Scutellaria amoena
Scutellaria amoena
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Scutellaria amoena
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5557
Chrysin480-40-0
Instructions
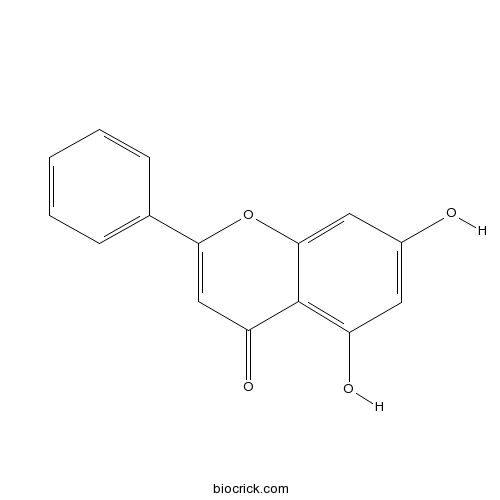
-
BCN5599
Baicalein491-67-8
Instructions
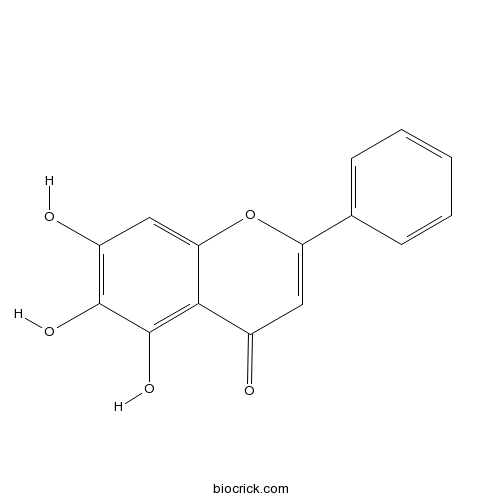
-
BCN4171
Wogonin632-85-9
Instructions

[Study on effect of total flavonoids from Scutellaria amoena on experimental arrhythmia].[Pubmed: 20450055]
To observe the effect of total flavonoids from Scutellaria amoena on the experimental arrhythmia.
[Study on rapid reproduction of Scutellaria amoena].[Pubmed: 17944178]
Tissue cultures of Scutellaria amoena were established from the young stem explants on MS + IAA 0.1 mg/L + BA 0. 5 (0.2) mg/L. Propagation cultures were established on MS + BA 0.2 (1.5) mg/L + IAA 0.1 mg/L + NAA 0.1 mg/L + 2, 4-D 0.5 (1.5) mg/L. Rooting of planlet was established on 1/2 MS + NAA 0.1 (0.2) mg/L + IBA 0.1 (0.2) mg/L + PP333 1.0 mg/L and the rate can reach 100%.
Baicalin synergy with beta-lactam antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and other beta-lactam-resistant strains of S. aureus.[Pubmed: 10757427]
Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a serious global problem and includes strains of beta-lactam-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). Novel antimicrobials and/or new approaches to combat the problem are urgently needed. The Chinese herb Xi-nan Huangqin (Scutellaria amoena C.H. Wright) has been used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat a wide range of infectious diseases. In this study we have examined the antibacterial action of baicalin, a flavone isolated from the herb. When combined with 16 microg mL(-1) baicalin, minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of benzylpenicillin against MRSA and penicillin-resistant S. aureus were reduced from 125 and 250 microg mL(-1) to 4 and 16 microg mL(-1), respectively. This activity of baicalin was dose-dependent. Viable counts showed that the killing of MRSA and beta-lactam-resistant S. aureus cells by 10 to 50 microg mL(-1) ampicillin, amoxycillin, benzylpenicillin, methicillin and cefotaxime was potentiated by 25 microg mL(-1) baicalin. From the study it was concluded that baicalin has the potential to restore the effectiveness of beta-lactam antibiotics against MRSA and other strains of beta-lactam-resistant S. aureus. In view of its limited toxicity baicalin offers potential for the development of a valuable adjunct to beta-lactam treatments against otherwise resistant strains of microorganisms.
[Studies on the structure of scuteamoenin from the root of Scutellaria amoena].[Pubmed: 2281792]
In containing our studies on the flavonoids from Scutellaria amoena C.H. Wright, a new flavanone (I) and six known compounds (II-VII) were isolated from the roots of this plant. On the basis of spectroscopic analysis (UV, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, MS and CD) and chemical evidence, the structure of the new compound was elucidated as (2S) -2',5,6'-trihydroxy-7-methoxyflavanone (I) and named scuteamoenin, the other six known compounds were identified as (2R,3R) -3,5,7-trihydroxyflavanone (II), 2',3,5,6,7-pentahydroxyflavone (III), 2',5,7-trihydroxy-6-methoxyflavone (IV), skullcaflavone II (V), chrysin (VI) and beta-sitosterol (VII) respectively. Compounds II-VII were obtained from this plant for the first time.


