Schisandra rubriflora
Schisandra rubriflora
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Schisandra rubriflora
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2508
Schisanhenol69363-14-0
Instructions

-
BCN2875
Gomisin O72960-22-6
Instructions
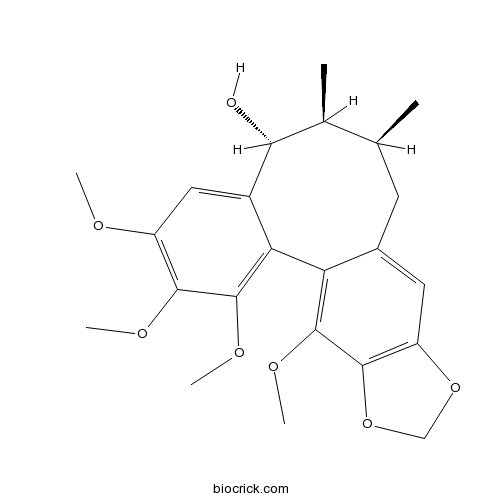
Schisanhenol improves learning and memory in scopolamine-treated mice by reducing acetylcholinesterase activity and attenuating oxidative damage through SIRT1-PGC-1α-Tau signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 30033800]
Schisanhenol is a compound derived from the fruit of a traditional Chinese herb Schisandra rubriflora. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of Schisanhenol on the cognitive impairment induced by scopolamine. The learning and memorial ability of mice was monitored by water morris maze. Hippocampus of mice were collected after behavioral testing and the activity of SOD, MDA, GSH-px, AChE were measured with standard biochemical procedures. Western blotting was used to analyze the expression of SIRT1, PGC-1α, phosphorylated Tau proteins. Intraperitoneal administration of Schisanhenol (10, 30 or 100 mg/kg) significantly attenuated scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment in water morris maze. In addition, Schisanhenol increased the activity of SOD and GSH-px while decreased the content of AChE and MDA. Furthermore, western blotting analysis revealed that Schisanhenol increased the levels of SIRT1 and PGC-1α and decreased the level of phosphorylated Tau protein (Ser 396) significantly in the hippocampal tissues. Taken together, the present study suggests that Schisanhenol may block scopolamine-induced learning deficit and enhance cognitive function, the mechanism via improve the cholinergic system and antioxidant ability, activate SIRT1-PGC1α signaling, inhibit the phosphorylation of Tau, and would be an effective candidate against cognitive disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease.
Evaluation of four commonly used DNA barcoding Loci for chinese medicinal plants of the family schisandraceae.[Pubmed: 25938480]
Many species of Schisandraceae are used in traditional Chinese medicine and are faced with contamination and substitution risks due to inaccurate identification. Here, we investigated the discriminatory power of four commonly used DNA barcoding loci (ITS, trnH-psbA, matK, and rbcL) and corresponding multi-locus combinations for 135 individuals from 33 species of Schisandraceae, using distance-, tree-, similarity-, and character-based methods, at both the family level and the genus level. Our results showed that the two spacer regions (ITS and trnH-psbA) possess higher species-resolving power than the two coding regions (matK and rbcL). The degree of species resolution increased with most of the multi-locus combinations. Furthermore, our results implied that the best DNA barcode for the species discrimination at the family level might not always be the most suitable one at the genus level. Here we propose the combination of ITS+trnH-psbA+matK+rbcL as the most ideal DNA barcode for discriminating the medicinal plants of Schisandra and Kadsura, and the combination of ITS+trnH-psbA as the most suitable barcode for Illicium species. In addition, the closely related species Schisandra rubriflora Rehder & E. H. Wilson and Schisandra grandiflora Hook.f. & Thomson, were paraphyletic with each other on phylogenetic trees, suggesting that they should not be distinct species. Furthermore, the samples of these two species from the southern Hengduan Mountains region formed a distinct cluster that was separated from the samples of other regions, implying the presence of cryptic diversity. The feasibility of DNA barcodes for identification of geographical authenticity was also verified here. The database and paradigm that we provide in this study could be used as reference for the authentication of traditional Chinese medicinal plants utilizing DNA barcoding.
Schisanhenol derivatives and their biological evaluation against tobacco mosaic virus (TMV).[Pubmed: 25598185]
Schisanhenol (Sol) was isolated from Schisandra rubriflora, and a series of derivatives (1-16, 15a-16a, and 15b-16b) were designed and prepared by chemical modification. The curative and protective effects of these dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan analogues against tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) were evaluated. Most analogues exhibited stronger protective effects than the positive control ningnanmycin. Dibromoschisanhenol (6) at 0.25mM exhibited the strongest protective activity (83.5±1.8% at 0.25mM), and 14-(3, 5-dibenzyloxy)-benzoyloxyschisanhenol (16) showed a significant curative effect (78.0±3.8% at 0.15mM) that was much stronger than that of the commercial virucide ningnanmycin. This study is the first to demonstrate that natural dibenzocyclooctadiene lignans and analogues are active against plant viruses.
Total synthesis of rubriflordilactone A.[Pubmed: 25360986]
The first and asymmetric total synthesis of rubriflordilactone A, a bisnortriterpenoid isolated from Schisandra rubriflora, has been accomplished in a convergent manner. Two enantioenriched fragments were forged together to give a functionalized cis-triene. A 6π-electrocyclization/aromatization sequence assembled the penta-substituted arene, and a formal vinylogous Mukaiyama aldol reaction introduced the butenolide side chain.
Effect of nigranoic acid on Ca²⁺ influx and its downstream signal mechanism in NGF-differentiated PC12 cells.[Pubmed: 24674947]
Schisandra chinensis has a long history of use as a famous traditional Chinese medicine. The plants of genus Schisandra, especially Schisandra neglecta, Schisandra rubriflora, and Schisandra sphaerandra are used in the same way as Schisandra chinensis in the folk medicine to treat insomnia, fatigue, increasing intelligence, and tranquilizing. Many studies showed that lignans were the major active components of Schisandra genus, whereas the bioactivity of abundant triterpenoids in Schisandra genus, such as nigranoic acid (SBB1, 3,4-secocycloartene triterpenoid), has not been examined yet in neuropathology.
[Determination of lignans in four fruits of Schisandra genus in Qinling mountains].[Pubmed: 24417136]
To determine the content of four lignans in the fruits of Schisandra sphenanthera, Schisandra grandiflora, Schisandra rubriflora and Schisandra propinqua subsp. sinensis.
Dibenzocyclooctadiene lignans from the fruits of Schisandra rubriflora and their anti-HIV-1 activities.[Pubmed: 21534036]
Two new dibenzocyclooctadiene lignans, rubrilignans A and B (1, 2), together with 17 known ones, were isolated from the fruits of Schisandra rubriflora. The structures of 1 and 2 were elucidated by spectroscopic methods including extensive 1D and 2D NMR techniques. Compounds 1 and 2 were also evaluated for their anti-HIV-1 activities and showed weak anti-HIV-1 activity with EC(50) values of 2.26 and 1.82 μg/ml, and therapeutic index values of 35.5 and 18.6, respectively.
Anti-HIV-1 activity of lignans from the fruits of Schisandra rubriflora.[Pubmed: 20512467]
This study investigated the 70% aqueous acetone extract of the fruits of Schisandra rubriflora which led to the isolation of eight lignans, including a new isolate, rubrisandrin C (1), and seven known lignans (2-8). The structure of 1 was established by extensive 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy and its absolute stereochemistry was determined by CD spectrum. Compounds 1-5 and 7-8 were evaluated for their anti-HIV-1 activity that showed inhibitory activity on HIV-1(IIIB) induced syncytium formation with EC(50) values in the range of 2.26 approximately 20.4 microg/mL. Compounds 1 and 7 exerted their obvious protection of HIV-1(IIIB) inducted MT-4 host cells lytic effects with a selectivity index of 15.4 and 24.6, respectively.
Chemical constituents from the leaves and stems of Schisandra rubriflora.[Pubmed: 20146529]
Six new nortriterpenoids, schirubridilactones A-F (1-6), as well as 14 known compounds, were isolated from the leaves and stems of Schisandra rubriflora. The structures of 1-6 were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic methods including HSQC, HMBC, (1)H-(1)H COSY, and ROESY NMR experiments. The relative stereochemistry of 1 was confirmed through single-crystal X-ray analysis. In addition, compounds 1-6 showed anti-HIV-1 activity with EC(50) values in the range 14.3-80.8 microg/mL and selectivity indices in the range 2.2-9.0.


