Siegesbeckia pubescens
Siegesbeckia pubescens
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Siegesbeckia pubescens
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN4096
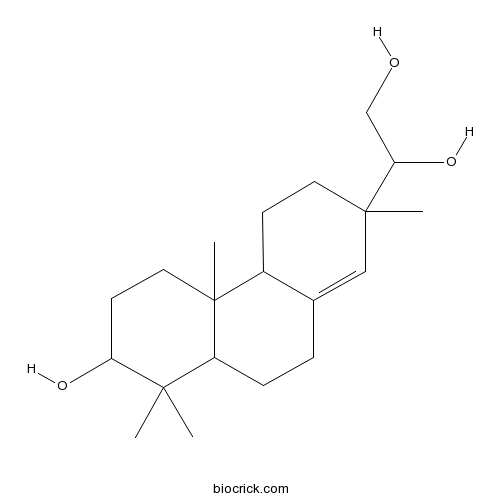
Darutigenol5940-00-1
Instructions
Nitric oxide inhibitory constituents from Siegesbeckia pubescens.[Pubmed: 29890361]
None
Comparison of the chemical profiles and inflammatory mediator-inhibitory effects of three Siegesbeckia herbs used as Herba Siegesbeckiae (Xixiancao).[Pubmed: 29720145]
Herba Siegesbeckiae (HS, Xixiancao in Chinese) is a commonly used traditional Chinese medicinal herb for soothing joints. In ancient materia medica books, HS is recorded to be the aerial part of Siegesbeckia pubescens Makino (SP) which is also the only origin of HS in the 1963 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopeia (ChP). The aerial parts of Siegesbeckia orientalis L. (SO) and Siegesbeckia glabrescens Makino (SG) have been included as two additional origins for HS in each edition of ChP since 1977. However, chemical and pharmacological comparisons among these three species have not been conducted.
Discrimination of three Siegesbeckiae Herba species using UPLC-QTOF/MS-based metabolomics approach.[Pubmed: 29305931]
The plant origin is one of the most important factors for the quality control of traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) and highly affected on their safety and effectiveness in clinical applications. Multi-origin has been widely observed for many TCMs. Siegesbeckiae Herba (SH) is a traditional anti-rheumatic TCM which is originated from the plants of Siegesbeckia pubescens Makino (SP), S. orientalis L. (SO), and S. glabrescens Makino (SG). In the present study, an UPLC-QTOF/MS method were validated and successfully applied for the determination of the chemical profiles in the three SH species. The data were statistical analyzed with the OPLS-DA analysis and One-Way ANOVA F-test. Obvious differences in chemistry were observed in different SH species and 40 components were identified. Finally, 6 components were selected as potential chemical markers for the discrimination of SP, SO and SG based on the characteristic distribution in individual SH species.
Isolation and characterization of diterpene glycosides from Siegesbeckia pubescens.[Pubmed: 28302401]
None
Essential oil from Siegesbeckia pubescens induces apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway in human HepG2 cells.[Pubmed: 28224421]
Siegesbeckia pubescens (SP) has been used as a traditional medicine for the treatment of and inflammatory diseases. However, the activities of SP against hepatocellular carcinoma and the related mechanisms remain unclear. The present study aimed to examine the effects of the essential oil of SP (SPEO) on the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and the possible mechanisms. The growth inhibition of HepG2 cells was analyzed by MTT assay. Hoechst 33258 and fluorescence microscopy were utilized to observe the nuclear morphological changes of apoptotic cells. Flow cytometry was used to detect cell apoptosis and cell cycle. The expressions of the target proteins were detected by Western blotting. The results showed that SPEO obviously inhibited the proliferation of HepG2 cells in a dose-dependent manner. SPEO activated a series of apoptotic proteins in HepG2 cells, increasing expression levels of Bax, caspase-3 and caspase-9, and decreasing the bcl-2 expression level. SPEO displayed promising anti-hepatocellular carcinoma activities in vitro, partly by inducing apoptosis in HepG2 cells through activating the mitochondrial pathway.
ent-Strobane and ent-Pimarane Diterpenoids from Siegesbeckia pubescens.[Pubmed: 28009521]
None
Secondary metabolites from Colletotrichum capsici, an endophytic fungus derived from Siegesbeckia pubescens Makino.[Pubmed: 27892688]
A rare new tremulane sesquiterpenoid analogue, 11,12-epoxy-5,6-seco-1,6(13)-tremuladien-5,12-olide (1), together with five known altenuene derivatives (2-6) was isolated from the cultures of Colletotrichum capsici, which was isolated as an endophytic fungus from fresh leaves of Siegesbeckia pubescens Makino (Compositae). Their structures were elucidated by means of spectroscopic methods and comparison with literature data. All compounds isolated were reported for the first time from the fungus C. capsici.
Quercetin 3,7-O-dimethyl ether from Siegesbeckia pubescens suppress the production of inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophages and colon epithelial cells.[Pubmed: 27405734]
Siegesbeckia pubescens (Compositae) is an annual herb indigenous to Korean mountainous regions. Recent reports have been issued on some compounds derived from S. pubescens for its anti-inflammatory activity or mode of action. The quercetin 3,7-O-dimethyl ether (QDE) isolated from the herbs of S. pubescens suppressed the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) protein production in mouse macrophages. QDE downregulated pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor -α levels in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Also, QDE decreased the expression of LPS-induced iNOS and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) protein and the production of IL-8 in LPS-induced HT-29 cells. Macrophages and colon epithelial cells are important for regulating the colon immune systems, thus QDE may regulate inflammatory colon disease via LPS-induced inflammation in macrophages and colon epithelial cells. QDE, anti-inflammatory constituent of S. pubescens herbs, can be expected to be a potential candidate for therapeutics against inflammatory bowel disease.


