Sinomenium acutum
Sinomenium acutum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Sinomenium acutum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN6265
Sinomenine115-53-7
Instructions
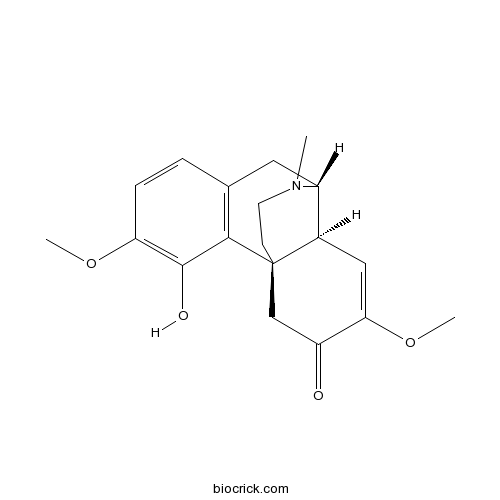
-
BCN7827
Cheilanthifoline483-44-3
Instructions
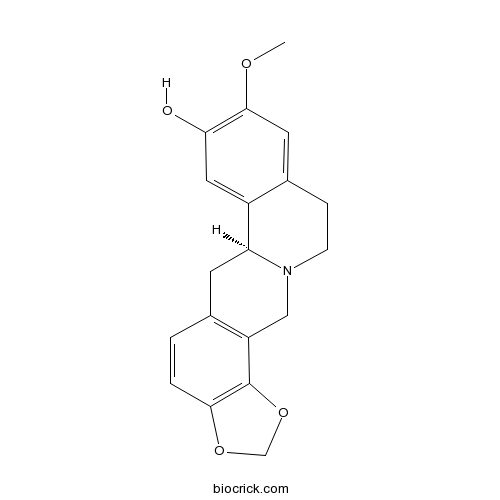
-
BCN5387
Epiberberine6873-09-2
Instructions

Sinomenine alleviates dextran sulfate sodium‑induced colitis via the Nrf2/NQO‑1 signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 30106158]
Sinomenine (SIN), a pure alkaloid isolated from Sinomenium acutum, has been widely used in arthritis for its anti‑inflammatory effect, but little is known about the effect of SIN on human ulcerative colitis (UC). In the present study, the effect and mechanism of SIN was examined in a dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)‑induced murine colitis model, which mimics human UC. Oral administration of SIN significantly suppressed the elevated disease activity index and ameliorated colonic histological damage in a DSS‑induced colitis model. Tumor necrosis factor‑α, interleukin‑6 and inducible nitric oxide synthase levels were also reduced as detected by reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction. In addition, SIN reversed the decreased colon length and colonic superoxide dismutase activity. Furthermore, western blot analysis revealed that nuclear factor‑erythroid 2‑related factor 2 (Nrf2) and its downstream genes, heme oxygenase‑1 and NADP(H) quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO‑1), were markedly activated by SIN. The current results indicated that SIN alleviated DSS‑induced colitis in mice, which may be due to its antioxidant properties and was at least in part dependent on the Nrf2/NQO‑1 signaling pathway. Therefore, SIN may have potential applications as a protective drug for patients with UC.
Sinomenine relieves oxygen and glucose deprivation-induced microglial activation via inhibition of the SP1/miRNA-183-5p/IκB-α signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 30084807]
Studies have shown that the inflammatory activation of miroglia (MG) and nuclear factor kappa B ( NF-κB ) play a dominant role in inflammatory response. Previous studies have shown that sinomenine, an anti-inflammatory agent extracted from Sinomenium acutum, can directly protect neurons against cerebral ischemia injury. However, there are no reports on its effect on ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammatory activation of MG. In the present study, an in vitro ischemia/reperfusion model was developed with mouse BV-2 microglia cells, a model of oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R), and the inhibitory effect of sinomenine pretreatment on inflammatory activation was confirmed through measurement of inflammatory indicators. Mechanistically, sinomenine suppressed OGD/R-induced inflammatory activation through the SP1/miRNA-183-5p/IκB-α pathway. In conclusion, this study shows that sinomenine effectively inhibits OGD/R-induced inflammatory activation in MG by suppressing the activation of transcription specificity protein 1 (SP 1). This finding is of significance for the clinical use of sinomenine in treating cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Sinomenine alleviates mechanical hypersensitivity in mice with experimentally induced rheumatoid arthritis.[Pubmed: 29911599]
Background and aims We have previously reported that sinomenine, an alkaloid isolated from the root of the plant Sinomenium acutum, had antinociceptive effect in rodent models of acute inflammatory or neuropathic pain. As a traditional medicine, sinomenine is used in China to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Methods In the present study, we evaluated the potential antinociceptive effect of sinomenine in a mouse model of RA, collagen type II antibody (CII Ab) induced arthritis (CAIA) after acute and chronic administration. Results As single administration, sinomenine at 40 or 80 mg/kg significantly reduced mechanical hypersensitivity both at the time of peak joint inflammation (days 11-19 after CII Ab injection) or during the post-inflammatory phase (days 35-54). No tolerance to the effect of 80 mg/kg sinomenine was observed during repeated injection twice a day for 5 days from day 11 to day 19 or from day 49 to day 53 after CII Ab injection in CAIA mice. Conclusions We have shown that sinomenine is effective in alleviating localized and spread hypersensitivities in CAIA mice both during acute inflammation and in post-inflammatory phase. Further, repeated sinomenine administration has elevated the baseline mechanical threshold without producing tolerance. Implications Sinomenine may be clinically useful to treat chronic pain in RA, including wide-spread pain which appears to be a difficult clinical problem despite the improvement in the acute treatment of RA by disease modifying agents.
Sinomenine Induces G1-Phase Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Malignant Glioma Cells Via Downregulation of Sirtuin 1 and Induction of p53 Acetylation.[Pubmed: 29756546]
Sinomenine, a bioactive alkaloid isolated from the traditional Chinese herb Sinomenium acutum, possesses antiinflammatory, antinociceptive, antifibrotic, and antitumorigenic properties. In this work, we sought to explore the biological effects of sinomenine on glioma cells. It was found that sinomenine caused a concentration-dependent inhibition of viability in both U87 and U251 glioma cells. Sinomenine at 16 μmol/L caused 55% to 60% reduction in the proliferation of U87 and U251 cells. Moreover, sinomenine treatment induced a G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mechanistically, sinomenine promoted p53 expression and acetylation and reduced the expression of sirtuin 1. Ectopic expression of sirtuin 1 significantly prevented sinomenine-induced p53 acetylation and growth suppression in glioma cells. Moreover, sinomenine inhibited the growth of U87 xenograft tumors in vivo and raised the p53 protein expression. Collectively, sinomenine shows antiproliferative effects against glioma cells which is mediated through downregulation of sirtuin 1 and induction of p53 activity.


