Polygala japonica
Polygala japonica
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Polygala japonica
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2785
Sibiricose A5107912-97-0
Instructions

-
BCN2790
Polygalasaponin V162857-65-0
Instructions
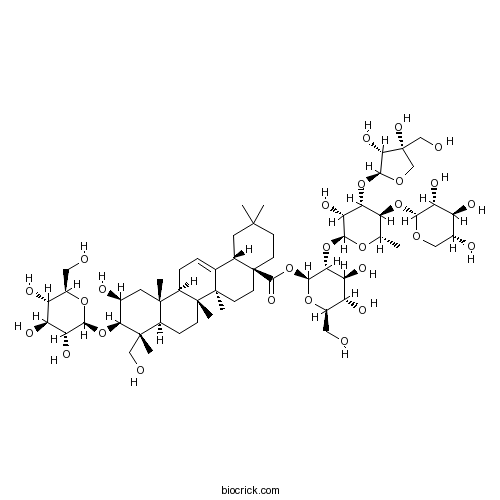
-
BCN2786
Sibiricose A6241125-75-7
Instructions
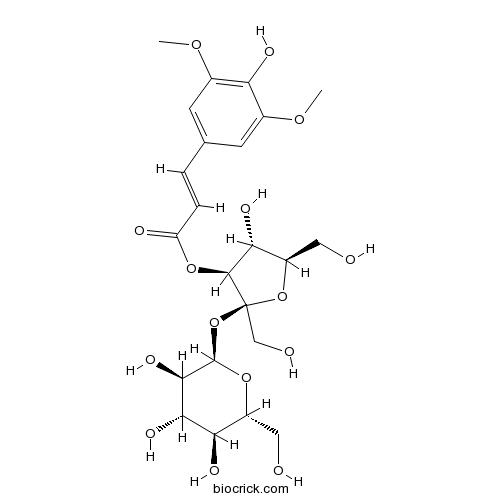
-
BCN2317
Polygalasaponin F882664-74-6
Instructions

-
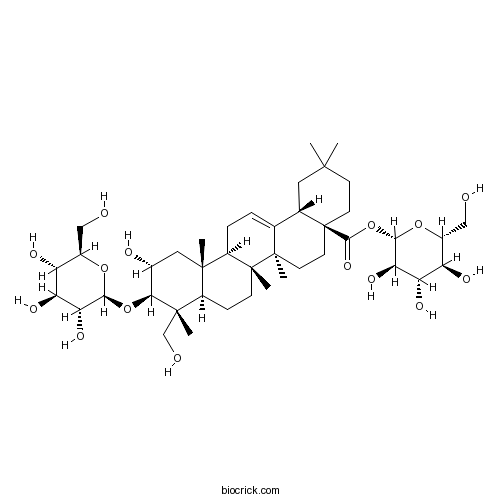
BCN7811
Lucyoside B91174-19-5
Instructions
Polygala japonica Houtt. reverses depression-like behavior and restores reduced hippocampal neurogenesis in chronic stress mice.[Pubmed: 29710497]
Polygala japonica Houtt. (PJ) has been reported have positive effect on the nerves system including depression, but the underlying mechanism is needed to be understood. Here we show that PJ counteracts behavioral effects induced by chronic restraint, a model of depression mimicking exposure to stress, through adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN) enhancement. Chronic stress increased the immobility time in the tail suspension test (TST) and forced swim test (FST) and decreased the time in the center of elevated plus maze (EPM) relative to controls. Moreover, chronic stress also induced the cognitive deficit in novel object recognition test, object location test and barnes maze. These behavioral alterations were accompanied by the decreased AHN. Treatment with PJ reversed the behavioral and AHN alterations. We also found that PJ had no significant effect on cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation in dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus, but it inhibited the apoptosis of the newborn neurons by activation of bcl-2 and phopho-erk1/2 and increased the number of the newborn neurons. Our results demonstrate that administration of PJ to chronic stress mice alleviates depression-like behaviors and normalizes the deficit in hippocampal neurogenesis with inhibiting newborn neuron apoptosis.
The molecular mechanism of polygalasaponin F-mediated decreases in TNFα: emphasizing the role of the TLR4-PI3K/AKT-NF-κB pathway.[Pubmed: 26235355]
Polygalasaponin F (PS-F), an oleanane-type triterpenoid saponin extracted from Polygala japonica, decreases the release of the inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), but the precise molecular mechanisms by which this event occurs are not fully understood. To study the anti-neuroinflammatory mechanisms of PS-F, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to detect the secretion of TNFα from BV-2 microglial cells. Nuclear proteins extracted from BV-2 microglial cells stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and pretreated with/without inhibitors were measured by Western blotting, and cell viability was evaluated by MTT analysis. The results indicated that inhibition of toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 (CLI-095 1 μg/ml), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) (Ly294002 10 μM) or IκBα phosphorylation (Bay11-7082 10 μM) completely prevents the release of TNFα induced by LPS without affecting cell viability and attenuated the nuclear translocation of p65 stimulated by LPS. In addition, PS-F exhibited a similar trend regarding TNFα release, AKT phosphorylation and NF-κB translocation. These results suggest that PS-F reduces neuroinflammatory cytokine secretion through the regulation of the TLR4-PI3K/AKT-NF-κB signaling pathway.
Three triterpenoid saponins from the roots of Polygala japonica Houtt.[Pubmed: 22796402]
Three new triterpenoid saponins polygalasaponins LI-LIII (1-3) with two acylation groups in oligosaccharide chain, together with three known saponins were isolated from the roots of Polygala japonica Houtt. (4-6). The neuroprotective effects of these compounds on neuron-like PC12 cells were evaluated in vitro. Compounds 5 and 6 show neuroprotective effects in Aβ₂₅₋₃₅ model at the concentration of 10 μM.
Polygalasaponin F induces long-term potentiation in adult rat hippocampus via NMDA receptor activation.[Pubmed: 22286914]
To investigate the effect and underlying mechanisms of polygalasaponin F (PGSF), a triterpenoid saponin isolated from Polygala japonica, on long-term potentiation (LTP) in hippocampus dentate gyrus (DG) of anesthetized rats.
Three new xanthones from the roots of Polygala japonica Houtt.[Pubmed: 19504390]
Three new xanthones, 1,3-dihydroxy-2,5,6,7-tetramethoxyxanthone (1), 3-hydroxy-1,2,5,6,7-pentamethoxyxanthone (2), and 3,8-dihydroxy-1,2,6-trimethoxyxanthone (3), together with two known compounds were isolated from the roots of Polygala japonica Houtt. Their structures were determined on the basis of spectroscopic data.
Polygalasaponin G promotes neurite outgrowth of cultured neuron on myelin.[Pubmed: 19446604]
Myelin contains many axonal outgrowth inhibitory components which contribute to regeneration failure after neuronal injury in the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). In an attempt to develop small molecular agents to promote axonal outgrowth, we screened a compound library purified from traditional Chinese herbs, and found a small molecular compound polygalasaponin G (PS-G), extracted from Polygala japonica, which has a potent neurotrophic activity on PC12 cells and cultured cortical neurons. We reported, to our knowledge for the first time, that PS-G could promote neurite outgrowth of neurons cultured on the myelin substrates and inhibit the activation of RhoA. Thus, our results could represent a therapeutic approach to improve axon regeneration after CNS injuries.
Chemical constituents isolated from Polygala japonica leaves and their inhibitory effect on nitric oxide production in vitro.[Pubmed: 18825536]
A methanolic extract of dried leaves of Polygala japonica Houtt (Polygalaceae) significantly attenuated nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-simulated BV2 microglia. Five anthraquinones chrysophanol (1), emodin (2), aloe-emodin (3), emodin 8-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (4) and trihydroxy anthraquinone (5), and four flavonoids kaempferol (6), chrysoeriol (7), kaempferol 3-gentiobioside (8) and isorhamnetin (9) were isolated from the methanolic extract using bioactivity-guided fractionation. Among them, compounds 1-4, 6 and 7 showed significant inhibitory effect on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in BV2 microglia at the concentrations ranging from 1.0 to 100.0 microM.
Oligosaccharide polyester and triterpenoid saponins from the roots of Polygala japonica.[Pubmed: 18353407]
An oligosaccharide polyester, 1-O-(E)-p-coumaroyl-(3-O-benzoyl)-beta-D-fructofuranosyl-(2-->1)-[6-O-(E)-feruloyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)]-[6-O-acetyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-(4-O-acetyl)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)]-4-O-[4-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(E)-p-coumaroyl]-alpha-D-glucopyranoside (polygalajaponicose I), and four triterpenoid saponins, 3beta, 23, 27-trihydroxy-29-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-olean-12-en-28-oic acid (polygalasaponin XLVII), 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl presenegenin 28-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->2)-beta-D-fucopyranosyl ester (polygalasaponin XLVIII), 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl presenegenin 28-O-beta-D-galactopyranosyl-(1-->5)-beta-D-apiofuranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-xylopyranosyl-(1-->4)-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->2)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (polygalasaponin XLIX) and 2beta, 27-dihydroxy-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl 11-oxo-olean-12-en-23, 28-dioic acid 28-O-beta-D-galactopyranosyl-(1-->5)-beta-D-apiofuranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-xylopyranosyl-(1-->4)-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->2)-beta-D-fucopyranosyl ester (polygalasaponin L), in addition to five known compounds have been isolated from the roots of Polygala japonica.


