Quercus mongolica
Quercus mongolica
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Quercus mongolica
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
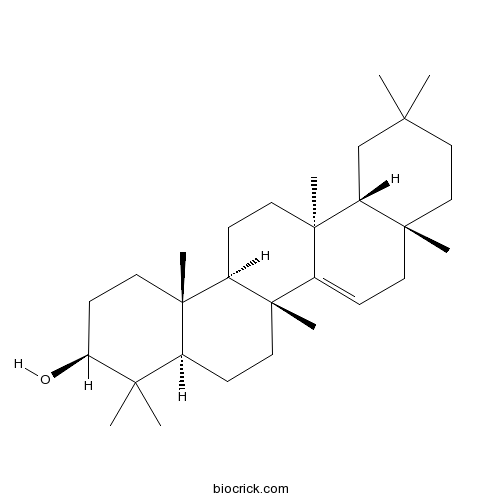
BCN6148
Taraxerol127-22-0
Instructions
-
BCN2208
Ergocalciferol50-14-6
Instructions
-
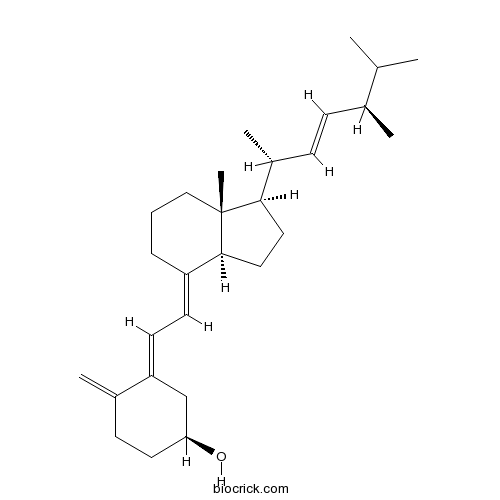
BCN5636
Taraxerone514-07-8
Instructions

[Geostatistical analysis on the spatial pattern of Quercus mongolica population in different communities.][Pubmed: 29797887]
None
Selective predation on acorn weevils by seed-caching Siberian chipmunk Tamias sibiricus in a tripartite interaction.[Pubmed: 29777342]
Although food-hoarding animals benefit plant seeds by generating predation pressure on granivorous insects, we lack experimental evidence of whether the tripartite interactions maintain a mutualistic relationship between the third trophic level and primary producers. Relying on the behavior of shelling, Siberian chipmunks (Tamias sibiricus) selectively consumed weevil larvae infested in acorns of Mongolian oak (Quercus mongolica) but chose the non-infested acorns to scatter-hoard. Shelling not only reduced volatile emission from acorns but also decreased cache loss to pilferers, weevil larvae and fungi, allowing T. sibiricus to gain more rewards from their caches. Moreover, shelling by T. sibiricus enhanced acorn germination and seedling establishment of Q. mongolica, possibly due to the diminishment of the negative effects of weevil infestation on acorn viability. Here, we show that both food-hoarding animal T. sibiricus and oak Q. mongolica can be conditionally benefited from selective predation on weevil larvae inside acorns. Our results highlight the need to integrate the mutualisms between the third and first trophic level into the tripartite interaction model. We suggest that more efforts should be made in the tripartite interactions of food-hoarding animals, seeds and granivorous insects.


