-[12-hydroxypentatriaconta-(13E,15Z)-dienoyl]-sn-glycerol (11), a new diacylglycerol, 1-(heptadeca-6Z,9Z-dienoyl)-3-(octadeca-6Z,9Z,12Z-trienoyl)-sn-glycerol (12), as well as a new diacylglycerol aminoglycoside, 1-octadecanoyl-2-nonadecanoyl-3-O-(6-amino-6-deoxy)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-sn-glycerol (13). The structures of new compounds were elucidated, based on spectroscopic, zymologic and chemical methods. Among the compounds tested, compounds 3, 4 and 13 showed significantly antiproliferative effects against the human tumor cell lines (K562, HL-60, HepG2, and CNE-1) with the IC₅₀ of 10-65 μM. To our knowledge, this is first report of the occurrence of ceramides and acylglycerols in the genus Livistona.


