Rhododendron anthopogonoides
Rhododendron anthopogonoides
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Rhododendron anthopogonoides
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5827
Noreugenin1013-69-0
Instructions

-
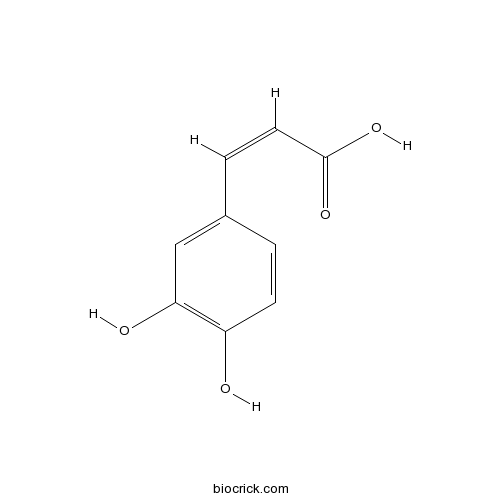
BCN5979
Caffeic acid331-39-5
Instructions
-
BCN5570
Hyperoside482-36-0
Instructions

-
BCN4327
Ursolic acid77-52-1
Instructions

Antioxidant potential, total phenolic and total flavonoid contents of Rhododendron anthopogonoides and its protective effect on hypoxia-induced injury in PC12 cells.[Pubmed: 26283543]
Rhododendron anthopogonoides Maxim, a kind of traditional Tibetan medicine, has been used to remove body heat, body detoxification, cough, asthma, stomachic and swelling, eliminate abundant phlegm and inflammatory for a long time. In the present study, the total phenols and total flavonoid contents as well as antioxidative properties of the crude extract and solvent fractions of R. anthopogonoides were determined using seven antioxidant assays. Additionally, the protective effect of the extracts on hypoxia-induced injury in PC12 cells was also investigated.
Nematicidal activity of the essential oil of Rhododendron anthopogonoides aerial parts and its constituent compounds against Meloidogyne incognita.[Pubmed: 24066516]
Hydrodistilled essential oil from Rhododendron anthopogonoides Maxim. (Ericaceae) aerial parts was analysed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). A total of 42 compounds, accounting for 95.48% of the total oil, were identified. The main constituents of the essential oil were benzyl acetone (34.41%), nerolidol (10.19%), 1,4-cineole (8.41%), beta-caryophyllene (5.63%), gamma-elemene (5.10%), and spathulenol (3.06%). Four constituents were isolated from the essential oil based on fractionation. The essential oil of R. anthopogonoides possessed nematicidal activity against the root knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) with an LC50 value of 130.11 microg/ml. The main compound of the essential oil, benzyl acetone, exhibited nematicidal activity against M. incognita with an LC50 value of 74.17 microg/ml while 1,4-cineole, nerolidol, and beta-caryophyllene were not nematicidal at a concentration of 5 mg/ml. The essential oil of R. anthopogonoides and benzyl acetone show potential for their development as possible natural nematicides for the control of the root knot nematode.
Toxicity of Rhododendron anthopogonoides essential oil and its constituent compounds towards Sitophilus zeamais.[Pubmed: 22143541]
The screening of several Chinese medicinal plants for insecticidal principles showed that essential oil of Rhododendron anthopogonoides flowering aerial parts possessed significant toxicity against maize weevils, Sitophilus zeamais. A total of 37 components were identified in the essential oil and the main constituents of the essential oil were 4-phenyl-2-butanone (27.22%), nerolidol (8.08%), 1,4-cineole (7.85%), caryophyllene (7.63%) and γ-elemene (6.10%), followed by α-farnesene (4.40%) and spathulenol (4.19%). Repeated bioactivity-directed chromatographic separation on silica gel columns led us to isolate three compounds, namely 4-phenyl-2-butanone, 1,4-cineole, and nerolidol. 4-Phenyl-2-butanone shows pronounced contact toxicity against S. zeamais (LD₅₀ = 6.98 mg/adult) and was more toxic than either 1,4-cineole or nerolidol (LD₅₀ = 50.86 mg/adult and 29.30 mg/adult, respectively) against the maize weevils, while the crude essential oil had a LD₅₀ value of 11.67 mg/adult. 4-Phenyl-2-butanone and 1,4-cineole also possessed strong fumigant toxicity against the adults of S. zeamais (LC₅₀ = 3.80 mg/L and 21.43 mg/L) while the crude essential oil had a LC₅₀ value of 9.66 mg/L.
New cannabinoid-like chromane and chromene derivatives from Rhododendron anthopogonoides.[Pubmed: 22041081]
Two new cannabinoid-like chromane and chromene derivatives named anthopogocyclolic acid (1) and anthopogochromenic acid (2) and five related compounds (3-7) which are known as synthetic analogues of cannabinoids: cannabichromene (CBC) type, cannabicyclol (CBL) type, and cannabicitran (CBT) type, have been isolated together with geranyl orsellinic acid (8) from the Chinese medicinal plant Rhododendron anthopogonoides. Their structures were elucidated based on spectroscopic and chemical evidence. The absolute configuration of the asymmetric carbons at C-2 of 1-7 was determined to be S from their circular dichroism (CD) spectra. Compounds 2, 4 and 6 inhibited compound 48/80-induced histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells.
Tetracyclic chromane derivatives from Rhododendron anthopogonoides.[Pubmed: 20586436]
Four new chromane derivatives, anthopogochromane (1), anthopogochromene A (2), anthopogochromene B (3), and anthopogochromene C (4), and two known compounds, daurichromenic acid (5) and ilicicolinic acid B (6), have been isolated from the Chinese medicinal plant Rhododendron anthopogonoides. The S absolute configuration of the stereogenic carbons in the chromane and chromene rings of 1-4 was determined from their circular dichroism spectra. Compounds 1 and 2 inhibited compound 48/80-induced histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells.
[Drought resistibility of main tree species in water conservation forest of Qilian Moutains].[Pubmed: 16515165]
With P-V techniques, this paper determined and analyzed the water parameters of main tree species in the water conservation forest of Qilian Moutains. The results showed that the test water parameters varied with tree species, reflecting the complicacy of the drought-resistance mechanism of trees. Among 10 parameters, /phi pi100 - phi pi0/, RCV, ROWC0 epsilon(max) could reflect most information of drought resistibility. Based on their drought resistibility, the test tree species could be classified into 4 groups, i.e., high drought resistibility (Picea crassifolia and Rhododendron thymifolium ), sub-high drought resistibility (Sabina przeualwkii, Rhododendron anthopogonoides, Rhododendron capitaturn and Rhododendron przewalskii), low drought resistibility (Populus cathyana), and inferior drought resistibility (Poentilla fruticosa, Siraea salicifolia and Betula albosinensis). The relationships between predawn leaf water potential and soil water content could be well modeled by hyperbola function, power function or exponent function. Meanwhile, the test tree species could be also grouped as high potential delay dehydration species (Betula albosinensis and Rhododendron przeualskii), sub-high potential delay dehydration species (Picea crassifolia, Rhododendron thymifolium and Rhododendron capitatum), inferior potential tolerance species (Sabina przewalskii), and low potential tolerance species (Potentilla fruticosa, Spiraea salicifolia and Rhododendron anthopogonoides), based on their drought-resistance mechanism.
[Studies on the flavonoid compounds of Rhododendron anthopogonoides].[Pubmed: 15709380]
To investigate the flavonoid constituents of the Rhododendron anthopogonoides systematically.


