Rhus chinensis
Rhus chinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Rhus chinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN7859
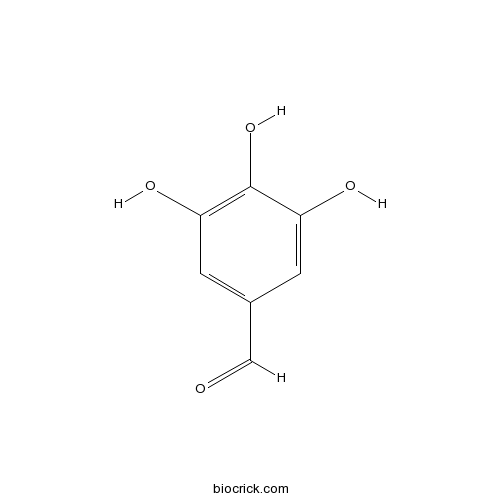
Gallic aldehyde13677-79-7
Instructions
-
BCN8390
Myristic acid544-63-8
Instructions

-
BCN4373
Ethyl gallate831-61-8
Instructions

Acute and subchronic toxicities of the ethanol and hot-water extracts from Chinese sumac (Rhus chinensis Mill.) fruits by oral administration in rats.[Pubmed: 29886233]
In the present work, acute and subchronic toxicities of the ethanol and hot-water extracts from Rhus chinensis Mill. fruits were performed by oral administration in pathogen-free SD rats. Acute toxicity study was performed at a single dose of 5000 mg/kg for 14 consecutive days. And subchronic toxicity test was conducted by daily oral administration of those two extracts at doses of 312, 625, 1250 and 2500 mg/kg for 30 days. Acute toxicity study showed that the LD50 of the ethanol and hot-water extracts were over 5000 mg /kg. The results of subchronic toxicity showed that no significant adverse effect of those two extracts was observed at 312 and 625 mg/kg. However, the weight gains of rats were significantly inhibited at both 2500 mg/kg groups of the ethanol and hot-water extracts. Moreover, those two extracts exhibited toxicities to heart, liver, spleen and kidney in rats determined by hematological, serum biochemical and/or histological analyses when daily oral administration of 1250 mg/kg and 2500 mg/kg. No significant neurotoxicity was observed in all groups. The results concluded that the low concentration of those two extracts from R. chinensis Mill. fruits can be regarded as safe and used in daily life.
Full-length cloning, sequence analysis and expression detection of the β-tubulin gene from the Chinese gall aphid (Schlechtendalia chinensis).[Pubmed: 28743930]
Some insect galls are formed on sumac plants by certain aphid species and have been used for medicinal and chemical purposes as they are rich in tannins. The most prominent species among gall aphids in China is Schlechtendalia chinensis, which formed horn-shaped galls on the winged rachis of Rhus chinensis. S. chinensis has a complex life cycle, with a switch of hosts between R. chinensis and certain mosses, and a switch of sexual and asexual reproduction (cyclical parthenogenesis). We have cloned a full-length cDNA of the β-tubulin gene from S. chinensis, using qPCR and RACE. This cDNA has 1606 base pairs with a 251 bp 5'-untranslated region (5'-UTR) and a 15 bp 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR). The gene encodes a protein with 376 amino acids residues. The expression levels of the β-tubulin gene in S. chinensis were investigated among fundatrigeniae and overwintering larvae rearing under either natural conditions, or at 7.5 °C and 18 °C. No significant differences (P > 0.01) in gene expression levels were found in insects under these conditions. It is indicates that the β-tubulin gene is highly conserved and then it may be used as a reference for further research in gene expression and reproduction determination in this important aphid.
Bioaccumulation and detoxification mechanisms for lead uptake identified in Rhus chinensis Mill. seedlings.[Pubmed: 28388478]
None
RNA-Seq-based transcriptome and the reproduction-related genes for the aphid Schlechtendalia chinensis (Hemiptera, Aphididae).[Pubmed: 28340266]
Chinese galls form on sumac plants (Rhus chinensis) and are used for medicinal and chemical purposes, due to their richness in tannins. The galls are formed by aphids, the most prominent of which is Schlechtendalia chinensis, which forms horn-shaped galls on the winged rachis of R. chinensis. S. chinensis has a complex life cycle, including both R. chinensis and certain mosses as hosts, as well as the existence of both sexual and asexual reproduction (cyclical parthenogenesis). Previous studies have shown that the alternate occurrence of sexual and asexual reproduction relies on many environmental factors, such as temperature, photoperiod, and host-plant. However, the sexual and asexual modes of reproduction are poorly understood on the molecular level. We aimed to identify genes that respond to changes in temperature that may be related to the reproduction process. We compared the transcriptome of two samples of S. chinensis, which had been reared at different temperatures. Using gene ontology analysis, a total of 51 evolutionary conserved genes related to reproduction determination in insects were identified. Of these genes, S. chinensis harbors 42 genes. When we analyzed aphids that had asexually or sexually produced offspring, eight out of these 42 genes were identified and expressed differently in two temperature conditions. This is the first report on genes associated with reproduction determination in S. chinensis, which has a complex life cycle. Genes, expressed differently in response to different temperature conditions will be helpful to understand the mechanism of aphid reproductive determination.
The attenuating effects of 1,2,3,4,6 penta-O-galloyl-β-d-glucose on inflammatory cytokines release from activated BV-2 microglial cells.[Pubmed: 28284353]
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common cause of neurodegeneration and dementia in the elderly. Dysregulated, chronic activation of microglia, the brain's resident macrophages, induces the release of excessive amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines which has been implicated in the early stages of AD pathology. Therefore, suppressing the expression of these inflammatory mediators may decrease or delay the progression of AD. Many natural compounds derived from plants have shown anti-inflammatory activity. The naturally occurring 1,2,3,4,6 Penta-O-Galloyl-β-d-Glucose (PGG), is a polyphenolic compound highly enriched in Rhus chinensis Millplant. It is a potent anti-inflammatory agent that act through the inhibition of many cytokines in different experimental models. In the present study, we investigated the role of PGG as an anti-inflammatory agent in LPS/IFNγ activated BV-2 microglia cells. Mouse cytokine antibody arrays were used to assess the effect of PGG on the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and ELISA experiments were performed to validate the results from the arrays. The results obtained from the cytokine arrays, and ELISA assays showed that PGG decreased the expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-5 (MCP-5) 8-fold, and pro-matrix metalloproteinase 9 (Pro MMP-9) 10-fold. Both of these cytokines are upregulated during the inflammatory process and have been shown to be involved in brain injury, inflammation, and neurodegeneration. Therefore, these findings suggest that the anti-inflammatory effect of PGG on activated microglia involving the attenuation of MCP-5 and Pro MMP-9 cytokines.
Phytoremediation potential of transplanted bare-root seedlings of trees for lead/zinc and copper mine tailings.[Pubmed: 27216539]
Selecting plant species that can overcome unfavorable conditions and increase the recovery of degraded mined lands remains a challenge. A pot experiment was conducted to evaluate the feasibility of using transplanted tree seedlings for the phytoremediation of lead/zinc and copper mine tailings. One-year-old bare-root of woody species (Rhus chinensis Mill, Quercus acutissima Carruth, Liquidambar formosana Hance, Vitex trifolia Linn. var. simplicifolia Cham, Lespedeza cuneata and Amorpha fruticosa Linn) were transplanted into pots with mine tailings and tested as potential metal-tolerant plants. Seedling survival, plant growth, root trait, nutrient uptake, and metal accumulation and translocation were assessed. The six species grew in both tailings and showed different tolerance level. A. fruticosa was highly tolerant of Zn, Pb and Cu, and grew normally in both tailings. Metal concentrations were higher in the roots than in the shoots of the six species. All of the species had low bioconcentration and translocation factor values. However, R. chinensis and L. formosana had significantly higher translocation factor values for Pb (0.88) and Zn (1.78) than the other species. The nitrogen-fixing species, A. fruticosa, had the highest tolerance and biomass production, implying that it has great potential in the phytoremediation of tailing areas in southern China.


