Ornithogalum caudatum
Ornithogalum caudatum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Ornithogalum caudatum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
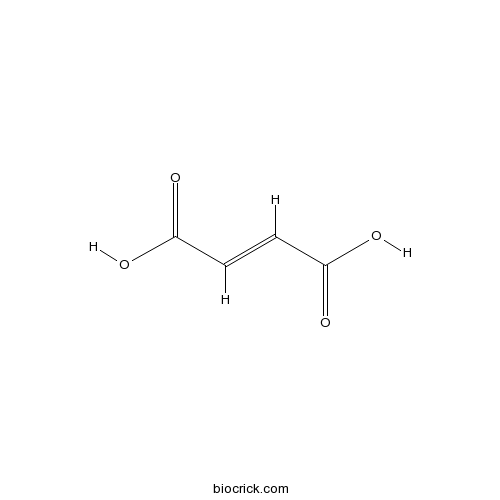
BCN5989
Fumaric acid110-17-8
Instructions
-
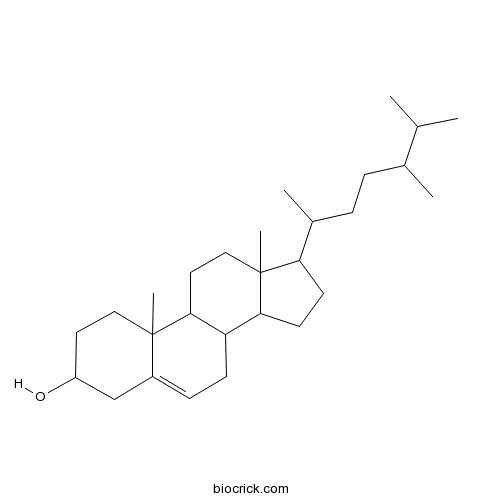
BCN3181
Campesterol474-62-4
Instructions
Isolation and characterization of a multifunctional flavonoid glycosyltransferase from Ornithogalum caudatum with glycosidase activity.[Pubmed: 29651040]
Glycosyltransferases (GTs) are bidirectional biocatalysts catalyzing the glycosylation of diverse molecules. However, the extensive applications of GTs in glycosides formation are limited due to their requirements of expensive nucleotide diphosphate (NDP)-sugars or NDP as the substrates. Here, in an effort to characterize flexible GTs for glycodiversification of natural products, we isolated a cDNA, designated as OcUGT1 from Ornithogalum caudatum, which encoded a flavonoid GT that was able to catalyze the trans-glycosylation reactions, allowing the formation of glycosides without the additions of NDP-sugars or NDP. In addition, OcUGT1 was observed to exhibit additional five types of functions, including classical sugar transfer reaction and three reversible reactions namely NDP-sugar synthesis, sugars exchange and aglycons exchange reactions, as well as enzymatic hydrolysis reaction, suggesting OcUGT1 displays both glycosyltransferase and glycosidase activities. Expression profiles revealed that the expression of OcUGT1 was development-dependent and affected by environmental factors. The unusual multifunctionality of OcUGT1 broadens the applicability of OcUGT1, thereby generating diverse carbohydrate-containing structures.
Effective cytotoxic activity of OSW-1 on colon cancer by inducing apoptosis in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 28440433]
As a natural compound, Ornithogalum caudatum Ait is primarily used as an anti-inflammatory and antitumor agent in Chinese folk medicine. In 1992, OSW-1 was isolated from this compound, which is a new member of cholestane saponin family. In numerous recent studies, OSW-1 has been shown to have powerful cytotoxic anticancer effects against various malignant cells. However, the therapeutic efficacy of OSW-1 on colon cancer and the underlying mechanism are not understood. To explore the mechanism underlying OSW-1 in antitumor therapy, a therapeutic function analysis of OSW-1 on colon cancer was performed in vitro and in vivo. It was shown that with low toxicity on normal colonic cells, OSW-1 suppresses colon cancer cells in vitro and this inhibition was via the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, which increased cellular calcium, changed mitochondrial membrane potential, disrupted mitochondrial morphology, and led to the release of cytochrome c and the activation of caspase-3. Furthermore, in a nude mouse model, OSW-1 had a powerful effect on suppressing colon tumor proliferation without significant side effects through the apoptosis pathway. Taken together, these results demonstrate that OSW-1 is a potential drug for colon cancer treatment.
Functional analyses of OcRhS1 and OcUER1 involved in UDP-L-rhamnose biosynthesis in Ornithogalum caudatum.[Pubmed: 27835851]
None
cDNA isolation and functional characterization of squalene synthase gene from Ornithogalum caudatum.[Pubmed: 27725246]
As the first step of ongoing efforts to investigate the genes responsible for the biosynthesis of steroidal saponins in the medicinal plant Ornithogalum caudatum, this investigation reported the cDNA isolation, prokaryotic expression and functional characterization of squalene synthase (SQS) gene from O. caudatum for the first time. Specifically, two unigenes showing high sequence identity to SQS were retrieved from RNA-Taq data, and then a full-length OcSQS1 corresponding to the two unigenes was isolated from O. caudatum genome by a nested PCR assay. The open reading frame of OcSQS1 was 1230 bp and encoded a polypeptide of 409 aa. OcSQS1 was predicted to be a membrane-bound protein with at least four conserved motifs associated with binding, regulatory and catalytic activities of OcSQS1 and two transmembrane domains. Next, many attempts to generate soluble OcSQS1 in heterologous Escherichia coli were made, including optimization of expression conditions, application of varied expression plasmids with different tags, secretory peptides and molecular chaperones, and truncated mutation of OcSQS1. Finally, the successful availability of a soluble, truncated OcSQS1 mutant was achieved by combinational use of the utensils from the vast genetic toolbook. Moreover, this truncated OcSQS1 mutant retained the folding capability as well as its catalytic activity, converting FPP to form squalene. Importantly, the present research tentatively verified the involvement of the second transmembrane domain in the proper folding of the recombinant OcSQS1 protein.
Transcriptome-guided gene isolation and functional characterization of UDP-xylose synthase and UDP-D-apiose/UDP-D-xylose synthase families from Ornithogalum caudatum Ait.[Pubmed: 27591771]
None
[Research ontherapeutics effect of extract of Ornithogalum caudatum on liver fibrosis].[Pubmed: 28901077]
Rat models of liver fibrosis were made by carbon tetrachloride, and the serum levels of AST, ALT, γ-GT, MDA, GSH-px, SOD were detected, serum markers of PCⅢ, IV-C, LN, HA were detected by ELISA method. HE and Masson staining were conducted in hepatic tissues to observe pathological variations. Collagen Ⅲ, TGF-β, α-SMA, E-cadherin were detected by Western blot. The curative effect of the extract of Ornithogalum caudatum on rat liver fibrosis induced by CCl4was observed and the mechanism was discussed. The experiment results showed that the extract of O. caudatum (50, 150, 500 mg•kg⁻¹) obviously decreased the serum levels of AST, ALT, γ-GT, MDA, increased the serum levels of GSH-px, SOD, decreased the expression of serum markers of PCⅢ, IV-C, LN, HA, and improved the liver pathological variations of fibrotic rats. The experiment proved that the extract of O. caudatum could treat the liver fibrogenesis induced by CCl4 in rats. The positive medicine may inhibit accumulation of extracellular and activate hepatic stellate cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Transcriptome-enabled discovery and functional characterization of enzymes related to (2S)-pinocembrin biosynthesis from Ornithogalum caudatum and their application for metabolic engineering.[Pubmed: 26846670]
(2S)-Pinocembrin is a chiral flavanone with versatile pharmacological and biological activities. Its health-promoting effects have spurred on research effects on the microbial production of (2S)-pinocembrin. However, an often-overlooked salient feature in the analysis of microbial (2S)-pinocembrin is its chirality.
[Complementary nuclear DNA in embryo sac cells of Haemanthus albiflos and Ornithogalum caudatum].[Pubmed: 11963552]
Cytophotometric measurements of Feulgen-DNA were carried out in the nuclei of embryo sac cells of Haemanthus albiflos and Ornithogalum caudatum. It was found that the nuclei of the egg system, haploid in the number of chromosomes, became polyploid in DNA amount at the final stages of gametophyte development.


