Panax japonicus var. major
Panax japonicus var. major
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Panax japonicus var. major
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN1064
Ginsenoside Rb211021-13-9
Instructions

-
BCN1072
Ginsenoside Rc11021-14-0
Instructions
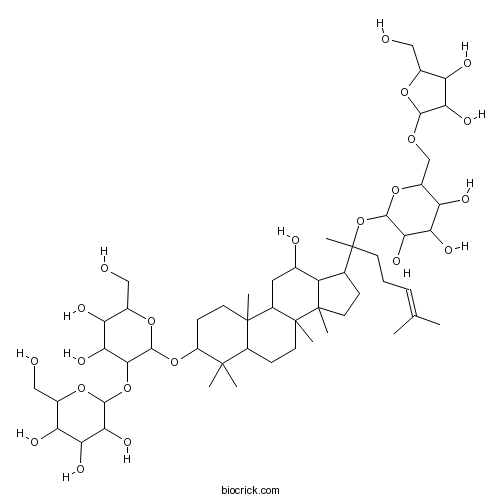
-
BCN1079
20(R)-Protopanaxatriol1453-93-6
Instructions
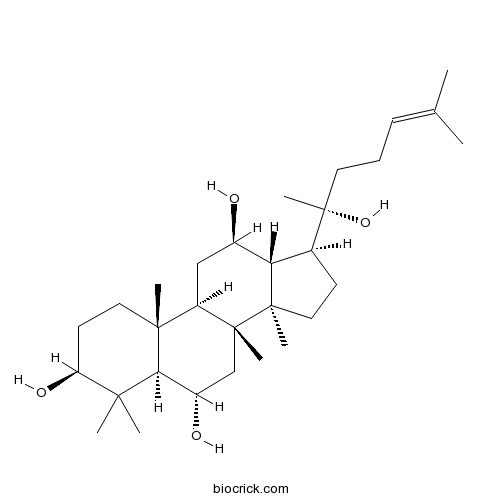
-
BCN5937
Ginsenoside Ro34367-04-9
Instructions

-
BCN5616
Oleanolic acid508-02-1
Instructions

-
BCN3432
Chikusetsusaponin IVa51415-02-2
Instructions
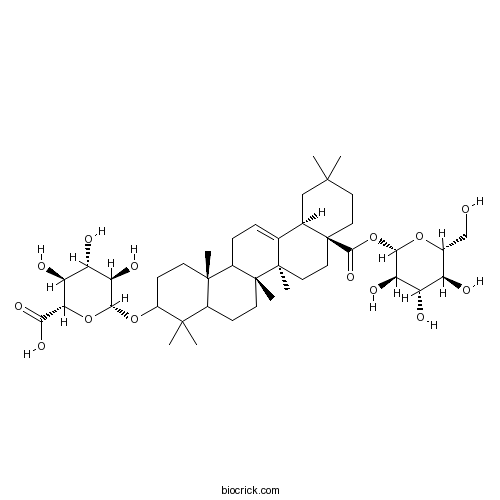
-
BCN1075
Ginsenoside Rf52286-58-5
Instructions

-
BCN1065
Ginsenoside Rb368406-26-8
Instructions

-
BCN2683
Chikusetsusaponin IV7518-22-1
Instructions
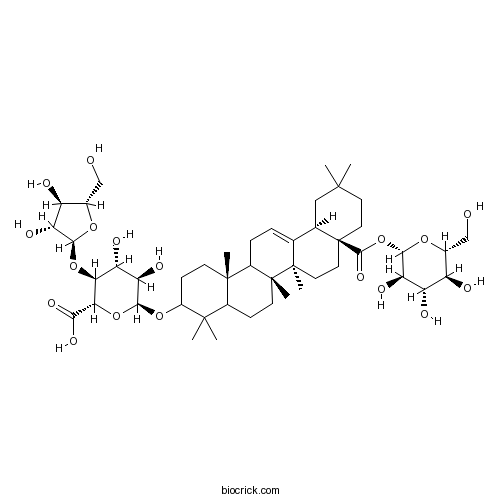
-
BCN2794
Pseudoginsenoside RT198474-74-9
Instructions

[Transcriptome profiling and analysis of Panax japonicus var. major].[Pubmed: 26552161]
The rhizome of Panax japonicus var. major have been used as the natural medicinal agent by Chinese traditional doctors for more than thousand years. Most of the therapeutic effects of P. japonicus var. major had been reported due to the presence of tetracyclic or pentacyclic triterpene saponins. In this study, Illumina pair-end RNA-sequencing and de novo splicing were done in order to understand the pathway of triterpenoid saponins in this species. The valid reads data of 15. 6 Gb were obtained. The 62 240 unigenes were finally obtained by de novo splicing. After annotation, we discovered 19 unigenes involved in ginsenoside backbone biosynthesis. Additionally, 69 unigenes and 18 unigenes were predicted to have potential function of cytochrome P450 and UDP-glycosyltransferase based on the annotation results, which may encode enzymes responsible for ginsenoside backbone modification. This study provides global expressed datas for P. japonicus var. major, which will contribute significantly to further genome-wide research and analysis for this species.
[Chemical constituents of leaves of Panax japonicus var. major].[Pubmed: 25095375]
Seven compounds were isolated from the leaves of Panax japonicus var. major by chromatographic methods including silica gel, Sephadex LH-20, ODS and semi-preparative HPLC. Their structures were elucidated by their physical and chemical properties and spectral data analysis as 5, 7-dihydroxy-8-methoxyl flavone (1), ginsenoside Rs2 (2), quinquenoside R1 (3), ginsenoside Rs1 (4), notoginsenoside Fe (5), ginsenoside Rd2 (6) and gypenosiden IX (7). Among them, compound 1 was obtained from the Panax genus for the first time, and compounds 2-7 were isolated from this plant for the first time.
Bioactive constituents from the roots of Panax japonicus var. major and development of a LC-MS/MS method for distinguishing between natural and artifactual compounds.[Pubmed: 21417387]
Two new saponins, panajaponol (1) and pseudoginsenoside RT1 butyl ester (2), together with 35 known compounds (3-37), were isolated from the roots of Panax japonicus var. major. The structures of 1 and 2 were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic analysis and chemical methods. Furthermore, a LC-MS/MS method was developed for confirming 2, 3, and 8 as natural compounds containing a butyl ester group. This method should be useful for distinguishing between minor natural and artifactual compounds in Panax species. Moreover, compounds 3, 6, 8, 9, 11, 13, and 15 exhibited strong inhibition of superoxide anion generation and elastase release by human neutrophils in response to formyl-l-methionyl-l-leucyl-l-phenylalanine/cytochalasin B (fMLP/CB), with IC(50) values ranging from 0.78 to 43.6 μM. In addition, 1 showed greater than 2- to 3-fold selective cytotoxic activity against KB and DU145 cancer cell lines.


