Ludwigia octovalvis
Ludwigia octovalvis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Ludwigia octovalvis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5533
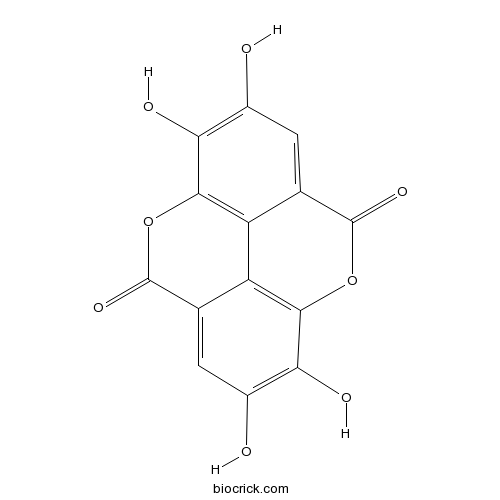
Ellagic acid476-66-4
Instructions
Ludwigia octovalvis (Jacq.) raven extract supplementation enhances muscle glycogen content and endurance exercise performance in mice.[Pubmed: 29962382]
Ludwigia octovalvis extract (LOE) is a widely used traditional Chinese herbal medicine. To date, few studies have demonstrated the effect of LOE supplementation on exercise performance, physical fatigue and biochemical profile. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the potential beneficial effects of LOE extract on fatigue and ergogenic functions following physiological challenge. Male ICR mice from 3 groups (n=8 per group) were orally administered LOE for 4 weeks at 0 (vehicle), 61.5 (LOE-1X) or 307.5 (LOE-5X) mg/kg/day. LOE supplementation was able to dose-dependently increase endurance swimming time (P<0.0001) and decrease levels of serum lactate (P=0.0022), ammonia (P<0.0001), creatine kinase (P<0.0001), blood urea nitrogen (P<0.0001) and glucose utilization (P<0.0001) after acute exercise challenge. The glycogen in gastrocnemius muscle also increased with LOE treatment in a dose-dependent manner (P<0.0001). Biochemically, AST, ALT, LDH, CK, BUN, creatinine and UA levels were decreased with LOE treatment. Our study shows that 4-week supplementation with LOE increases muscle glycogen content storage to enhance exercise performance and anti-fatigue effects.
Statistical optimization of the phytoremediation of arsenic by Ludwigia octovalvis- in a pilot reed bed using response surface methodology (RSM) versus an artificial neural network (ANN).[Pubmed: 29723047]
None
The Role of Leaf Volatiles of Ludwigia octovalvis (Jacq.) Raven in the Attraction of Altica cyanea (Weber) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae).[Pubmed: 28695387]
Larvae and adults of Altica cyanea (Weber) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) feed on the rice-field weed Ludwigia octovalvis (Jacq.) Raven (Onagraceae), commonly known as willow primrose, which is considered a biocontrol agent of the weed. Volatile organic compounds from undamaged plants, plants after 4, 12, and 36 h of continuous feeding by A. cyanea larvae or adult females and after mechanical damaging were identified by GC-MS and GC-FID analyses. Twenty nine compounds were identified from undamaged plants. 2Z-Penten-1-ol, geraniol, and 1-tridecanol were present in all plants damaged by larvae. In contrast, feeding by adults caused the release of 2Z-penten-1-ol only after 12 and 36 h; whereas geraniol and 1-tridecanol appeared only after 36 h. Farnesyl acetone was detected after 12 and 36 h of feeding by larvae and after 36 h of feeding by adults. Farnesene was detected after 36 h of feeding by larvae and adults. Linalool was unique after 36 h of feeding by larvae. In Y-shaped glass tube olfactometer bioassays, A. cyanea females were attracted to volatiles after 36 h of feeding by larvae or adults compared to volatiles released by undamaged plants. The insects were attracted to five synthetic compounds: 3-hexanol, α-pinene, linalool oxide, geraniol, and phytol. Synthetic blends were more attractive than individual compounds. Compared to undamaged plants, volatiles released by plants, damaged by conspecific individuals, were more attractive to A. cyanea females, due to elevated emissions of 3-hexanol, α-pinene, linalool oxide, geraniol, and phytol.
Ludwigia octovalvis extract improves glycemic control and memory performance in diabetic mice.[Pubmed: 28666833]
Ludwigia octovalvis (Jacq.) P.H. Raven (Onagraceae) extracts have historically been consumed as a healthful drink for treating various conditions, including edema, nephritis, hypotension and diabetes.
Long-chain alkanes and fatty acids from Ludwigia octovalvis weed leaf surface waxes as short-range attractant and ovipositional stimulant to Altica cyanea (Weber) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae).[Pubmed: 28132659]
The importance of leaf surface wax compounds from the rice-field weed Ludwigia octovalvis (Jacq.) Raven (Onagraceae) was determined in the flea beetle Altica cyanea (Weber) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Extraction, thin layer chromatography and GC-MS and GC-FID analyses of surface waxes of young, mature and senescent leaves revealed 20, 19 and 19 n-alkanes between n-C15 and n-C35, respectively; whereas 14, 14 and 12 free fatty acids between C12:0 and C22:0 fatty acids were identified in young, mature and senescent leaves, respectively. Tricosane was predominant n-alkane in young and mature leaves, whilst eicosane predominated in senescent leaves. Heneicosanoic acid, palmitic acid and docosanoic acid were the most abundant free fatty acids in young, mature and senescent leaves, respectively. A. cyanea females showed attraction to 0.25 mature leaf equivalent surface waxes compared with young or senescent leaves in a short glass Y-tube olfactometer bioassay. The insects were attracted to a synthetic blend of 0.90, 1.86, 1.83, 1.95, 0.50 and 0.18 µg ml-1 petroleum ether of hexadecane, octadecane, eicosane, tricosane, palmitic acid and alpha-linolenic acid, respectively, comparable with the proportions as present in 0.25 mature leaf equivalent surface waxes. A. cyanea also laid eggs on a filter paper moistened with 0.25 mature leaf equivalent surface waxes or a synthetic blend of 0.90, 1.86, 1.83, 1.95, 0.50 and 0.18 µg ml-1 petroleum ether of hexadecane, octadecane, eicosane, tricosane, palmitic acid and alpha-linolenic acid, respectively. This finding could provide a basis for monitoring of the potential biocontrol agent in the field.
Complete Plastome Sequence of Ludwigia octovalvis (Onagraceae), a Globally Distributed Wetland Plant.[Pubmed: 27856583]
Here, we present the first plastome of Ludwigia octovalvis (Onagraceae, Myrtales) as well as the first plastome in the subfamily Ludwigioideae. This genome is notable for its contracted inverted repeat regions and an expanded small single-copy region compared to other species in the orders Myrtales and Geraniales.
Phytoremediation of contaminated soils containing gasoline using Ludwigia octovalvis (Jacq.) in greenhouse pots.[Pubmed: 26330312]
Greenhouse experiments were carried out to determine the phytotoxic effects on the plant Ludwigia octovalvis in order to assess its applicability for phytoremediation gasoline-contaminated soils. Using plants to degrade hydrocarbons is a challenging task. In this study, different spiked concentrations of hydrocarbons in soil (1, 2, and 3 g/kg) were tested. The results showed that the mean efficiency of total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) removal over a 72-day culture period was rather high. The maximum removal of 79.8 % occurred for the 2 g/kg concentration, while the removal rate by the corresponding unplanted controls was only (48.6 %). The impact of gasoline on plants included visual symptoms of stress, yellowing, growth reduction, and perturbations in the developmental parameters. The dry weight and wet weight of the plant slightly increased upon exposure to gasoline until day 42. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) indicated change to the root and stem structure in plant tissue due to the direct attachment with gasoline contaminated compared to the control sample. The population of living microorganisms in the contaminated soil was found to be able to adapt to different gasoline concentrations. The results showed that L. octovalvis and rhizobacteria in gasoline-contaminated soil have the potential to degrade organic pollutants.
Immune-stimulating properties of 80% methanolic extract of Ludwigia octovalvis against Shiga toxin-producing E. coli O157:H7 in Balb/c mice following experimental infection.[Pubmed: 26091966]
Ludwigia octovalvis is an aquatic plant widely distributed throughout the tropical and sub-tropical regions. It is commonly consumed as a health drink and traditionally used for treating various ailments such as dysentery, diarrhea, diabetes, nephritisn and headache. No information is available on its in vivo antibacterial activity against an important foodborne pathogen, Shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli O157:H7.


