Opuntia dillenii
Opuntia dillenii
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Opuntia dillenii
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5890
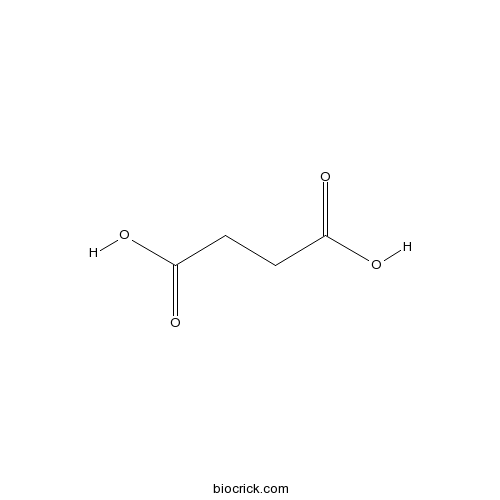
Succinic acid110-15-6
Instructions
-
BCN4546
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid99-96-7
Instructions

Fresh Fruit Juice of Opuntia dillenii Haw. Attenuates Acetic Acid-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Rats.[Pubmed: 29958056]
The present study aimed to evaluate the protective effect of fresh fruit juice of Opuntia dillenii Haw. (FJOD) on acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats. Fresh FJOD (2.5 and 5 ml/kg) and sulfasalazine (100 mg/kg) were given orally for seven consecutive days prior to colitis induction on the eighth day by intrarectal acetic acid (4% v/v) administration. Macroscopic, clinical activity scoring, biochemical, and histopathological examinations of colon were used to assess colonic damage. FJOD and sulfasalazine treatment significantly attenuated the macroscopic damage, clinical activity score, and wet weight of the colon when compared to disease control and further showed significantly reduced levels of myeloperoxidase, malondialdehyde, and serum lactate dehydrogenase and enhanced colonic levels of reduced glutathione. The protective effect of FJOD may be attributed to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities in ulcerative colitis. The observed effects may be due to the presence of phenolics, flavonoids, and betalains in the fruit juice of Opuntia dillenii.
Opuntia dillenii (Ker-Gawl) Haw cladode mucilage: Physico-chemical, rheological and functional behavior.[Pubmed: 27987807]
None
Extraction of Opuntia dillenii Haw. Polysaccharides and Their Antioxidant Activities.[Pubmed: 27886148]
None
Extraction optimization by response surface methodology of mucilage polysaccharide from the peel of Opuntia dillenii haw. fruits and their physicochemical properties.[Pubmed: 27474580]
In this study, response surface methodology (RSM) was employed to optimize microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) technology of mucilage polysaccharide from the peel of Opuntia dillenii haw. fruits (OFPP), and the physicochemical characteristics of OFPP were also investigated. The three parameters were the ratio of water to raw material (30-40ml/g), microwave power (300-400W) and extraction time (120-180s). The results indicated that the yield of OFPP was 15.62±0.37% under the optimum extraction conditions. Compared with MAE, the OFPP yield by hot water extraction (HWE) was 13.36±0.71%. In addition, the rheological properties of OFPP were also explored. The OFPP obtained by HWE exhibited a lower viscosity compared with that by MAE. The FT-IR spectra analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) revealed that there were strong interactions between Ca(2+) and OFPP, which resulted in the high viscosity, different microstructure and thermal stability of OFPP.
Technological characteristics and selected bioactive compounds of Opuntia dillenii cactus fruit juice following the impact of pulsed electric field pre-treatment.[Pubmed: 27211645]
Selected technological characteristics and bioactive compounds of juice pressed directly from the mash of whole Opuntia dillenii cactus fruits have been investigated. The impact of pulsed electric fields (PEF) for a non-thermal disintegration on the important juice characteristics has been evaluated in comparison to microwave heating and use of pectinases. Results showed that the cactus juice exhibited desirable technological characteristics. Besides, it also contained a high amount of phenolic compounds being the major contributors to the overall antioxidant activity of juice. HPLC-DAD/ESI-MS(n) measurements in the fruits' peel and pulp showed that isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside was determined as the single flavonol found only in the fruit's peel. Treating fruit mash with a moderate electric field strength increased juice yield and improved juice characteristics. Promisingly, the highest release of isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside from fruit's peel into juice was maximally achieved by PEF.
Opuntia dillenii cladode: Opuntiol and opuntioside attenuated cytokines and eicosanoids mediated inflammation.[Pubmed: 26900126]
Opuntia dillenii Haw (Nagphana) traditionally used against inflammation. The present study addressed the anti-inflammatory activity of O. dillenii derived methanol extract, fractions and pure compounds and their underlying mechanism of action.
[Therapeutic effects and mechanisms of Opuntia dillenii Haw on atherosclerosis of rats].[Pubmed: 26223127]
The research aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects and mechanisms of Opuntia dillenii Haw polysaccharide (OPS) on atherosclerosis of rats. First atherosclerotic rat models were established by high-fat and high-calcium diet. Thirty days later, the rats were treated with low dosage of OPS (0.2 g x kg(-1) x d(-1)) or high dosage of OPS (0.4 g x kg(-1) x d(-1)) by intraperitoneal injection for 60 days continuously. At the end of treatment, thoracic aorta rings were prepared and vasorelaxation of rat thoracic aorta in different experiment groups were determined by using 620M multi wire myograph system in vitro. Blood and livers of rats were collected. Then plasma levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG) and low density lipoprotein (LDL) of rats were separately determined using whole automatic biochemical analyzer; protein level of hepatic apolipoprotein B (ApoB) and that of hepatic diglyceride acyltransferase (Dgat1) were measured by Western Blot technique. Results showed that the ability of rat thoracic aorta to relax decreased markedly in the model group compared with that in the normal group, and significant differences existed in vasorelaxation ratios induced by different concentrations of carbamylcholine chloride (Carb) between these two groups (P < 0.01). After OPS treatment, the ability of rat thoracic aorta to relax improved markedly, the vasorelaxation ratios induced by Carb at 5 and 10 μmol x L(-1) were respectively 0.34 ± 0.08 and 0.62 ± 0.15 in the group treated with low dosage of OPS, while the ratios induced by Carb at 1 and 5 μmol x L(-1) were respectively 0.54 ± 0.08 and 0.98 ± 0.02 in the group treated with high dosage of OPS, which were all significantly different with those in the model group (P < 0.01). Plasma contents of TC, TG and LDL reduced significantly by the treatments both with low and high dosages of OPS compared with those in the model group (P < 0.01). Protein level of hepatic ApoB and that of hepatic Dgat1 decreased significantly after the treatment with high dosage of OPS compared with those in the model group (P < 0.01). These results indicate that OPS can markedly improve the vasorelaxation of thoracic aorta of atherosclerotic rats and has significant anti-atherosclerotic effect; inhibiting the expression of ApoB and Dgat1 and thus decreasing the amounts of TC, LDL and TG serving as one of the molecular mechanisms of its antiatherosclerosis effect.


