Nervilia fordii
Nervilia fordii
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Nervilia fordii
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2280
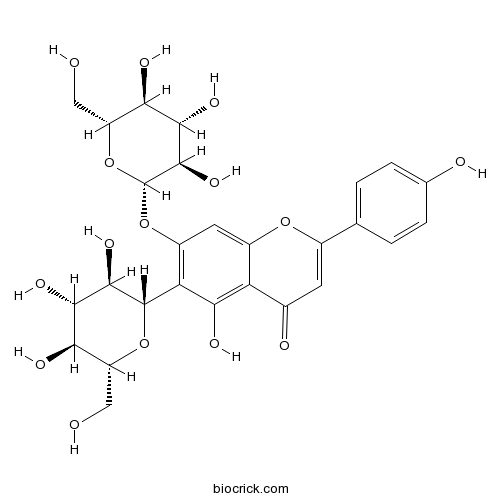
Saponarin20310-89-8
Instructions
-
BCN4546
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid99-96-7
Instructions

Structural characterization and immunomodulating activities of a novel polysaccharide from Nervilia fordii.[Pubmed: 29578012]
Nervilia fordii (Hance) Schltr. has been widely used as a medicinal and edible herb in Southwest China and Southeast Asia. In this study, NFP-1, a new water-soluble polysaccharidewith a purity of 97.8%, was purified from water extract of Nervilia fordii by DEAE-cellulose and Sephadex G-100 chromatography. NFP-1 has a relative molecular weight of 950 kDa determined by high performance gel-permeation chromatography (HPGPC). Its monosaccharide compositions were analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) after pre-column derivatizing its hydrolysate with 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP). NFP-1 mainly consists of galactose, arabinose, rhamnose, and galacturonic acid. Based on FT-IR, methylation and GC-MS analysis, and NMR, the structure unit of NFP-1 was established as →4)-α-Rhap-(2→ 4)-α-GalpA-(1→2)-α-Rhap-(1→2)-α-Rhap-(4→1)-β-Galp-T containing two branch chains of →2,4)-α-Rhap-(1→5)-α-Araf-(1→3)-α-Araf-(1→, and →2,4)-α-Rhap-(1→4)-β-Galp-(1→. The immunomodulatory assays revealed the dual-functionalities of NFP-1. NFP-1 could significantly induce the secretion of nitric oxide (NO), and promote the secretions of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in RAW264.7 macrophages. NFP-1 could also significantly inhibit the production of NO, depress the secretions of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in RAW264.7 macrophages activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and promote the production of IL-10 meanwhile. Our study suggested that Nervilia fordii could be an ideal medicinal or functional food due to its dual immunomodulatory activities.
[Two new flavonoid glycosides from Nervilia fordii].[Pubmed: 29883073]
Two new flavonoid glycosides were isolated from the aerial parts of Nervilia fordii by various chromatographies such as D101 macroporous resin, ODS and preparative HPLC chromatographic techniques. Their structures were elucidated as rhamnocitrin-3-O-β-glucopyranosyl-4’-O-β-galactosyl-(1→3)-glucopyranoside(1) and 7,3’-di-O-methylquercetin-4’-O-[β-galactosyl-(1→3)-β-glucopyranosyl]-3-O-β-glucopyranoside(2) on the basis of extensive spectroscopic analyses, including 1D-, 2D-NMR, HR-ESI-MS and analytical hydrolysis.
[Effect of Nutrient Solution in Soilless Cultivation on Growth, Antioxidase Activities and Amino Acid Contents of Nervilia fordii].[Pubmed: 26080491]
To select the best formula for soilless cultivation of Nervilia fordii.
A new labdane diterpenoid glycoside from Nervilia fordii.[Pubmed: 25151736]
To study the chemical constituents of Nervilia fordii (Hance) Schltr., various chromatographic methods were used, including D101 macroporous resin, silica gel, ODS and preparative HPLC chromatographic techniques. A new labdane diterpenoid glycoside named as nervilifordoside A was isolated from 60% EtOH extract of Nerviliafordii. The structure of compound 1 was elucidated as 12, 17-epoxy-3-hydroxy-17-methoxy-labdan-13-en-16, 15-olide 3-O-alpha-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 --> 2)-O-beta-glucopyranoside on the basis of HR-MS, 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic data as well as chemical methods.
A flavonoid 8-C-glycoside and a triterpenoid cinnamate from Nervilia fordii.[Pubmed: 23844721]
One new flavonoid glycoside (1) and one new triterpenoid cinnamate (2) were isolated from Nervilia fordii. The structures of 1 and 2 were determined by extensive NMR and HRESIMS to be 7-O-β-d-glucopyranosylapigenin-8-C-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 2)-β-d-glucopyranoside and 24(S/β)-dihydrocycloeucalenol-3-(Z)-p-hydroxycinnamate, respectively.
Five new flavonoid glycosides from Nervilia fordii.[Pubmed: 23659497]
Five new flavonoid glycosides, namely nervilifordins F-J (1-5), were isolated from the 60% EtOH extract of the aerial parts of Nervilia fordii, along with three first isolated flavonoids (7, 8, and 13) and five known flavonoids (6, 9-12). The structures of new compounds were elucidated on the basis of 1D and 2D NMR and MS studies. Their anti-inflammatory activities were tested by measuring their inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW264.7 macrophages. Compounds 2 and 5 showed interesting inhibition effects with their EC50 values of 15.15 μM and 14.80 μM, respectively.
Three new cycloartane glycosides from Nervilia fordii.[Pubmed: 22428755]
From the water-soluble extract of the aerial part of herbal plant Nervilia fordii, three new cycloartane glycosides, named as nervisides A (1), B (2), and C (3), were isolated. Their structures were elucidated through a combination of spectroscopic analysis and hydrolysis. At the same time, the new compounds were tested for their cytotoxicities in vitro against human tumor cell lines (CNE, Hep-2, and HepG2) using MTT method.
[Simultaneous determination of seven flavonoids in Nervilia fordii with HPLC].[Pubmed: 22242457]
The study is to develop an HPLC method for simultaneous determination of rhamnazin (1), rhamnocitrin (2), rhamnetin (3), rhamnazin-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (4), rhamnazin-3-O-beta-D-xylopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranoside (5), rhamnazin-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranoside (6), and rhamnocitrin-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranoside (7) in Nervilia fordii. The separation was performed on a Kromasil C18 column (250 mm x 4.6 mm, 5 microm) with 0.4% phosphoric acid-acetonitrile as the mobile phase in a gradient elution at a flow rate of 1.0 mL x min(-1). The detect wavelength was set at 256 nm, and the column temperature was set at 40 degrees C. There were good linear relationships between the logarithm values of concentrations and those of the peak areas of seven flavonoids (1-7) in the range of 0.55-70.00 microg x mL(-1) (r = 0.9997), 0.86-110.00 microg x mL(-1) (r = 0.9997), 0.39-50.00 microg x mL(-1) (r = 0.999 7), 0.55-70.00 microg x mL(-1) (r = 0.999 5), 1.33-170.00 microg x mL(-1) (r = 0.9998), 1.33-170.00 microg x mL(-1) (r = 0.9998), 0.16-20.00 microg x mL(-1) (r = 0.9995), respectively. The recoveries of the seven flavonoids were between 97.19%-99.45%, the relative standard deviations (RSDs) were between 0.91%-2.69%. The established method is rapid, accurate with high repeatability, which could provide scientific evidence for the quality control of Nervilia fordii.
[Effect of Nervilla fordii on lung aquaporin 1 and 5 expression in endotoxin-induced acute lung injury rat].[Pubmed: 21038658]
To explore the protective mechanism of Nervilia fordii (NF) by observing the effect of its pretreatment on lung aquaporin 1 and 5 (AQP-1, AQP-5) expression in rats with endotoxin-induced acute lung injury (ALI).


