Rosa chinensis
Rosa chinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Rosa chinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
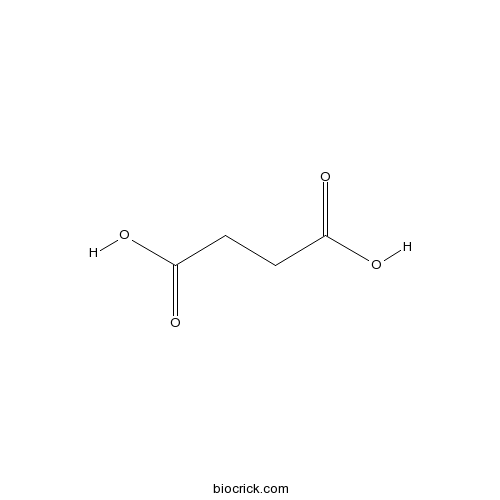
BCN5890
Succinic acid110-15-6
Instructions
-
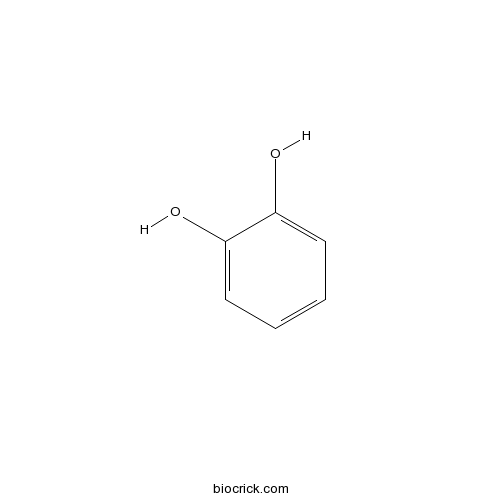
BCN6103
1,2-Benzenediol120-80-9
Instructions
-
BCN4889
Tiliroside20316-62-5
Instructions

Genome-wide transcriptome analysis of the salt stress tolerance mechanism in Rosa chinensis.[Pubmed: 30048505]
Plants regulate responses to salt stress using biological pathways, such as signal perception and transduction, photosynthesis, and energy metabolism. Little is known about the genetics of salt tolerance in Rosa chinensis. Tineke and Hiogi are salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive varieties of R. chinensis, respectively, and are good choices for studying salt-tolerance genes. We studied leaf and root tissues from 1-year-old Hiogi and Tineke plants simultaneously grown under the same conditions. A 0.4%-mmol/L salt ion mixture was added to the basic growth medium. Illumina sequencing was used to identify differentially expressed transcripts. GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses were performed to identify differentially expressed genes. We identified many differentially expressed genes associated with salt tolerance. The abscisic acid-dependent signaling pathway was the main pathway that mediated the salt stress response in R. chinensis. Two pathways (plant hormone signal transduction and glutathione metabolism) were also active in salt stress responses in R. chinensis. The difference in salt tolerance in the cultivars was due to different gene sensitivity to salt in these two pathways. Roots also play a role in salt stress response. The effects of salt stress in the roots are eventually manifested in the leaves, causing changes in processes such as photosynthesis, which eventually result in leaf wilting. In Tineke, Snrk2, ABF, HSP, GSTs, and GSH1 showed high activity during salt stress, indicating that these genes are markers of salt tolerance.
A high-quality genome sequence of Rosa chinensis to elucidate ornamental traits.[Pubmed: 29892093]
Rose is the world's most important ornamental plant, with economic, cultural and symbolic value. Roses are cultivated worldwide and sold as garden roses, cut flowers and potted plants. Roses are outbred and can have various ploidy levels. Our objectives were to develop a high-quality reference genome sequence for the genus Rosa by sequencing a doubled haploid, combining long and short reads, and anchoring to a high-density genetic map, and to study the genome structure and genetic basis of major ornamental traits. We produced a doubled haploid rose line ('HapOB') from Rosa chinensis 'Old Blush' and generated a rose genome assembly anchored to seven pseudo-chromosomes (512 Mb with N50 of 3.4 Mb and 564 contigs). The length of 512 Mb represents 90.1-96.1% of the estimated haploid genome size of rose. Of the assembly, 95% is contained in only 196 contigs. The anchoring was validated using high-density diploid and tetraploid genetic maps. We delineated hallmark chromosomal features, including the pericentromeric regions, through annotation of transposable element families and positioned centromeric repeats using fluorescent in situ hybridization. The rose genome displays extensive synteny with the Fragaria vesca genome, and we delineated only two major rearrangements. Genetic diversity was analysed using resequencing data of seven diploid and one tetraploid Rosa species selected from various sections of the genus. Combining genetic and genomic approaches, we identified potential genetic regulators of key ornamental traits, including prickle density and the number of flower petals. A rose APETALA2/TOE homologue is proposed to be the major regulator of petal number in rose. This reference sequence is an important resource for studying polyploidization, meiosis and developmental processes, as we demonstrated for flower and prickle development. It will also accelerate breeding through the development of molecular markers linked to traits, the identification of the genes underlying them and the exploitation of synteny across Rosaceae.
The Rosa genome provides new insights into the domestication of modern roses.[Pubmed: 29713014]
Roses have high cultural and economic importance as ornamental plants and in the perfume industry. We report the rose whole-genome sequencing and assembly and resequencing of major genotypes that contributed to rose domestication. We generated a homozygous genotype from a heterozygous diploid modern rose progenitor, Rosa chinensis 'Old Blush'. Using single-molecule real-time sequencing and a meta-assembly approach, we obtained one of the most comprehensive plant genomes to date. Diversity analyses highlighted the mosaic origin of 'La France', one of the first hybrids combining the growth vigor of European species and the recurrent blooming of Chinese species. Genomic segments of Chinese ancestry identified new candidate genes for recurrent blooming. Reconstructing regulatory and secondary metabolism pathways allowed us to propose a model of interconnected regulation of scent and flower color. This genome provides a foundation for understanding the mechanisms governing rose traits and should accelerate improvement in roses, Rosaceae and ornamentals.
The Complete Chloroplast Genome of a Key Ancestor of Modern Roses, Rosa chinensis var. spontanea, and a Comparison with Congeneric Species.[Pubmed: 29439505]
None
Comparative transcriptome analysis of the floral transition in Rosa chinensis 'Old Blush' and R. odorata var. gigantea.[Pubmed: 28729527]
The floral transition is a crucial developmental event, but little is known about the underlying regulatory networks in seasonally and continuously flowering roses. In this study, we compared the genetic basis of flowering in two rose species, Rosa chinensis 'Old Blush', which flowers continuously, and R. odorata var. gigantea, which blooms in early spring. Gene ontology (GO) terms related to methylation, light reaction, and starch metabolism were enriched in R. odorata var. gigantea and terms associated with sugar metabolism were enriched in R. chinensis 'Old Blush' during the floral transition. A MapMan analysis revealed that genes involved in hormone signaling mediate the floral transition in both taxa. Furthermore, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) involved in vernalization, photoperiod, gibberellin (GA), and starch metabolism pathways converged on integrators, e.g., LFY, AGL24, SOC1, CAL, and COLs, to regulate the floral transition in R. odorata var. gigantea, while DEGs related to photoperiod, sugar metabolism, and GA pathways, including COL16, LFY, AGL11, 6PGDH, GASA4, and BAM, modulated the floral transition in R. chinensis 'Old Blush.' Our analysis of the genes underlying the floral transition in roses with different patterns of flowering provides a basis for further functional studies.


